Categories: Novice electricians, Electric motors and their application
Number of views: 15625
Comments on the article: 0
Causes of malfunctions of induction motors and methods for their elimination
Asynchronous electric motors are more common than others in production and are often found in everyday life. With their help, various machines are driven: turning, milling, grinding, lifting mechanisms, such as an elevator or crane, as well as various kinds of fans and hoods. This popularity is due to the low cost, simplicity and reliability of this type of drive. But it happens that a simple technique breaks down. In this article, we look at typical malfunctions of squirrel-cage induction motors.
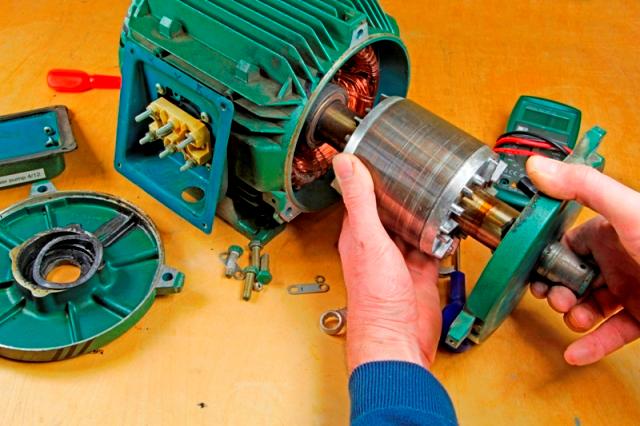

Types of malfunctions of induction motors
Faults can be divided into three groups:
-
The engine is warming;
-
The shaft does not rotate or does not rotate normally;
-
Noises, vibrates.
In this case, the engine housing can be completely heated or some separate place on it. And the motor shaft may not budge at all, not develop normal speed, overheat its bearings, make sounds abnormal for its operation, vibrate.
But first, refresh your design, and the illustration below will help you.
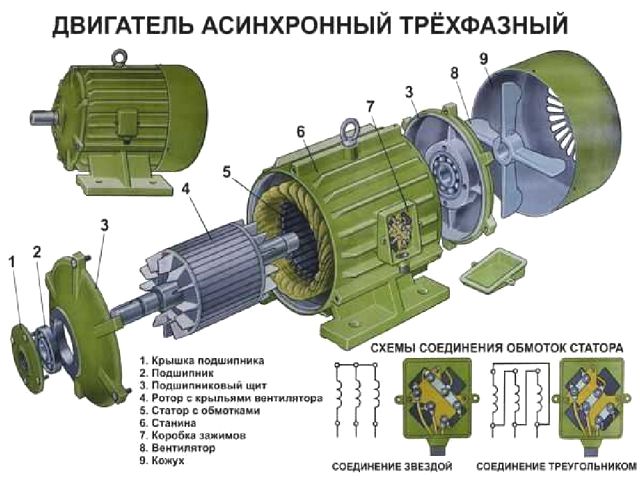
The causes of malfunctions can also be divided into two groups:
-
Electric;
-
Mechanical.
Most faults diagnosed using current clamps - by comparing phase currents and rated current, and other measuring devices. Let's consider typical malfunctions.
The electric motor does not start
When voltage was applied, the engine did not begin to rotate and did not make any sounds and the shaft did not "try" to budge. First of all, check whether the power comes to the engine. This can be done either by opening the motor and measuring at the points where the power cable is connected, or by measuring the voltage at the power switch, contactor, starter or circuit breaker.
However, if there is voltage at the motor terminals, then the entire line is normal.
By measuring the voltage at the beginning of the line - on the machine you will only know that the voltage is applied, but it may not reach the end user as a result of cable breaks, poor connection along its entire length or due to malfunctioning contactors or magnetic starters, as well as low-current circuits.

If you make sure that the voltage comes to the motor, its further diagnosis consists in ringing the windings for a break. Check the integrity of the winding megaohmmeter, so you at the same time and check the breakdown on the case. You can ring the windings and regular dial, but such a check is not considered accurate.
To check the windings without ringing them and without opening the boron motor, you can use current clamps. To do this, measure the current in each of the phases.
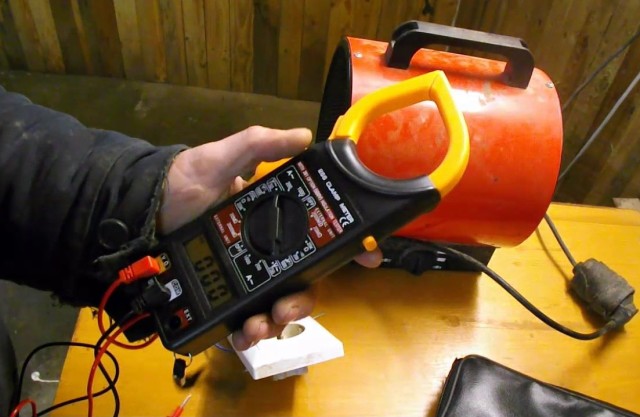

If the motor windings are connected by a star and two windings are cut off, there will be no current in any of the phases. If you break in one of the windings, you will find that the current is in two phases, and it is increased. When connecting according to the triangle circuit, even when two windings burn out, a current will flow in two of the three phase wires.
In the event of a break in one of the windings, the motor may not start under load, or start, but rotate slowly and vibrate. Below is a device for measuring engine vibration.
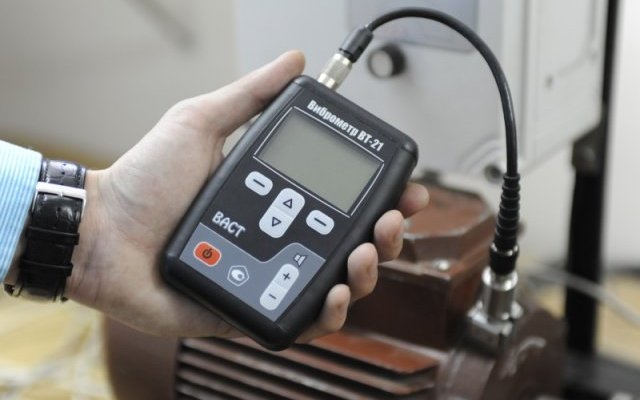

If the windings are in good condition, and the current during measurement is increased and at the same time the circuit breaker blows out or the fuse blows, the shaft or the actuator driven by it are probably jammed. If this is possible - after turning off the power, they try to turn the shaft by hand, while it is necessary to disconnect it from the mechanism set in motion.
When you determine that the motor shaft does not rotate, check the bearings. In electric motors, either plain bearings or rolling bearings are installed. Worn bushings (plain bearings) are checked for lubrication, if the bushings do not have external flaws, it is possible to simply lubricate them, having previously cleaned them of dust, chips and other contaminants. But this rarely happens, and such a repair method is more relevant for low-power engines of household appliances. In powerful engines, bearings are often simply replaced.
Problems with reduced speed, heating, shaft immobility and increased bearing wear can be associated with uneven load on the shaft, its distortion, deformation and bending. If the first two cases are correctable by the correct installation of the shaft or actuator, as well as by reducing the load, then the deformation and sagging of the middle part of the shaft requires its replacement or complex repair. This is especially common in powerful motors with a long shaft.
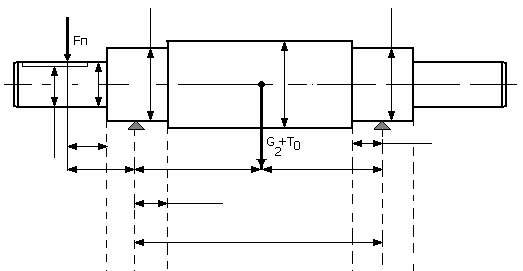
When one of the bearings is worn, the shaft often bites. In this case, as a result of the expansion of the metal due to heating during friction, the shaft may first begin to rotate, but either not gain full speed, and in a particularly neglected case, it will completely stop.
Rolling bearings also require regular lubricant filling and wear out during operation, especially quickly if the lubricant is low or contaminated.
The engine is warming up
The first cause of engine heating is problems with the cooling system. With such a malfunction, the motor housing heats up completely. Most engines use air cooling. For this case, they are made with fins, and on one of the sides a cooling fan is installed on the shaft, the air flow of which is directed by the casing along the ribs.
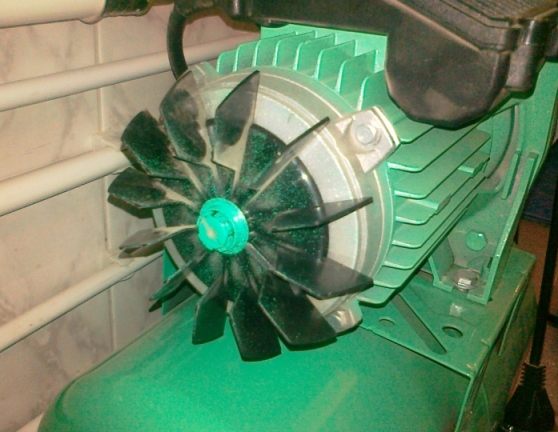

If the fan is damaged, or if it, for example, flies off the shaft, there is a problem of overheating. Powerful engines use a liquid cooling system. In addition, there are motors without fans - cooled by natural convection.
If the fan is normal, continue to diagnose.

When heating the engine, check the heating of the bearings. To do this, use your hand to feel the surface of the case from the back cover side (where there are no protruding rotating shafts - safety is above all).
If the bearing caps are hotter than other parts of the housing surface, you need to check the presence and condition of the lubricant in them, and when using liners, replace them.

In the case when replacing the grease in the ball bearing did not correct the situation, they should also be replaced.

Local heating of the case - a situation in which some part of it is clearly hotter than all the others, is observed with interturn closures. In such cases, diagnostics are carried out using current clamps - currents in phases are compared. If in one of the phases the current clearly exceeds the currents in the other phases, then the malfunction of the motor windings is confirmed. In this case, the repair consists in partially or completely rewinding the stator.
Increased heating of the induction motor can occur when the stator plates are closed.
The engine vibrates, makes noise and makes abnormal sounds.
Engine noise can also be associated with bearing wear. You must have noticed how howling old drills and kitchen appliances - that’s the reason. Shaft vibrations occur during axial shear and deformation of which we spoke earlier.
Vibrations, noise or overheating of active steel are also possible if the rotor touches the stator during rotation. This occurs either when the rotor is bent, or when the stator plates are damaged. In the latter case, it is disassembled and the plates are repressed. The place of contact of the plates can be found by irregularities or it will be polished with a rotor.

Conclusion
We examined a number of motor failures, how to eliminate them and the causes of their occurrence. Operation of an overheating motor is fraught with premature failure of the winding insulation. After a long period of inactivity, the engine cannot be started without measuring the resistance between the windings and the housing with a megohmmeter.
Insulation resistance of the order of 1 MΩ per 1 kV of the supply voltage is considered normal. That is, a motor in which the insulation resistance of the windings is not less than 0.5 MΩ can be considered suitable for operation in a network with a voltage of 380 V. Otherwise, you risk damaging it. If the insulation resistance is less, the engine is dried, often removing the casing or back cover from it. During operation, the resistance of the winding gradually increases - due to evaporation of moisture during heating.
Subject to the operating mode, operation and maintenance rules, as well as normal power supply, the induction motor serves for a long time, often processing its resource at times. In this case, the main repair consists in the lubrication and replacement of bearings.
See also on this topic: 10 most common causes of failure of various electrical equipment
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
