Categories: Featured Articles » Practical Electronics
Number of views: 81341
Comments on the article: 0
Types of transistors and their application
The word "transistor" is formed from two words: transfer and resistor. The first word is translated from English as "transmission", the second - "resistance." Thus, transistor Is a special kind of resistance, which is regulated by the voltage between the base and the emitter (base current) at bipolar transistors, and the voltage between the gate and the source of field-effect transistors.
Initially, several names were proposed for this semiconductor device: a semiconductor triode, a crystalline triode, a lotatron, but as a result, they focused on the name “transistor” proposed by John Pierce, an American engineer and science fiction writer, friend of William Shockley.
To begin with, we will plunge a little into history, then we will consider some types of transistors from the electronic components that are common on the market today.
William Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardin, working as a team in Bell Labs laboratories, on December 16, 1947 created the first functional bipolar transistor, which was demonstrated by scientists officially and publicly on December 23 of that year. It was a point transistor.

After almost two and a half years, the first germanium junction transistor appeared, then a fused, electrochemical, diffusion mesa transistor, and finally, in 1958 Texas Instruments released the first silicon transistor, then, in 1959, the first planar silicon transistor was created by Jean Ernie, as a result, germanium was superseded by silicon, and planar technology took pride of place in the main technology for the production of transistors.
In fairness, we note that in 1956, William Shockley, John Bardin and Walter Brattain received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the study of semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect."
As for field-effect transistors, the first patent applications have been filed since the mid-20s of the 20th century, for example, physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in Germany patented the principle of field-effect transistors in 1928. However, the direct field-effect transistor was patented for the first time in 1934 by the German physicist Oscar Hail.
The operation of a field effect transistor basically uses the electrostatic effect of the field, it is physically simpler, because the idea of field effect transistors appeared earlier than the idea of bipolar transistors. The first field effect transistor was manufactured for the first time in 1960. As a result, closer to the 90s of the 20th century, MOS technology (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor technology) began to dominate in many industries, including the IT sector.
In most applications, transistors have replaced vacuum tubes, a real silicon revolution has occurred in the creation of integrated circuits. So, today in analog technology bipolar transistors are more often used, and in digital technology - mainly field-effect transistors.
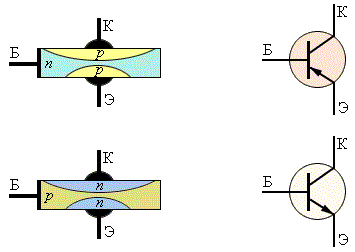
The device and principle of operation of field and bipolar transistors - these are the topics of individual articles, so we will not dwell on these subtleties, but consider the subject from a purely practical point of view with specific examples.
As you already know, according to manufacturing technology, transistors are divided into two types: field-effect and bipolar. Bipolar in turn are divided by conductivity into n-p-n transistors of reverse conductivity, and p-n-p transistors of direct conductivity. Field effect transistors are, respectively, with an n-type and p-type channel. The field effect transistor gate can be isolated (IGBTs) or as a pn junction. IGBT transistors come with an integrated channel or with an induced channel.
Fields of application of transistors are determined by their characteristics, and transistors can operate in two modes: in key or in amplifier.In the first case, the transistor is either fully open or completely closed during operation, which allows you to control the power of significant loads, using a small current for control. And in the amplifying, or in another way - in the dynamic mode, the property of the transistor is used to change the output signal with a small change in the input, control signal. Next, we consider examples of various transistors.

2N3055 - bipolar n-p-n-transistor in the TO-3 package. It is popular as an element of output stages of high-quality sound amplifiers, where it works in dynamic mode. Typically used in conjunction with the complementary p-n-p assembly MJ2955. This transistor can also work in key mode, for example, in transformer low-frequency inverters 12 to 220 volts 50 Hz, a pair of 2n3055 controls a push-pull converter.
It is noteworthy that the collector-emitter voltage for this transistor during operation can reach 70 volts, and the current 15 amperes. The TO-3 case allows you to conveniently fix it on a radiator if necessary. The static current transfer coefficient is from 15 to 70, this is enough to effectively control even powerful loads, despite the fact that the base of the transistor can withstand current up to 7 amperes. This transistor can operate at frequencies up to 3 MHz.
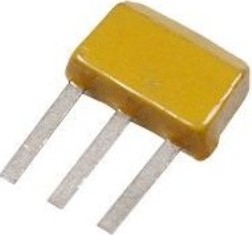
KT315 - a legend among domestic low power bipolar transistors. This n-p-n-type transistor first saw the light of 1967, and to this day is popular in the amateur radio environment. A complementary pair to it is KT361. Ideal for dynamic and key modes in low power circuits.
At the maximum permissible collector-emitter voltage of 60 volts, this high-frequency transistor is capable of passing a current of up to 100 mA through itself, and its cutoff frequency is at least 250 MHz. The current transfer coefficient reaches 350, despite the fact that the base current is limited to 50 mA.
Initially, the transistor was produced only in a plastic case KT-13, 7 mm wide and 6 mm high, but recently it can also be found in the TO-92 case, for example, manufactured by Integral OJSC.

KP501 - low-power field-effect n-channel transistor with insulated gate. It has an enriched n-channel, the resistance of which is from 10 to 15 Ohms, depending on the modification (A, B, C). This transistor is designed, as it is positioned by the manufacturer, for use in communication equipment, in telephones and other electronic equipment.
This transistor can be called a signal. Small TO-92 package, maximum drain-source voltage - up to 240 volts, maximum drain current - up to 180 mA. Shutter capacity less than 100 pF. It is especially noteworthy that the threshold voltage of the shutter is from 1 to 3 volts, which allows you to implement control with very, very low costs. Ideal as a signal level converter.
irf3205 - n-channel HEXFET field effect transistor. It is popular as a power key for boosting high-frequency inverters, for example automobile ones. Through the parallel connection of several buildings, it is possible to build converters designed for significant currents.
The maximum current for one such transistor reaches 75A (the construction of the TO-220 enclosure restricts it), and the maximum drain-source voltage is 55 volts. The channel resistance is only 8 mOhm. A shutter capacity of 3250 pF requires the use of a powerful driver for controlling at high frequencies, but today this is not a problem.
FGA25N120ANTD Power Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) in TO-3P package. Able to withstand the voltage drain-source 1200 volts, the maximum drain current is 50 amperes. A feature of manufacturing modern IGBT transistors of this level allows us to classify them as high-voltage ones.
The scope is inverter-type power converters, such as induction heaters, welding machines and other high-frequency converters, designed for high voltage supply. Ideal for high-power bridge and half-bridge resonant converters, as well as for operation in hard switching conditions, there is a built-in high-speed diode.
We examined here only a few types of transistors, and this is only a tiny fraction of the abundance of models of electronic components on the market today.
One way or another, you can easily choose the suitable transistor for your purposes, since the documentation for them is available today in the form of datasheets, in which all the characteristics are comprehensively presented. The types of cases of modern transistors are different, and for the same model both SMD and output versions are often available.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
