Categories: Featured Articles » Interesting Facts
Number of views: 1449
Comments on the article: 0
The use of transformers in power supplies
Different parts of electrical appliances, as a rule, need a different voltage supply. In order to ensure this, transformers with several secondary windings issuing different voltages are used in the power supply units of these devices, or several separate transformers are used, each of which provides its own specific voltage.
So, for example, in old TVs (with CRT tubes), 5-7 volts for powering transistors, microcircuits, or lamps were obtained from one transformer, and several kilovolts for powering a picture tube anode, from another high-voltage so-called lowercase transformer.
This transformer further fed the voltage multiplier, which several times increased the high voltage received from the secondary winding of the line generator.
Transformer yesterday and today
In the old days, when pulsed semiconductor technology was not as popular as it is today, power transformers operated only at the mains frequency - 50 or 60 Hz.

Modern radio engineering and electronic equipment, such as power supplies for TVs, monitors, computers, etc. everywhere use high frequency pulse transformersconverting voltage with a frequency of tens and hundreds of kHz.
In such schemes, the ac mains voltage is first rectified by the diodes, so that 300-310 volts of direct voltage are obtained. Then this constant voltage using an inverter field effect transistors It is converted into pulses following at a high frequency and supplied to the primary winding of a pulse transformer.
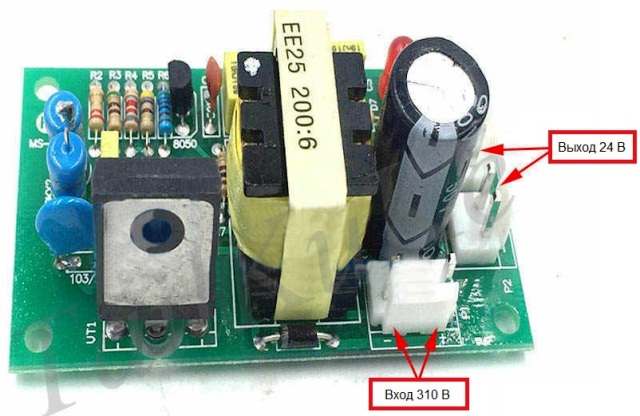

The power supply circuit of a pulse transformer is controlled pulse width modulation (abbreviated PWM)that allows you to stabilize the voltage received from the secondary (secondary) winding (s) of the pulse transformer. The voltage from the secondary winding of the pulse transformer is rectified, filtered and stabilized. Thus, a constant voltage is obtained, which is required for powering a particular unit, for example 24 volts.
Lower frequency - heavier transformer
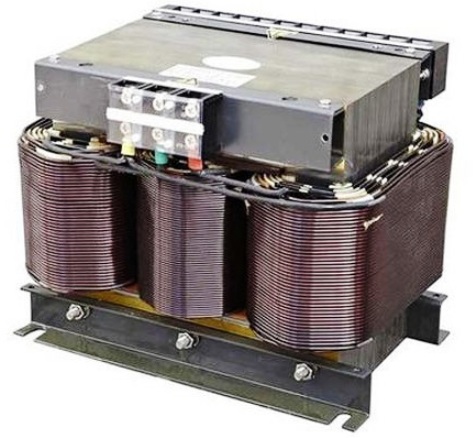
Previously, network transformers operating at a network frequency (50 or 60 Hz) could be found in each power supply unit of a tape recorder, television, radio, player, and this was the heaviest part of the device, often quite large, it took up a lot of space inside the case or was in a separate remote heavy power supply.
The bottom line is that the size of any transformer is the greater, the greater the power converted by this transformer, and in the case of a network low-frequency transformer (“iron”), this dependence turns out to be such that the rated power is proportional to the linear dimensions of the core by 4 degrees!
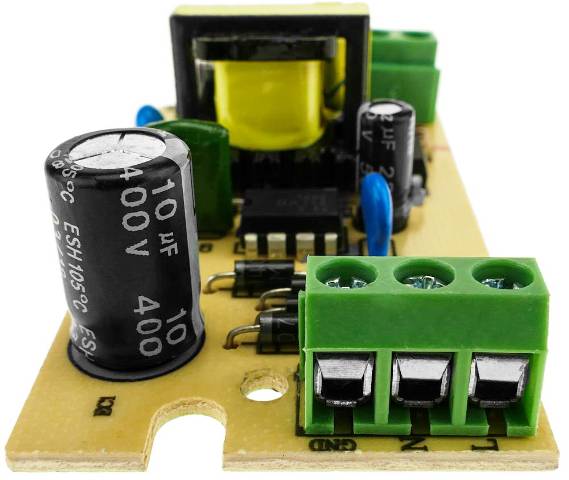
But the size of the transformer with the same transmitted power can be reduced, for this it is necessary to increase the frequency of voltage conversion, which is implemented in pulse transformers of modern switching power supplies and inverters, which are obtained much easier due to the increase in the conversion frequency due to the use of transistors and much higher frequency ferromagnetic core materials rather than transformer iron, which used to be used in network transforms all the time atora.
Sometimes a transformer on iron is irreplaceable
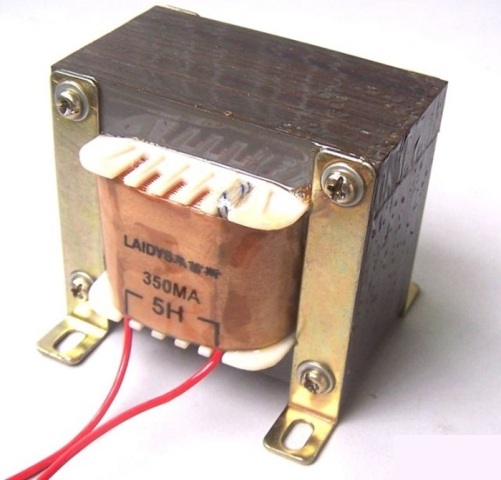
However, despite the disadvantages of network transformers with heavy iron magnetic circuits, they continue to be used in some exceptional power supply units when it is necessary to ensure a minimum level of high-frequency interference and distortion.
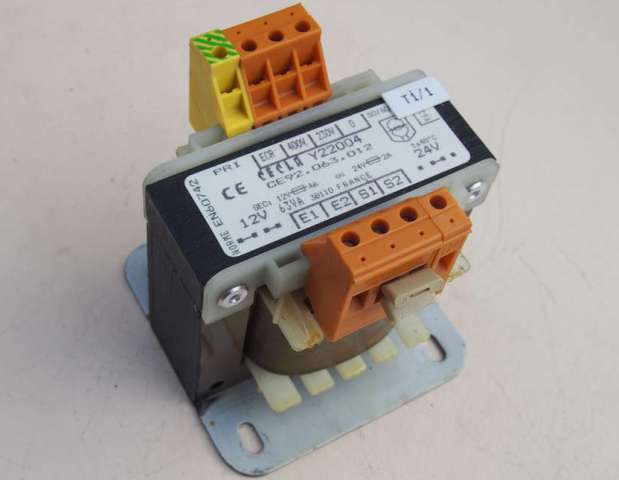

So, for example, when designing a high-quality tube acoustic amplifier, network transformers are traditionally continued to be used both as incandescent and as anode ones.
For if you put a pulsed power supply instead of a classic transformer on a tube amplifier, then inevitably there will be interference from the operation of transistor switches and other processes characteristic of pulsed devices, which will degrade the quality of the reproduced sound.
In addition, it is transformer iron that best transmits the frequencies of the acoustic range, therefore, output transformers in tube acoustic amplifiers are precisely “iron” transformers that are always manufactured with great care.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
