Categories: Automata and RCD
Number of views: 68839
Comments on the article: 8
Types and types of RCD
 Residual current circuit breakers save a person from electrical injuries by removing voltage from the wiring when leakage currents occur through it. Invisible and uncontrolled violations of the insulation layer can cause enormous damage to our lives and property. Therefore, such protections are gradually gaining more and more popularity among the population.
Residual current circuit breakers save a person from electrical injuries by removing voltage from the wiring when leakage currents occur through it. Invisible and uncontrolled violations of the insulation layer can cause enormous damage to our lives and property. Therefore, such protections are gradually gaining more and more popularity among the population.
Manufacturers produce these devices with a rather large assortment and endow them with various electrical characteristics, which make it possible to optimally select devices for the specific operating conditions of each electrical wiring.
To the functions carried out RCD, relate:
1. the inclusion of consumers, powered by the device, under voltage;
2. reliable transmission of the calculated load current without false positives;
3. shutdown of consumers under load under normal conditions;
4. blackout of the controlled circuit when a critical difference is reached between the currents entering and leaving the device.
The RCD task shown by the fourth paragraph provides:
-
protection of a person from falling under the influence of electric current of an electrical installation;
-
prevention of the causes of fires due to irregularities in the wiring.
The RCD does not have the ability to turn off excess currents passing through it, and itself can fail if they occur. For this reason, it is used in combination with a circuit breaker endowed with this function.
A single device that combines the functions of an RCD and a circuit breaker is called a differential machine.
In order for an ordinary consumer to be able to understand the diverse models of residual current devices, a classification system has been created that is based on such characteristics as:
-
mode of action;
-
maximum permissible current flowing through the device;
-
setpoint of the differential organ and the possibility of its regulation;
-
number of poles;
-
installation method;
-
working voltage.
Mode of action
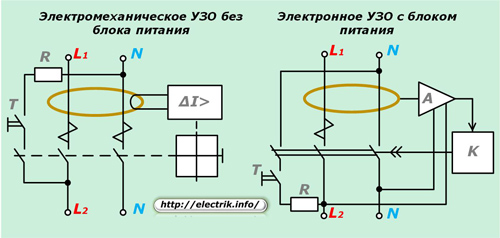
There are UZO designs that have an auxiliary power supply that provides electronic circuitry or those that do without it due to the electromechanical design.
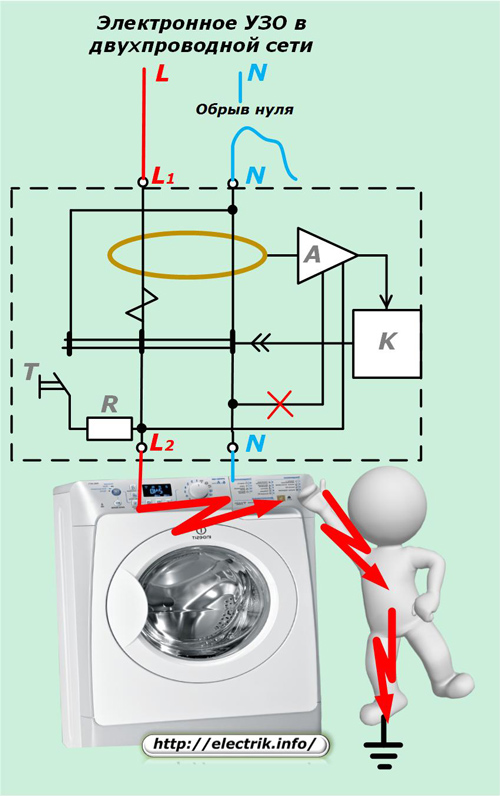
The operation of RCDs on electronic components depends on the presence of voltage in the network. To turn off current leakage Logic power with built-in amplifier is required. For this reason, such devices are considered less reliable: they, as a rule, will not be able to fulfill their protective functions in the event of a zero break, when there is a case of the passage of the phase potential through the human body.
This option is shown in the picture: the power supply does not receive mains voltage, and the phase through the breakdown of insulation on the washing machine body passes through the victim to the ground. The protective function cannot be performed due to the design features of the device.
Electromechanical RCDs are triggered directly from the leakage current, using not the electrical energy of the supply network, but the potential of a preloaded mechanical spring. Therefore, when a similar situation arises, they perform their protective function.
The picture shows the most difficult case for the operation of an electromechanical RCD connected to a two-wire circuit.
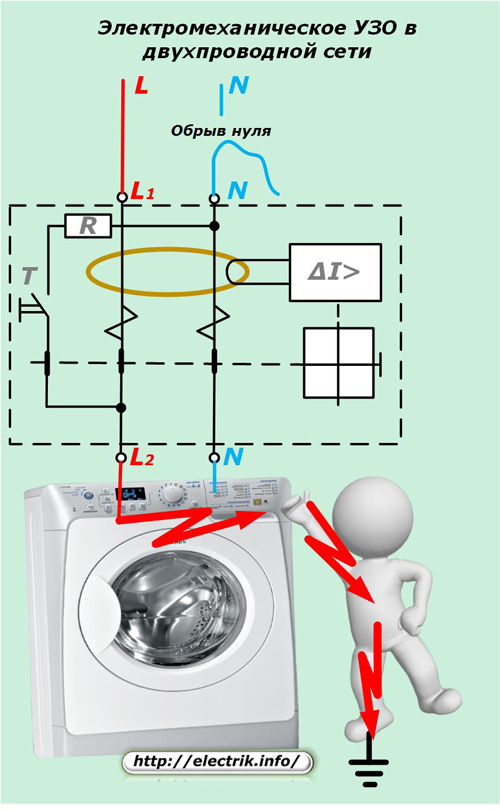
At the initial moment of the occurrence of the malfunction, the leakage current will pass through the human body, but, after a short time necessary for the electromechanical device to operate, the phase potential will be removed from the circuit.
Since this period of time is less than the period of onset of cardiac fibrillation, it can be considered that the protective function of the electromechanical RCD in this case is fulfilled.
It is quite natural that if in the examples considered the washing machine body will be connected to the PE-conductor, then:
-
An electronic circuit will usually not work either;
-
an electromechanical device will disconnect the phase at the time of breakdown of insulation and this will completely prevent the passage of current through the human body.
UZO-D
Please note that when describing the possibilities of disconnecting leakage currents with electronic RCDs, the addition “as a rule” is made. This is due to the fact that now manufacturers have taken into account the shortcomings of previous designs and launched production of devices with power supplies that ensure the operation of the device when the voltage is removed from it.
Such RCDs are marked with the letter "D" and denote "RCD-D". They can turn off the voltage when there is no power:
-
with set time delay;
-
or without her.
At the same time they are endowed with the ability:
-
perform automatic reclosing (AR) of the circuit under load when voltage is restored;
-
prohibition of reclosure.
UZO-D can be endowed with the conditions of selective operation necessary for devices using automatic standby (ATS) when the main power line disappears. Such appliances are marked with the letters S and G.
They differ in the duration of the delayed response. RCD-D type S has a longer time than type G.
The table of standard values of tripping and non-tripping times during RCD operation due to the appearance of a differential current according to GOST P 51326.1-99 is represented by a picture.
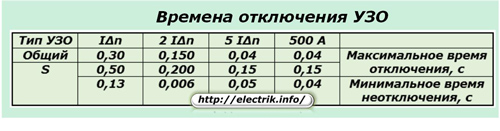
To compare these values, you can use the graphs created for the RCD of a general type with a differential current of 30 mA and type S disconnected - 100 mA.
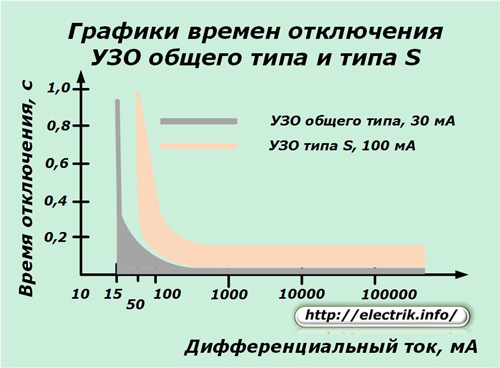
Type G devices operate with a response time of the order of 0.06 ÷ 0.08 seconds.
RCDs of types S and G make it possible to ensure the principle of selectivity for the formation of cascade protection circuits with unacceptable leakage currents and the creation of an algorithm for a specific turn-off sequence for consumers.
The second way to ensure the selective operation of such devices is the selection or adjustment of the differential organ setting.
The load current passing through the RCD
On the case of each device and in the technical documentation the value of the rated operating current of the device and the protected consumers is indicated, according to which the design is selected. This numerical expression always corresponds to a number of rated currents of electrical equipment.
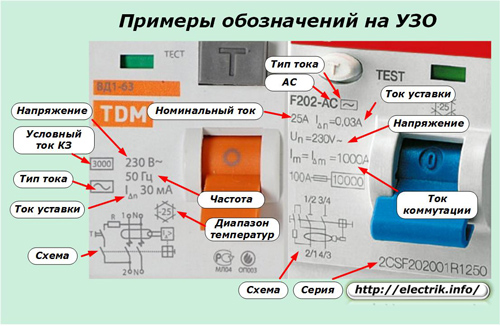
Each RCD is produced to process a current of a certain waveform. In order to indicate this characteristic, lettering and / or graphic images of the type of device are made directly on the case.
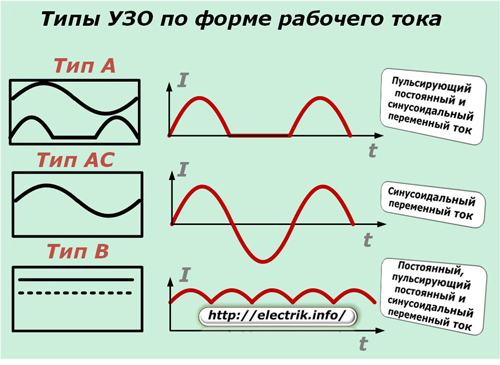
RCDs of types A and AC react both to a slow increase in the differential current, and to its rapid, stepwise change. Moreover, the type of speaker is most suitable for use in ordinary domestic conditions because it is designed to protect consumers who are eating variable sinusoidal harmonics.
Type A devices are used in those circuits where the load is adjusted by cutting off part of the sinusoid, for example, changing the speed of rotation of electric motors by thyristor or triac voltage converters.
Type B devices work effectively where electrical equipment is used, requiring the use of currents of various shapes. Most often they are installed in industrial plants and inside laboratories.
It should be noted that in recent years the number of electrical appliances with transformerless power has increased dramatically. Almost all personal computers, televisions, video recorders have switching power supplies, all the latest models of power tools are equipped with thyristor controls without an isolation transformer. Various luminaires with thyristor dimmers are widely used.
This means that the likelihood of a pulsating direct current leakage, and, consequently, human damage, has increased significantly, which was the basis for the introduction of RCD type A into widespread practice. In European countries, in accordance with the requirements of electrical standards, the last few years have been ubiquitous replacement of RCDs of type AC by type A.
The residual current device is connected to operation together with a circuit breaker to protect against overcurrents. Choosing their values, it should be taken into account that the machine is endowed with the functions of a thermal release and a tripping electromagnet.
At currents exceeding the rated value of the circuit breaker up to 30%, only the thermal release operates, but with a trip delay of about an hour. All this time, the RCD will be exposed to excessive loads and may burn out. For this reason, it is desirable to use its value one more than that of the machine.
Marketers of manufacturers for advertising purposes began to give RCDs the function of protecting the connected electrical circuit from overloads and overcurrents of short circuits. However, the electrician must understand that this is another device, called a differential automaton.
Differential setpoint
The selection of an RCD for leakage limitation current is important because it provides safety conditions. Devices operating in humid rooms must be connected to residual current circuit breakers with a setting of 10 mA. For residential environments, it is enough to choose a rating of 30 mA.
Protection of buildings from fire due to violation of the insulation of the wiring is ensured by the operation of a differential organ configured to 100 or 300 mA, depending on the design and materials of the structure.
All UZO devices can be divided into 2 conditional groups:
1. with the ability to adjust the settings of the differential body;
2. without settings.
Correction of devices of the first group can be carried out:
-
discretely;
-
smoothly.
However, regulation of the differential organ response for home appliances is not required. It is performed to solve the problems of special electrical installations.
Number of poles
Since the RCD works by comparing the currents passing through the differential organ, the number of poles of the device coincides with the number of current-carrying conductors.
In some cases, it is possible to use a four-pole residual current device for operation in a two-wire or three-wire network. In this case, it will be necessary to leave free phase poles in reserve. The device will perform its functions, realizing its own capabilities not fully, but partially, which is economically disadvantageous.

This method is used for emergency replacement of a faulty device or during the installation of a single-phase network, which will soon be transferred to work from three phases.
Installation method RCDs are manufactured in different cases for fixed mounting in electrical wiring or with the possibility of use as a portable device equipped with a flexible extension cable.
Din-rail mounted devices are installed in electrical panels located in the entrance or apartment.

The RCD-socket built into the wall ensures the safety of a person when using any electrical device connected to it.
An RCD plug connected by a wire to one problematic device protects it when used in places with different environmental conditions.
Rated voltage
Residual current circuit breakers used in a single-phase network are available at an operating voltage of 230 volts, and in a three-phase network - 400.
Additional functions
The ability of RCDs to protect a person from being exposed to electric current is constantly being improved by manufacturers. They give these devices more and more opportunities, connect additional elements and accessories to them, create housings with various degrees of protection against environmental influences.
For example, devices are known that are resistant to surge voltages due to the operation of the built-in varistor and those that turn off leakage currents in such situations.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
: