Categories: Automata and RCD
Number of views: 4120
Comments on the article: 0
Thermal circuit breaker release
Part of the design circuit breaker (automatic machine) is a thermal release. The fact is that inside the circuit breaker two ways of protection against current overload are implemented at once:
-
electromagnetic release, opening the circuit when the rated current is exceeded several times (with a short circuit);
-
thermal release, tripping at lower overload currents, but possessing, however, lower speed than its electromagnetic counterpart.
Of course, when the current passes through the wiring a little more than its rated current, the wiring does not burn out, so the speed of the thermal release is usually enough.

Kinematic circuit breaker:
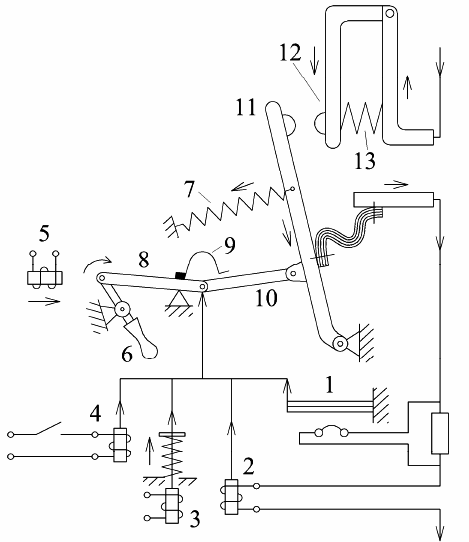
1 - thermal release; 2 - electromagnetic release; 3 - minimum release; 4 - an independent release; 5 - electromagnetic drive; 6 - control handle; 7 - spring accelerating shutdown; 8, 9, 10 - free trip mechanism; 11 - movable contact; 12 - fixed contact; 13 - contact spring.
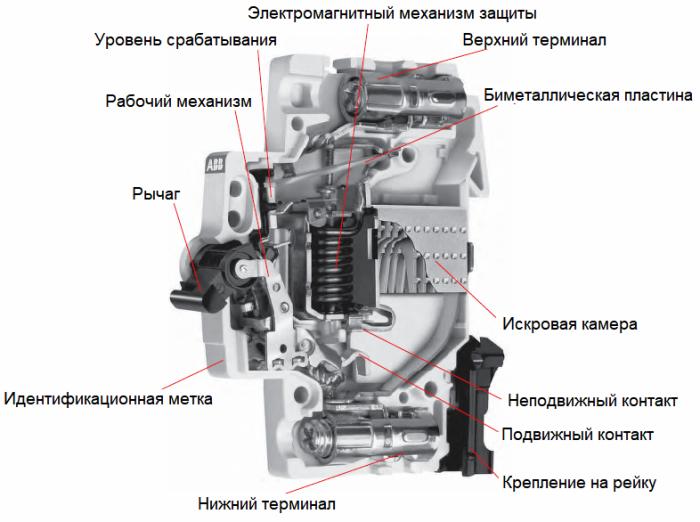
Trip units - devices that provide automatic opening of contacts by acting on the free trip mechanism in emergency operation of the circuit or serving to remotely open the circuit breaker.
Circuit Breaker Device:
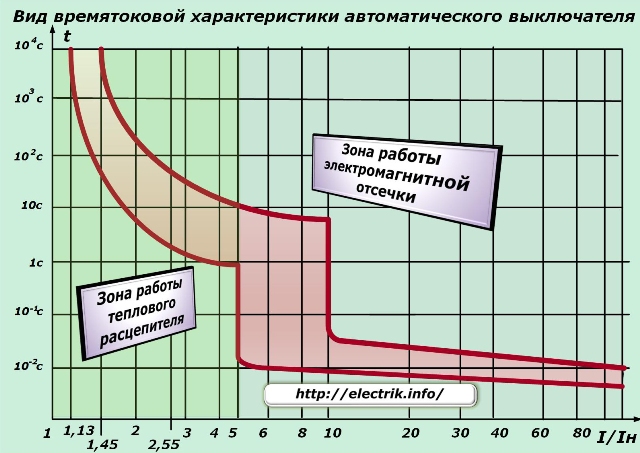
Time-current characteristic - the dependence of the response time of the protection device (time of fuse blown fuse) on the value of the current flowing through its measuring element (fuse fuse), the heating element of the electrothermal relay. Sometimes you can find other names for the time-current characteristic - ampere-second characteristic or just — protective characteristic.
The time-current characteristic is the main characteristic of the circuit breaker, reflecting the dependence of the response time of the circuit breaker in the event of an emergency on the value of the circuit current. It has the form of a hyperbola, so the more the current flowing through the protection device, the shorter the response time. However, this time cannot be less than its own response time.
Depending on the type of trip units installed in the circuit breaker, it can have such time-current characteristics as:
-
current-dependent response time characteristic. This characteristic has a thermal release. It is characterized by the response current during overload, and the response time depends on the magnitude of the current.
-
current-independent response time characteristic. This characteristic has an electromagnetic release. It is characterized by a cutoff current. Operation can be instantaneous or time delayed;
-
limited current-dependent (two-stage) response time characteristic. This characteristic has a combined release (thermal and electromagnetic).
The time-current characteristic, for simplicity, can be represented by a single line passing in the middle of the response.
Thermal release It is built on the basis of a bimetallic plate, which heats up from the current passing through it, while gradually bending, if the current becomes higher and higher relative to the nominal for this machine (the typical one that appears in the marking), which ultimately leads to the opening of the machine protected by this machine chains. When the plate bends, the force of its bending is transmitted to the thrust, which in turn presses the trigger of the release mechanism.
The minimum trip current for a specific thermal release is 1.45 of its rated current (setting), and the response time depends on the time-current characteristics of the machine in question, and depending on the magnitude of the overload current and on the initial temperature of the bimetal plate, it can be from several seconds up to an hour or even two, depending on the type of machine.
The thermal release device of the circuit breaker:
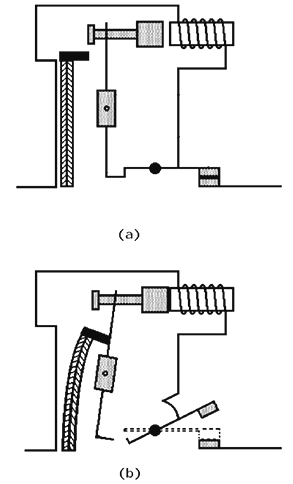
Thermal release operation:
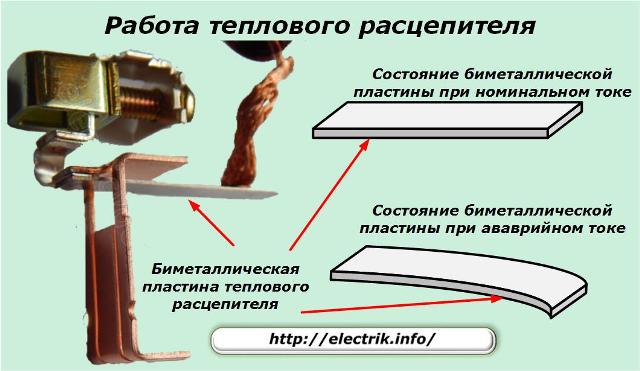
A cold machine with a current of 2.55 times the rated circuit will open after a maximum of one minute, and in a hot state after a few seconds (this is true for machines with a rating of up to 32A). Therefore, choosing an automatic machine for your shield, you need to understand that the rated current of the machine is not the current of its operation.
The maximum permissible current for wiring, at which the machine should be turned off, is desirable to compare with the time-current characteristic of the selected machine, focusing on its type (B, C, D).
The bimetallic plate of the circuit breaker is two metal strips tightly pressed against each other, but not fused, made of metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion. Two strips are fastened to each other from one end by soldering or welding. Their other ends are fixed in the switch housing motionless.
When the circuit breaker is installed in the circuit, the bimetallic plate is connected to this circuit in series with the load. As a result of its heating by passing electric current, the plate bends towards the metal with a lower coefficient of linear expansion. In case of overload, the bending of the plate ensures that the circuit breaker trips by activating the disconnect mechanism.
Designation of the thermal release on the Hager switch housing:

When the circuit breaker is just at the manufacturing stage, the trip current of the thermal release is set using a special adjustment (adjustment) screw, which is hidden inside the machine and located near one of its terminals.
As soon as the machine has worked, its bimetallic plate begins to cool and straighten, so after a while the machine is ready for full work again, you just need to re-cock its lever. The fuse does not boast of such abilities.
How currents are taken into account for circuit breakers
How the time-current characteristics of circuit breakers and fuses work
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
