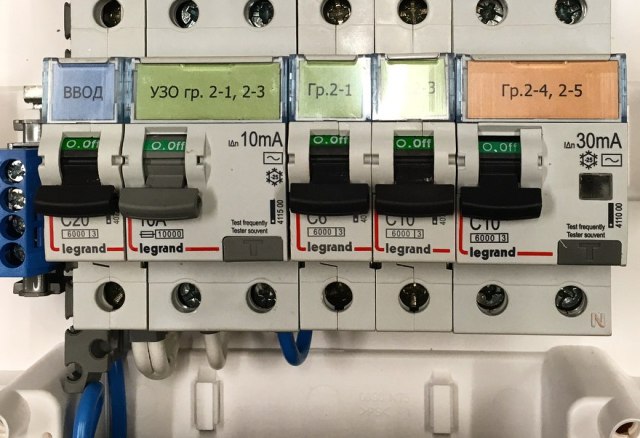
Categories: Electrician Secrets, Automata and RCD
Number of views: 13713
Comments on the article: 0
How to distinguish electronic RCD and electromechanical: features of the device and application
RCD - a residual current device or differential current switch is installed to protect a person from electric shock. However, not everyone knows that there are two types of RCDs: electronic and electromechanical. In this article we will talk about what are the differences between RCDs of different types and how to determine the type when buying.
Operating principle
In general terms, the principle of operation of the RCD is as follows: when the current through the phase wire differs from the current through the neutral wire, a relay is activated that disconnects the load. The current is detected using a differential transformer and a polarized relay.
A situation where currents of different sizes flow through a phase and neutral wire can occur if a device has a leak on the housing. A leak on the case occurs if the insulation of one of the conductors of the electrical appliance is damaged and touches the case, this applies both to the insulation of the winding wires of the electric motors and to the internal wiring of the device.
If the case is grounded - RCD will work. If the case is not grounded, the current will have nowhere to flow, but if you touch it with your hand, the current will go to the ground through your body, at that moment the RCD will trip and protect you. Even if you accidentally touch an open phase wire, nothing will shock you, because An RCD will open the circuit, because there will be a leakage of current along the circuit: Phase wire - your body - earth.
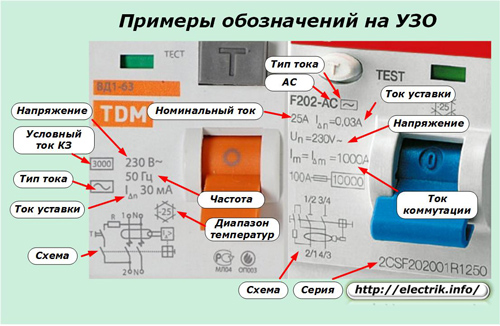
Each of the RCDs is configured for some kind of leakage current, this is such a characteristic that describes at what current the relay in the RCD will disconnect the load from the input of electricity. This is the main characteristic.
Electronic and Electromechanical
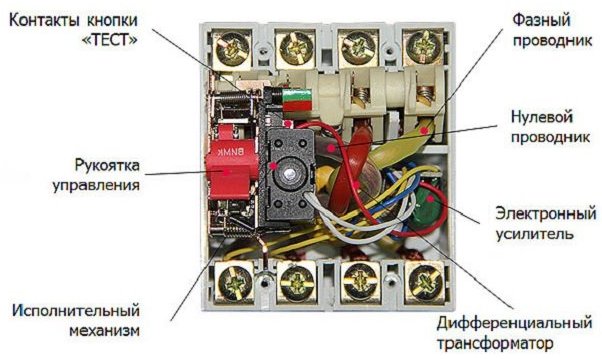
Electronic - as the name implies, it contains a board with electronic components in its case, which are responsible for its work. Electromechanical - contains a differential transformer in its housing. On the body of the RCD of both types there is a trip indicator and a button for checking the health.
When you press the button, you close the phase to zero through the resistor. In this case, the button closes the phase before the transformer to zero after the current transformer or vice versa, depending on how you connect the wires. As a result, the transformer also detects the current difference between phase and zero.
The current of this circuit is set using a resistor, and to ensure the correct correspondence of the sensitivity of the RCD to the nominal one, its corresponding resistance is selected, but as consumers and users, these subtleties do not particularly concern us.
Differences in operation
For the operation of the electronic RCD, power must be supplied to the board, it is taken directly from the already connected phase and zero. The electromechanical RCD will work without voltage. A logical question arises:
If an RCD protects against electric shock, then how will it occur if there is no voltage?
We are talking about emergency situations in the wiring. For example, if zero has burnt out on the distribution board at the entrance or at the entrance to the house / apartment. No electrical appliance will work in the apartment. The phase will remain in the outlets, and if somewhere there is a breakdown on the case, and you touch it, you will certainly get an electric shock, unless of course you have an RCD at the input.
But this is not so straightforward. The electromechanical RCD will work, because a full-fledged power supply is not necessary for it, but the current difference between the wires is needed. That is, when you touch a phase wire or the case of a damaged electrical appliance, a leakage current will flow through your phase wire through your body to the ground, but not through a zero wire.There is a current difference - the relay is triggered.
If you use an electronic protective shutdown device, the protection will not work, since its board is de-energized.
Also, do not forget that voltage jumps happen quite often in our networks, and electronics do not like such “accidents”.
How to distinguish RCD of various types upon purchase
First of all, when buying, pay attention to the diagram shown on the case, in the figure it is enclosed in a red square.
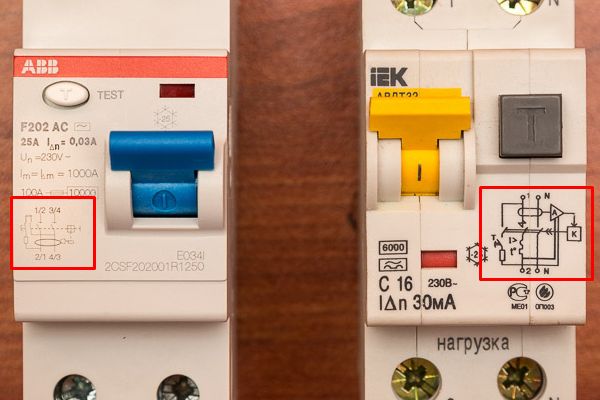

On the left is an electromechanical, and on the right is an electronic RCD. But the circuits are very similar, at first glance you may not notice the differences, let's take a closer look at them.
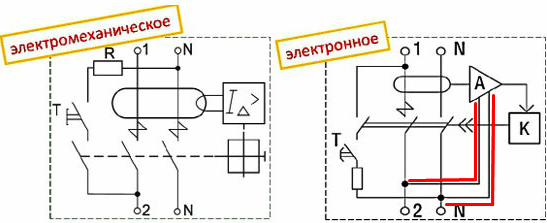
In this figure, you see the decoding of the circuit elements of the electromechanical protective apparatus. Pay attention to what is highlighted in red - this is the power supply line of the board with electronics.
Let's take a look at a selection of RCD circuits for fixing.
Here is an example of difavtomaty with electronic RCD. We draw attention to the two lines supplying the board.

This device is electromechanical. In the diagram you see that only the signal from the differential transformer is connected to the relay.

The verification method is to connect the battery to one of the poles of the RCD, the principle of operation is similar - the battery current will go through one of the lines, a differential transformer will work, this method only works with ELECTROMECHANICAL devices. Electronic in this case will not work, because the board remains de-energized.

Well, do not forget about the phenomena of electromagnetic induction, because if you use the field of a permanent magnet to bring the EMF to a differential transformer, the relay will also work and the RCD will turn off, again the ELECTROMECHANICAL method works.

Differences in the internal design
In addition to the article, it was decided to show several photographs of disassembled RCDs of various types.
The following is the electromechanical:
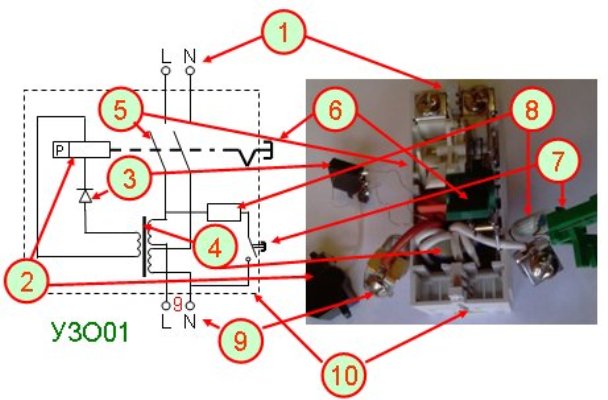
Three-phase instance:
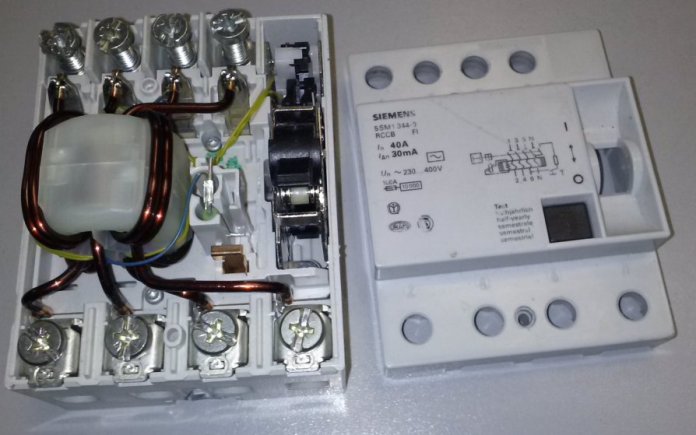

The following is an exploded view of an electronic RCD:
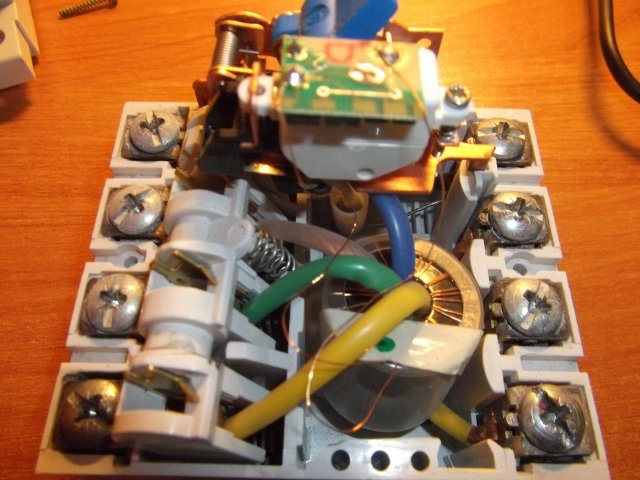
Conclusion
To summarize, an electromechanical RCD provides more reliable protection than electronic. It will work even if there is no power. In residential premises it is better to use electromechanical. To check it when buying, pay attention to the circuit, and if the seller-consultant allows you, use the battery method, it is worth noting that if the RCD does not work from the battery, change its polarity.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
