Categories: Electrician at home, Automata and RCD
Number of views: 22954
Comments on the article: 1
How is difavtomat arranged and what is it used for
Difavtomat or differential circuit breaker is a device that combines two protective switching devices - RCD and circuit breaker. They are used in 220/380 Volt switchboards in everyday life and in production. In this article we will consider what a difavtomat is, how it is structured and where it is used.
Destination
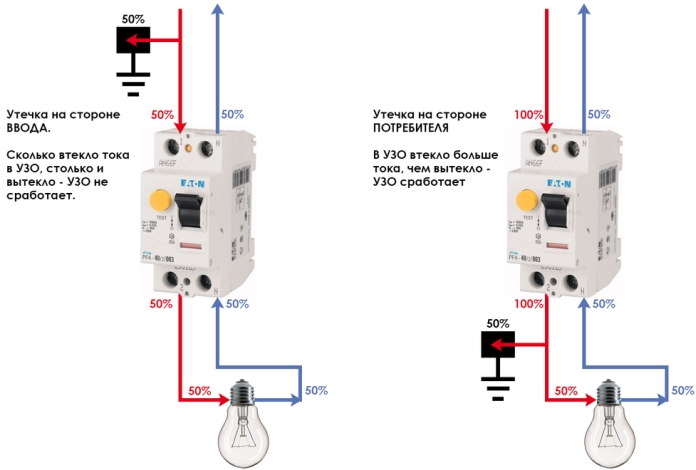
Difavtomats are used to protect wiring from overload, overcurrents, short circuit, as well as to protect a person from electric shock during leaks. Leaks may occur as a result of a breakdown on the housing. electric heaters (TENOV), for example, in boilers - water tanks, electric ovens, stoves, washing machines or dishwashers, as well as aging or damage to insulation.

All these problems can be localized by installing a device that compares currents between phase and zero, and if more, for example, 30 mA flows through the phase than through zero, then somewhere there is a leak and the circuit will break. It's called RCD (residual current device).
Interesting:
The word "differential" means the difference between something or between any states of a body, circuit or system. The synonyms of this word will be: various, unequal. Therefore, a device comparing currents in wires is called a differential automaton or differential protection.
The same reasons can cause short circuits. And if you connect too many electrical appliances on one line - your wiring will fail from overheating, therefore it is protected circuit breakers.

The differential machine combines an RCD and a circuit breaker, so it is a universal protective device.
Device and specifications
As already mentioned, the difavtomat consists of an RCD and a circuit breaker, this is shown in the diagram that is shown on the front side of such devices. This helps to determine what is installed in the electrical panel during its maintenance. Below we will tell you how to distinguish between an RCD, an automatic machine and a difavtomat.
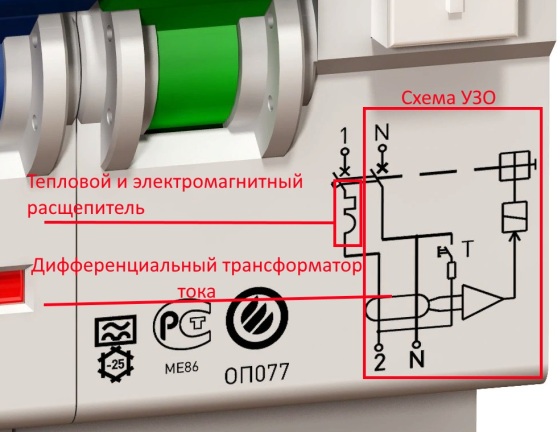
The figure shows the component functional units of the difavtomat.
An electromagnetic release is needed in order to instantly break the circuit during a short circuit, that is, when the currents suddenly increase tens or thousands of times higher than the nominal ones.
Thermal release - slower. This is a bimetallic plate, which under the influence of increased load (10% more than the nominal, for example) bends and also breaks the power contacts.
A differential transformer compares the currents between the wires (phase and zero), and if there is a leak, the power contacts open.
The test button simply closes the phase through the resistance to the transformer to zero - after it. There is a big difference in currents and the contacts are broken. Needed to safely test the differential part of the device.
What is inside the difiltomat? This question is often asked by those who first encountered this type of switching apparatus.

It has:
-
Thermal release;
-
Electromagnetic release;
-
Differential transformer;
-
A circuit for processing data from a transformer, if you can call it that;
-
Power contacts;
-
Interrupter chamber;
-
The “TEST” button is needed to check the operation of the differential part.
Unfortunately, modern protective devices that mounted on a din rail rarely intended for disassembly. Their cases are assembled on rivets and in practice they are disposable devices that, in case of malfunctions, cannot be sorted out or cleaned up, as was the case with the old APs and even automatic plugs.Inside the difavtomat, we can see all of the nodes listed above and indicated on the diagram. Details of his device are discussed in this video:
Characteristics for which difavtomat choose:
-
The value of the differential current is selected according to the same rules as for RCD;
-
The value of the rated current is selected as well as for the machine;
-
Switched current - determines which short-circuit current the device will withstand.
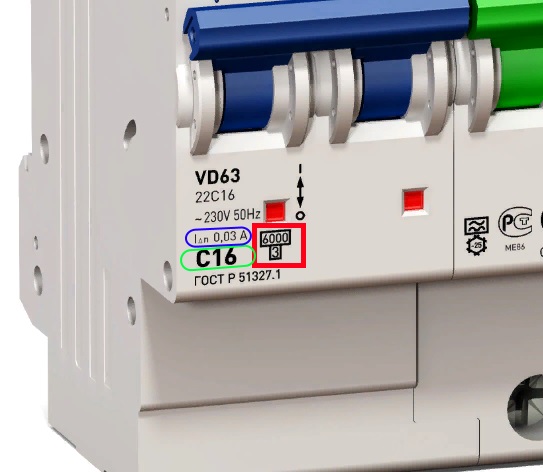

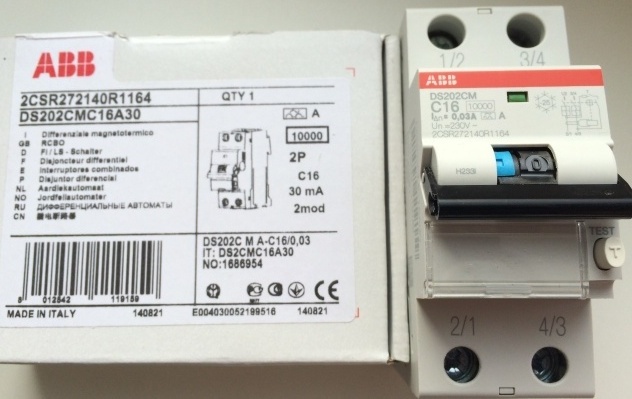
In the figure, a differential differential current of 0.03 A or 30 mA is highlighted in a blue oval. The rated current and speed class are highlighted in a green oval, here it is 16A and class C (determines by which curve of the time-current characteristic the device works). The conditional short-circuit current (switching capacity) - 6000 A is highlighted in a red square, figure 3 - current limiting class.
Important: Difavtomaty happen single-and three-phase.
Wiring diagram
Connecting a difavtomat is extremely simple, below you see an example of such a circuit for a three-phase network.
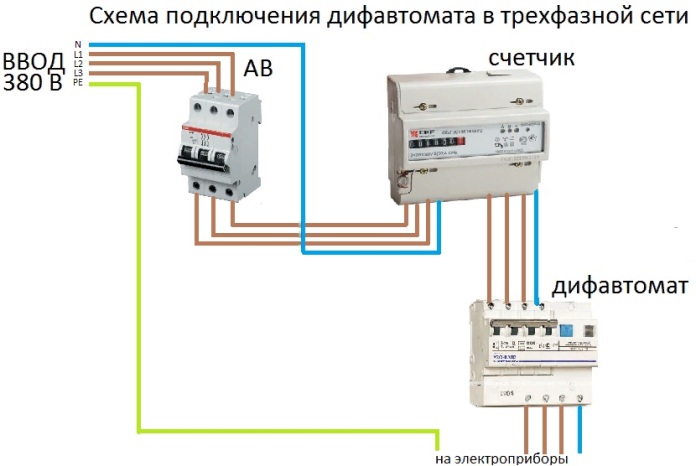
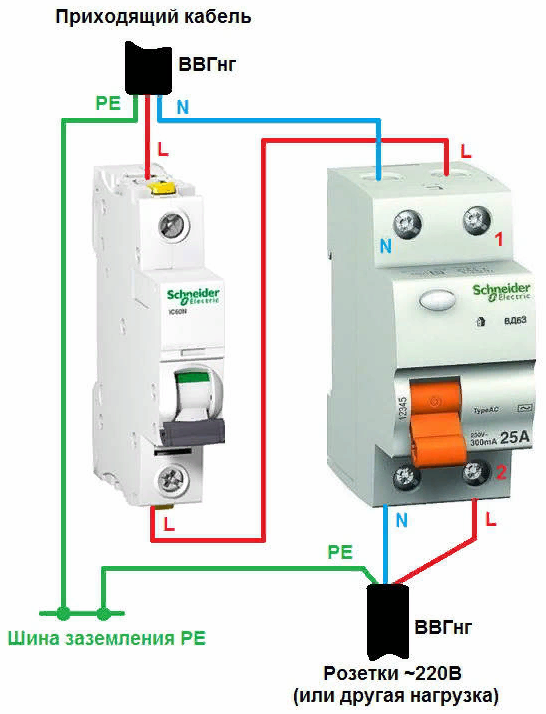
For a single-phase network:
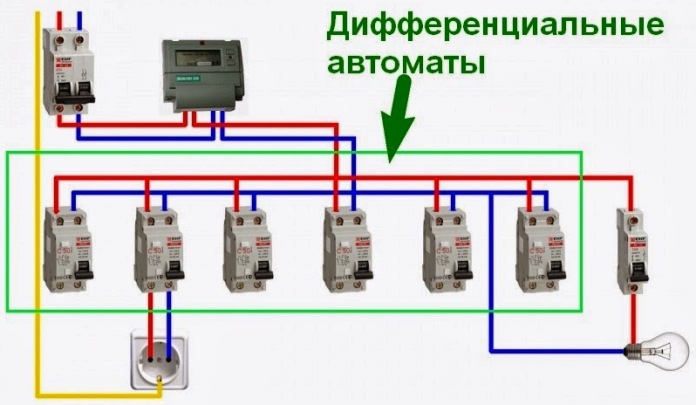
What is the difference between the difavtomat and the RCD and a simple machine
To begin with, RCDs are usually connected in series with a conventional machine. This is necessary in order to protect the line from short circuit and people from electric shock in case of leakage. Difavtomat performs both of these functions and combines these devices. For clarity, we have given you a diagram.
In order not to confuse the difavtomat with the RCD on the shield, you need to carefully examine the front panels of the modules, and find the circuit. They differ, in the figure below you can see what the difference is, the places for which to pay attention are highlighted.

The RCD marking usually indicates only the rated current that its contacts are able to withstand, in this form “25A”, that is, 25 Amps. As well as differential current. On the difavtomat, plus to this, indicate the speed class and switching ability (short circuit current), as on ordinary machines, for example, C16 - speed class C, 16 Amps.
If the front panel shows a diagram, then you can navigate along it. Trip units are also usually shown on the difavtomat circuit.
See also on this topic: How to choose a difavtomat and Diagrams of connecting difavtomatov and RCD
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
