Categories: Electrician Secrets, Automata and RCD
Number of views: 21401
Comments on the article: 2
Marking of circuit breakers: meaning and interpretation
Everyone knows the circuit breakers. In the people they are called simply "automatic". And everyone in the house or apartment has at least one, or even two such devices. Automatic machines protect wiring from emergency situations and prevent their development. Manufacturers print a whole series of text on their case, but not everyone understands what it says. This article will help you decipher the marking of circuit breakers.
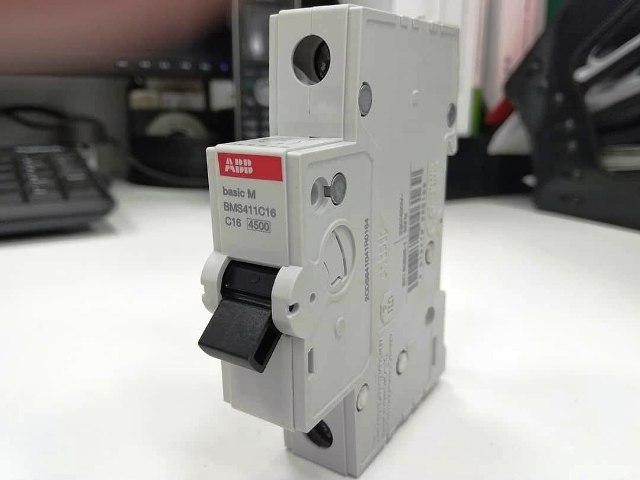

Decoding of marking machines
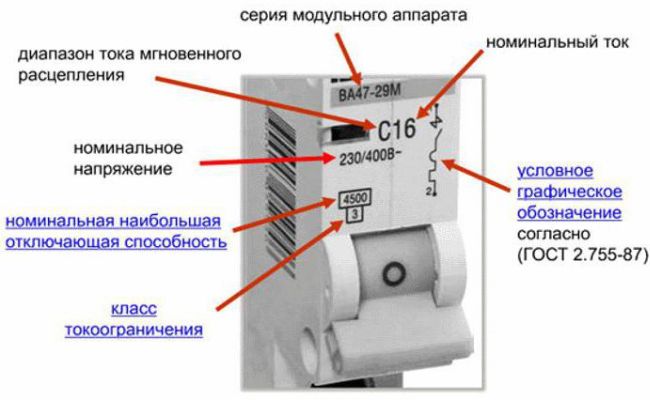
In terms of the appearance of the majority, it is impossible to determine what current it is rated for, the only thing you can guess from its size is that it passes a large or small current and how many phases (poles) it is rated. How to determine the characteristics of the machine? You just need to read the markings. And so you can see on the circuit breaker case:
1. Name of manufacturer.
2. Series or model.
3. Rated current.
4. Rated voltage and frequency.
5. Time current characteristic.
6. Sometimes depicts its internal structure.
But not every machine has a complete set of this information, somewhere it is more, somewhere less. You will be convinced of this by reading the article to the end and having examined all the illustrations.
Let's consider everything in order
Popular manufacturers of circuit breakers are:
-
ABB;
-
IEK;
-
Schneider electric;
-
Legrand.

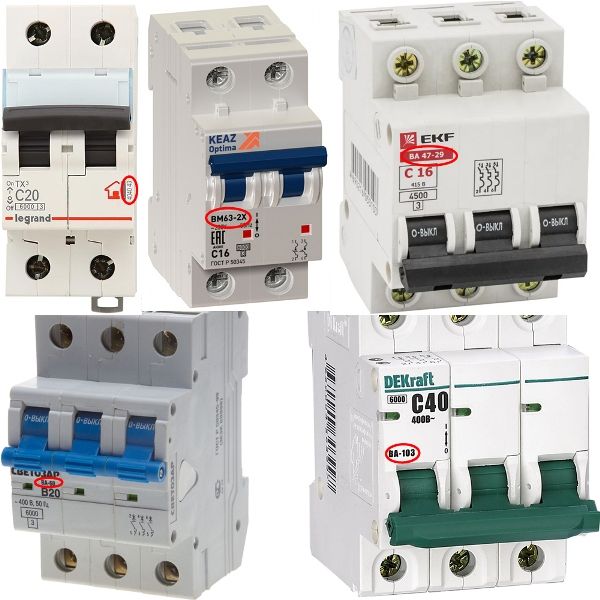
In fact, there are many more manufacturers. In the picture below you see where it is indicated:
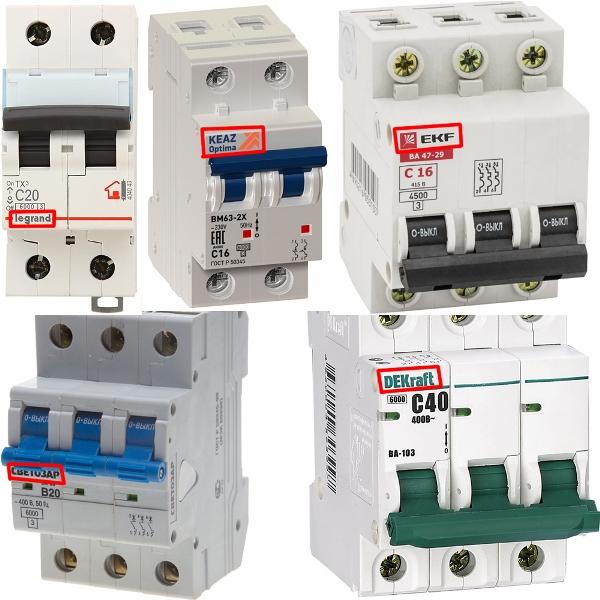

Series of machines
Marking a series of machines allows you to find complete documentation with all the technical characteristics and features of the model. It is indicated either under the logo of the manufacturer, or elsewhere.

Rated current
This is the main value by which a circuit breaker is selected. it current ratingwhich he can withstand for a long time. This is always indicated on circuit breakers, as in these examples:
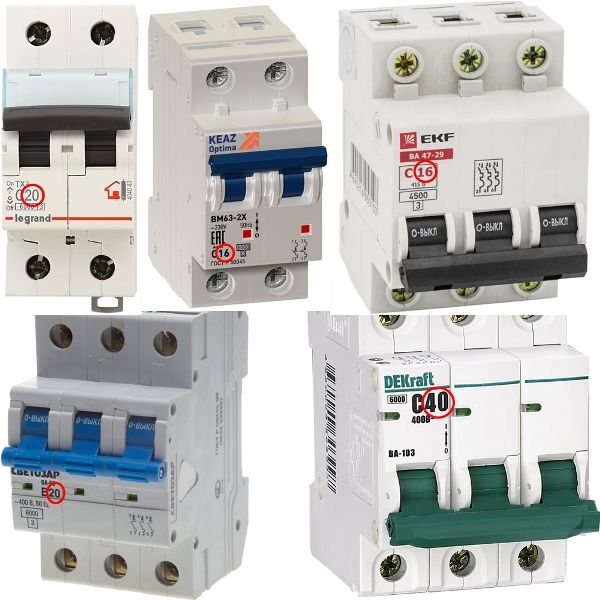

Depending on the needs, they select the appropriate machine, in apartments they usually put from 16 to 32A.
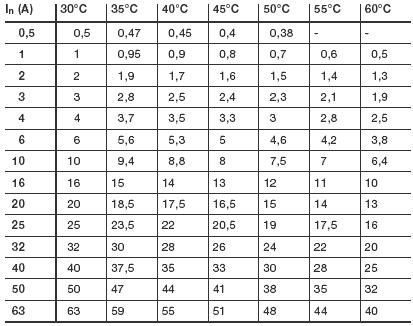
The table shows part of a number of circuit breakers and the values of rated currents at various ambient temperatures.
Tripping current limit and current limit class
On the marking, it is often surrounded by a square, indicated in small print:
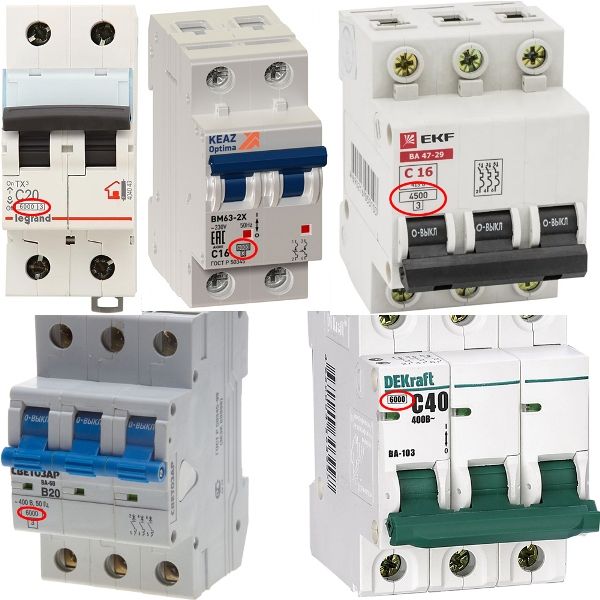

The breaking current is the value of the short-circuit current in thousands of amperes, for example 4500A or 6000A. With such a short-circuit current, the machine will turn off successfully and will not fail. It is necessary to take this moment into account, choosing a limit value higher than the short-circuit current on a given line.
In household circuits, this factor is almost not paid attention. The circuit breaker may burn out or stick if the short-circuit current in the protected circuit exceeds this value, if the circuit breaker sticks (i.e., the contacts remain closed), in the best case, the terminals on the wire will burn out, in the worst case, a fire may occur.
In other words, the breaking current limit is the switching capacity of the circuit breakers.
Immediately below it, the current limiting class is indicated, this is the number 1, 2 or 3. It indicates the time interval during which the machine can limit the short circuit current.
Time-current characteristic
The second most important characteristic when choosing a circuit breaker is time-current characteristic. If the rated current is exceeded, the circuit breaker opens and the current stops flowing through the wires. At what excess current and how quickly the circuit breaker disconnects depends on the time-current characteristic. It is usually indicated before the current.
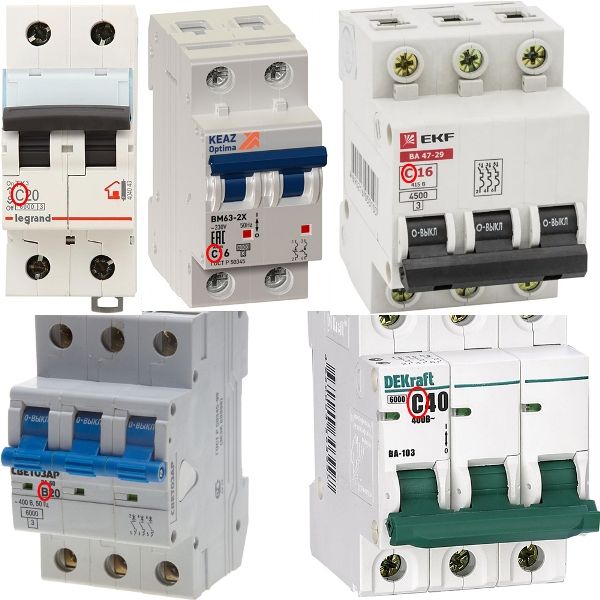

In everyday life, the most common are machines with the letters BCD, their time-current characteristic is shown below:
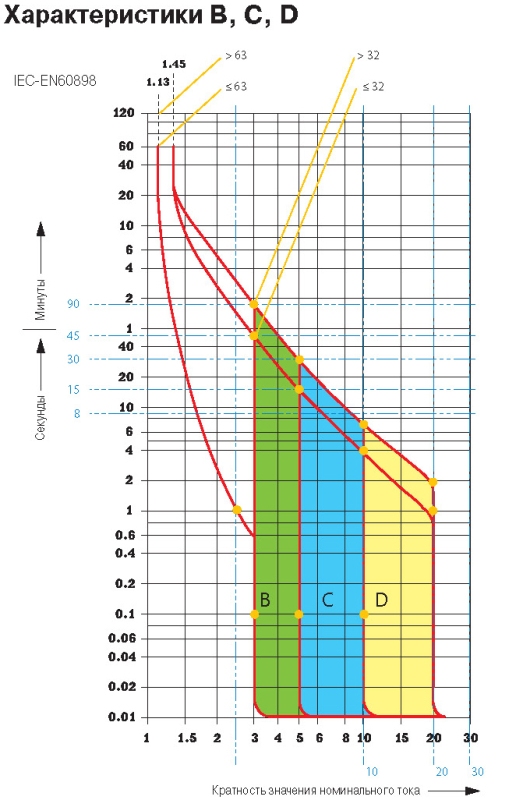
But there are other models.
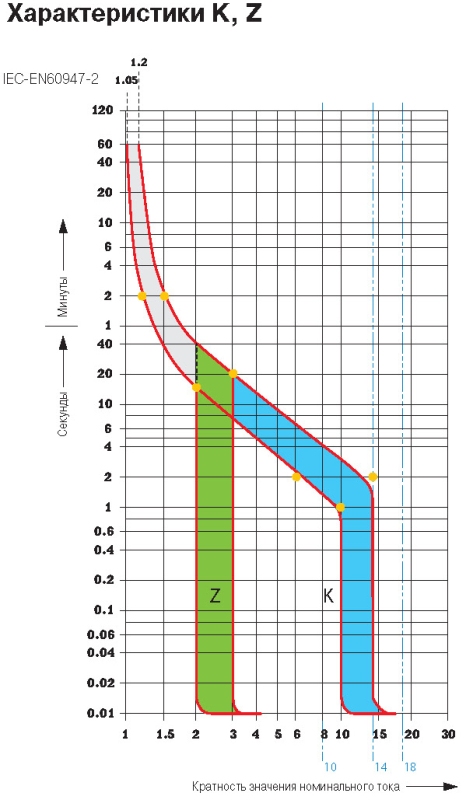
It is needed in order to determine for what purpose the machine is intended and what is its speed at shutdown. This is important, for example, when connecting motors, so that the machine does not work prematurely if a protracted start occurs and more.
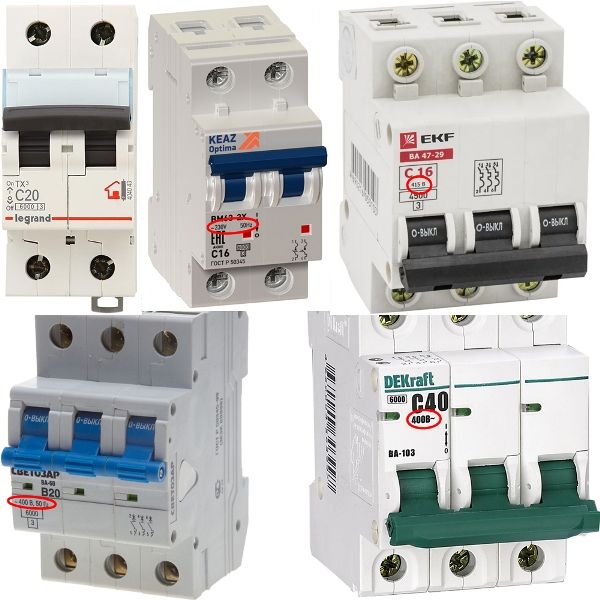
Voltage and frequency
The rated voltage for which it is designed is often indicated on the case of the circuit breaker.

Scheme
Among the numerous markings, you can find the circuit breaker, it does not carry much value for the electrician.

What is it for?
Such a wide marking is needed for the rapid replacement of failed circuit breakers and the selection of suitable devices during the installation of electrical circuits, without resorting to directories and technical documentation.
Label decoding examples
To consolidate the material we covered, we selected several examples of deciphering markings on various circuit breakers.
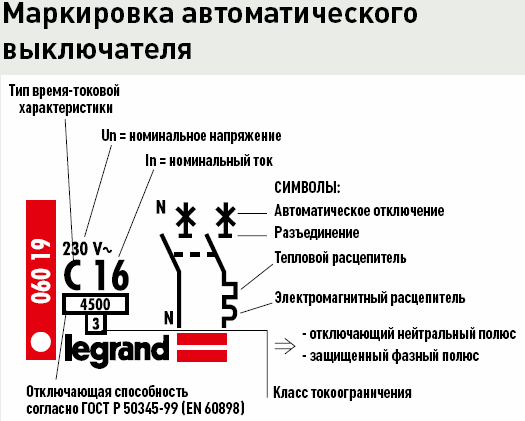

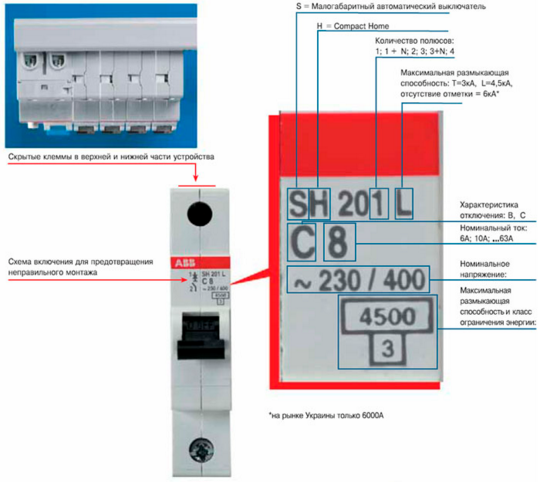
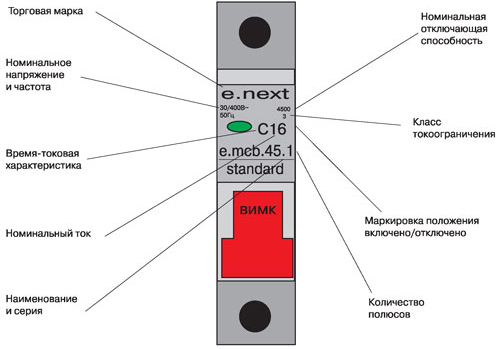
Conclusion
To summarize - the labeling of circuit breakers includes important and auxiliary data. Thanks to it, the electrician can determine the type, rated current, limit current, time-current characteristic of the circuit breaker and quickly select the one suitable for protecting a certain line.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
