Categories: Novice electricians, Automata and RCD
Number of views: 17402
Comments on the article: 0
The device and principle of operation of the circuit breaker
For an electrician, switching equipment is one of the main devices that you have to work with. Circuit breakers carry both switching and protective role. Not a single modern electrical panel can do without automatic machines. In this article we will look at how a circuit breaker is designed and operated.
Definition
A circuit breaker is a switching device designed to protect cables from critical currents. This is necessary in order to avoid damage to the conductive conductors of wires and cables in case of interphase faults and earth faults.
Important:The main task of the circuit breaker is to protect the cable line from the effects of short circuit currents.
The main characteristics of circuit breakers are:
-
Rated current (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 16, 20, 25, 32, 35, 40, 50, 63, 80, 100, 125, 160, 250, 400, 630 , 1000, 1600, 2500, 4000, 6300);
-
Switching voltage;
-
Time current characteristic.
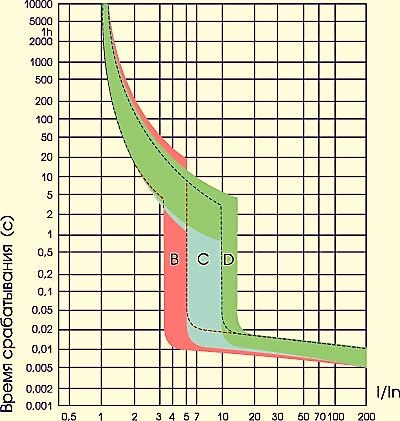
The machines are most widely used in household and industrial power networks with a voltage of 220/380 volts. Voltages are given for domestic power networks. Abroad, they may vary. High voltage lines use relay circuits and current transformers. Time-current characteristic Reflects through what period of time and at what magnitude of current relative to the rated one its contacts will open. An example of it is shown in the figure below:
Principle of operation
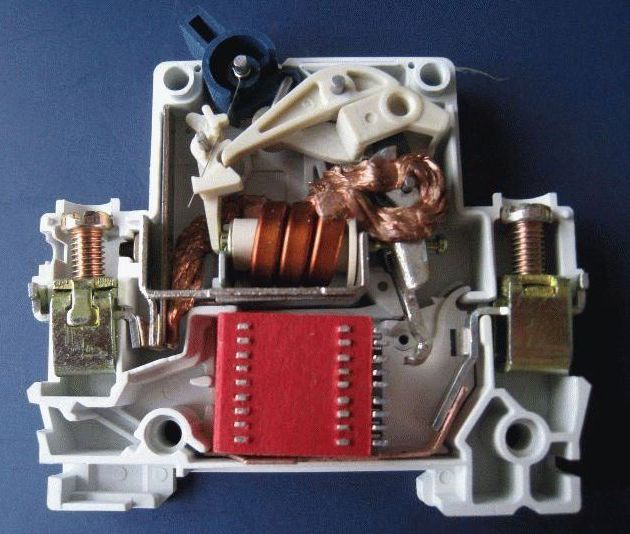
A circuit breaker (AB) is a switching device that contains two types of protection:
-
Electromagnetic release.
-
Thermal release.
Each of them performs the same work - opening power contacts, but under different conditions. Let's consider them in more detail.
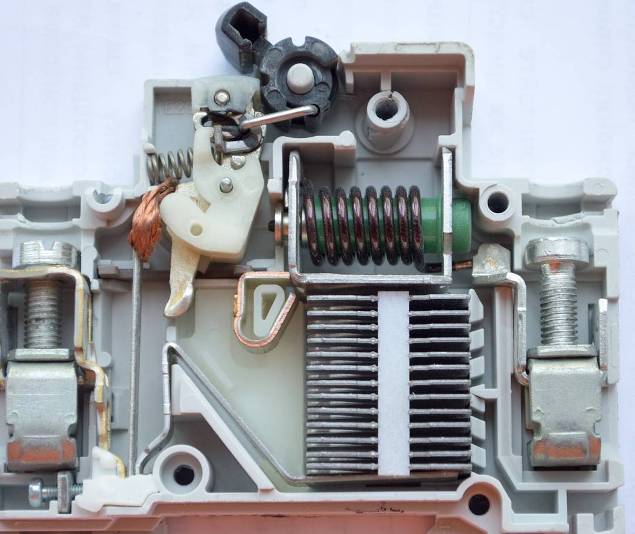
When currents flow through the circuit breaker below the rated current, its contacts will be closed indefinitely. But with a slight excess of current thermal releaserepresented by a bimetallic plate will open them.
The greater the current flowing through the contacts of the circuit breaker, the faster the bimetallic plate will heat up - this is described during the current characteristic and is indicated by the speed of the machine (letter about the rated current in the marking). Depending on how overloaded the machine is, the time it takes to turn off depends on it, it can be tens of minutes, or it can be a few seconds.
The electromagnetic release is triggered by a rapid increase in current. The magnitude of its operation current is orders of magnitude higher than the rated current.
This begs the question: "So why should the machine have two protections, if you can just design it so that it turns off immediately when the rated current is exceeded?"
There are two answers to this question:
1. The presence of two protections increases the reliability of the system as a whole.
2. When connecting devices to the circuit breaker, the current, which changes during the start-up and operation, so that there are no false positives. For example, in electric motors, the starting current can be tens of times higher than the rated current, and during their operation short-term overloads on the shaft (for example, a lathe) can occur. Then, with a protracted start, the machine will also be knocked out.
Device
Circuit breaker consists of:
-
Cases (in the figure - 6).
-
Terminal for connecting conductive conductors (in the figure - 2).
-
Power contacts (in the figure - 3, 4).
-
Arc chamber (in the figure - 8).
-
Levers connected to buttons or flags for turning it on and off (closing and opening contacts) (in the figure - 1 and what it is connected to).
-
Thermal disconnector (in the figure - 5).
-
Electromagnetic disconnector (in the figure - 7).
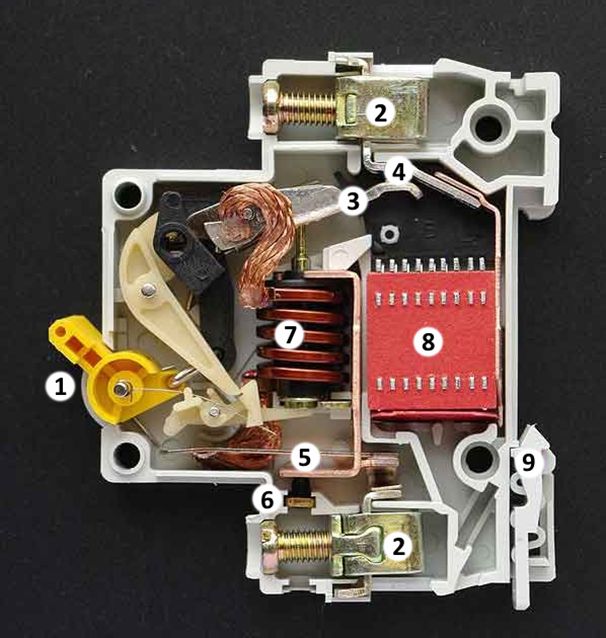
The number 9 indicates the latch for mounting on a din rail.
Power is connected to the terminals (usually the top ones, in practice, it does not really matter), the load is connected to the terminals on the opposite side. The current passes through the power contacts, the coil of the electromagnetic disconnector, the thermal disconnector.
The electromagnetic protection is made in the form of a coil of copper wire, it is wound on a frame inside which a movable core is located. The coil contains from several units to a couple of dozen turns, depending on its rated current. Moreover, the smaller the rated current, the more turns and the smaller the cross-section of the coil wire.
When current flows through the coil, a magnetic field is formed around it, which acts on the moving core inside. As a result, it extends and pushes the lever, as a result of which the power contacts open. If you look at the figure - then the lever is below the coil, and when its core falls - the mechanism is activated.
Thermal protection is needed for continuous overcurrents. It is a bimetallic plate, which, when heated, bends to one side. When a critical state is reached, she pushes the lever, and the contacts disconnect. The arcing chamber is needed to extinguish the arc, which occurs as a result of the circuit opening under load.
The process of arcing depends on the nature of the load and its magnitude. In this case, when disconnecting the inductive load (electric motor), stronger arcs arise than when switching the active load. Gases resulting from its combustion are discharged through a special channel. This significantly increases the service life of power contacts.
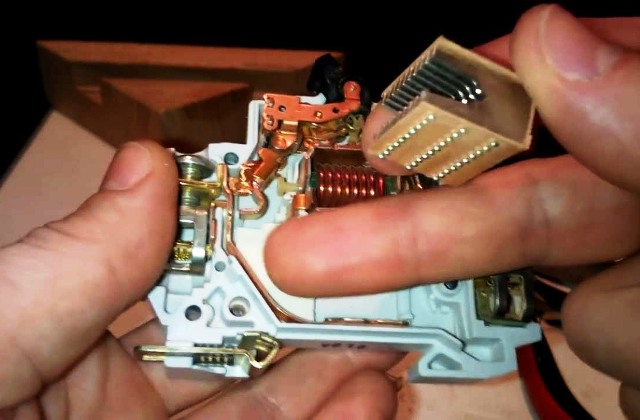
The arcing chamber consists of a set of metal plates and dielectric covers. Conclusion Previously, circuit breakers were repaired, and it was possible to assemble from several one normally functioning one. It was possible to adjust and replace the power contacts and its other components.
Currently, the machines are enclosed in a non-separable cast or riveted case. Their repair is impractical, complicated and will take a lot of time. Therefore, machines are simply replaced with new ones.
See also:
The unusual story of a conventional circuit breaker
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
