Categories: Novice electricians, Automata and RCD
Number of views: 27603
Comments on the article: 2
How the time-current characteristics of circuit breakers and fuses work
Electric current has one distinguishing feature: it is able to flow only in a closed loop. If this chain is broken, then its action immediately ceases. This property is embodied in the operation of overcurrent protection based on the use of fuses and circuit breakers.
They are selected in such a way that they can withstand the nominal value of the current flowing through them for a long time. This ensures the reliability of power supply to consumers. At the same time, fuses and circuit breakers have protective functions: during emergency conditions in a controlled circuit, they break the dangerous current passing through them.
At the same time, two factors are taken into account in the complex:
1. the magnitude of the flowing load current;
2. The duration of its exposure.
The fuse fuse blows out from the heat created by the current passing through it.

The circuit breaker also takes into account the temperature overheating of the circuit and opens its power contacts due to the operation of the thermal release. At the same time, it includes another device - an electromagnetic release, which responds to excess electromagnetic energy, which occurs even in a pulsed mode.
More details about the device, the principle of operation and operation features of circuit breakers and fuses are described here:
Fuse or circuit breaker - which is better?
Fuses automatic threaded type PAR
Selection of circuit breakers by basic parameters
The operation of all these devices is judged by certain technical characteristics, which are usually called time-current because they accurately determine the response time of the protections, given its dependence on the frequency of exceeding the emergency current relative to the nominal state.
Time-current characteristics (VTX) expressed in graphs in Cartesian coordinates. The ordinate axis is the time measured in seconds, and the abscissa is the ratio of the flowing emergency current I to the nominal value In of the switching device.
Why is the protective characteristic of the fuse-link created?
For the correct operation of the fuse inside the electrical circuit, it must be taken into account:
-
technical capabilities;
-
inspection conditions;
-
appointment.
The main parameters of the protective characteristics of the fuse
The fuse trip graph for various currents is expressed by a curve line dividing the working space of the coordinates into two parts:
1. the working area in which the fuse-link remains intact and reliably ensures the flow of current in the protected circuit;
2. the zone of the flow of currents of the limiting shutdown, in which the circuit breaks.
The first part of the graph is shown in light green, and the second is highlighted in beige.
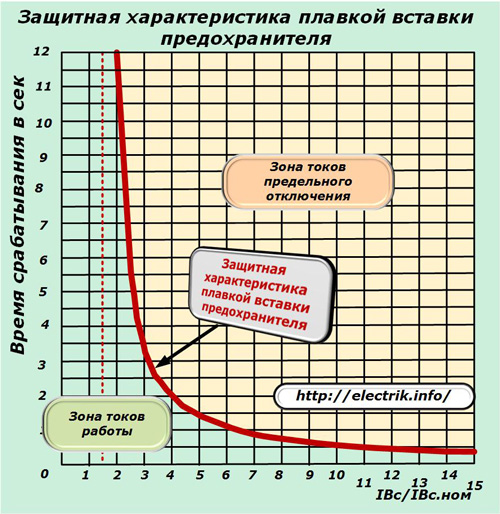
The protective characteristic of the fuse-link lies at the boundary of these two zones. In the space of working currents, the fuse remains intact, and when their values increase above the critical state, it blows.
The current limit zone is dangerous for the equipment and must be switched off as quickly as possible.
The protective characteristic of the fuse box expresses the length of time from the start of the emergency mode to the moment it was turned off, presented depending on the excess of the hazardous current over the rated fuse.
The fuse-link is characterized by three types of currents:
1. rated, which it can withstand almost unlimited time;
2. minimum test, under the action of which it can work more than one hour;
3. The maximum test, which causes its burnout in less than one hour.
The fuse insert protects the circuit connected to it from two types of emergency conditions:
1. overloads with increased loads that turn off with a delay;
2. short circuits - short circuit requiring the fastest possible elimination.
All these modes and types of currents are taken into account when choosing a fuse and fuse. For this, mathematical relations are developed, transformed by graphs and tables in a convenient form.
How to create a protective fuse characteristic
The fuse-link is able to operate the protection only once. After that, it burns out. Therefore, its characterization can only be created indirectly.
To do this, the plant randomly selects a certain number of samples from each batch of finished products. They are used for further electrical tests under various currents. According to their results, tables and graphs are compiled that allow judging the quality of the released series of fuses.
Assignment of fuse protection characteristic
The fuse-link is evaluated by electrical parameters to solve a purely practical task: to ensure its correct choice in terms of working and protective properties.
To do this, take into account:
-
the value of the operating voltage of the circuit in which the fuse should operate;
-
limit breaking current at the fusible insert, capable of breaking it (disconnect);
-
the value of the rated current of the fuse, taking into account the coefficients of its load and the detuning from overloads.
Without using the protective characteristics of the fuse-link, it is impossible to choose the fuse for its reliable operation in the electrical circuit.
How does the current-time characteristic of a circuit breaker work?
The choice of time-current characteristics is influenced by:
-
design features of built-in protections;
-
configuration of the selected schedule.
The influence of the design of the protection of the machine on the form of its response characteristics
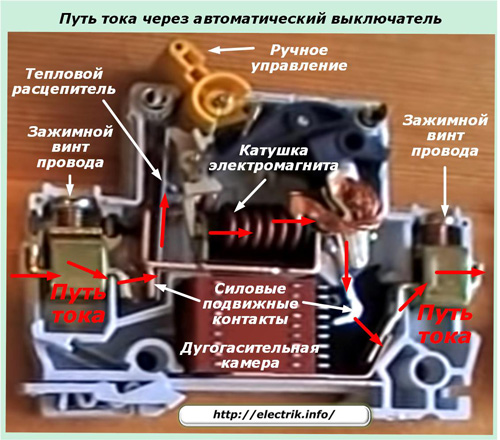
Providing protective properties in the circuit breaker are two built-in devices that operate on the principles of direct-acting relays. They disconnect the power contacts of the machine when the nominal values are exceeded according to the restriction criteria:
1. heat load;
2. electromagnetic exposure.
The bimetal plate of the thermal release senses the heating of the winding wires. When it is exceeded, it bends, removing the clutch assembly from retention.
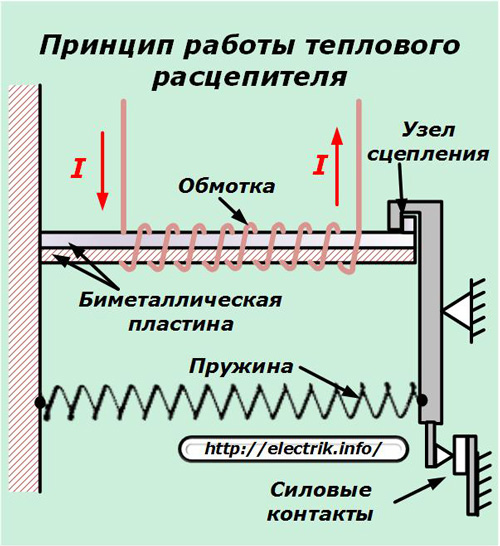
Under the action of the spring tension force, the movable rocker released from holding is rotated, and its power contacts break the power circuit.
In an electromagnetic release, the disconnection of the power contacts occurs due to the knocking out of the holding lever of the spring by the impact of the pusher, which occurs under the influence of the emergency current.
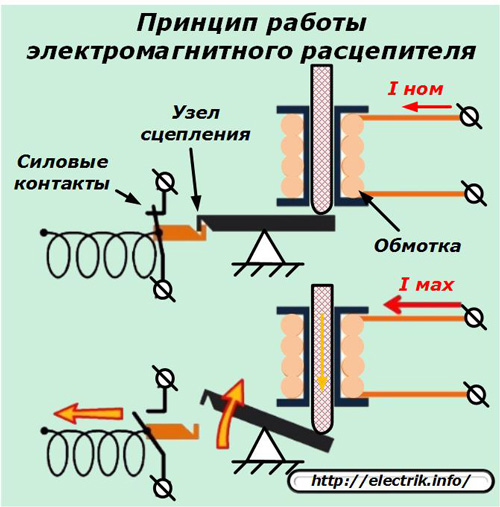
Unlike a fuse with a blown fuse, both of these devices are designed for reusable use. They allow you to quickly restore circuit outages after preventing abnormal situations.
The operation of the thermal release and electromagnetic cutoff is included in the circuit breaker tripping algorithm and is comprehensively taken into account when it trips during the current-current characteristic.
See also:How to make sure when buying a machine in a store that it is working
Since the ambient temperature and the bimetallic plate affect the speed of the shields, all measurements are usually taken at +30 degrees Celsius.
The time-current curve for a circuit breaker is a complex line highlighted by the letters ABC.The upper section AB corresponds to the operation of the thermal release, and its lower part to the electromagnetic cutoff.
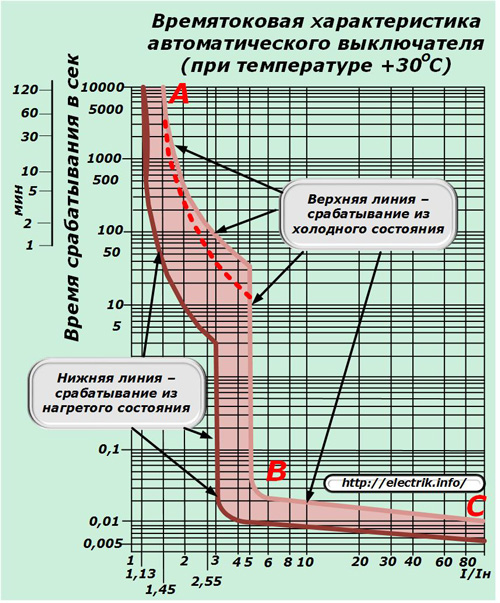
The main parameters of the graph of the time-current characteristic
Temperature effects
In contrast to the protective characteristic of the fuse insert for the circuit breaker, the VTX graph is represented by two lines:
1. top, taking into account the operation of the protection directly from the cold state +30ABOUT FROM;
2. lower, created after repeated switching on, when the design of the machine did not have time to cool.
The area between these two extreme plots is highlighted. When operating a circuit breaker, it should be borne in mind that it can be located somewhere inside the area shown. In this case, the shutdown time of the emergency currents is somewhat reduced in the warmed state and increases in the cold. Due to this, a spread in the response parameters is created.
The temperature of structural elements can have a significant impact on the response time of the machine. This becomes especially relevant when conducting electrical checks that require several measurements. For their repetitions, it is necessary to provide time for cooling of the protections to +30 degrees.
Division of BTX into zones
Circuit breakers strictly separate time zones -
current characteristics for distinguishing operational areas: inside the first, reliable flow of operating currents should be ensured, and in the second, shutdown of emergency conditions should occur.
Line of conditional non-tripping currents
In order to indicate the first region on the abscissa of the graph, 1.13 I / I nom is selected. It is called the conditional non-disengagement point. Below these currents, the circuit breaker must not trip.
When it is reached, circuit breakers with a rated current value of up to 63 amperes must be switched off after 1 hour, and with large ratings - after two.
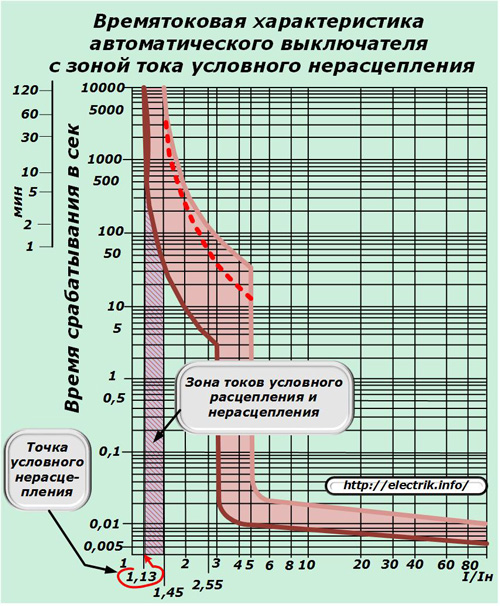
The location of the conditional trip point is indicated on the BTX chart without fail.
Line conditional tripping
A point on the abscissa axis with a value of 1.45 I / I nom is the second boundary value of the zone of currents of conditional tripping and non-tripping of power contacts.
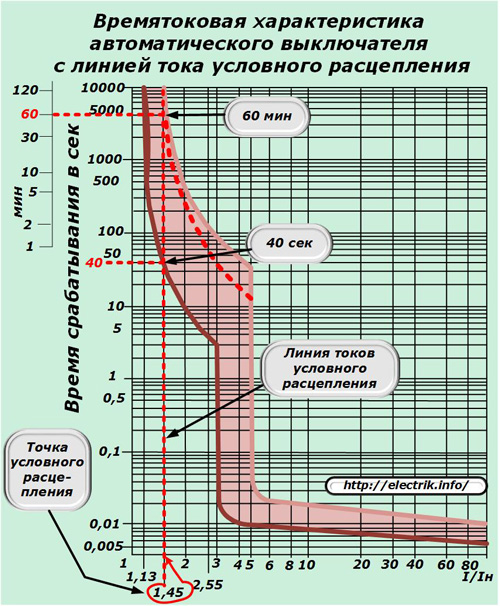
Point 1.45 I / I nom characterizes the currents of conditional tripping, it is also indicated on all graphs of VTX. When the load connected to the machine reaches this value, it must disconnect in a while:
-
less than 1 hour if its face value is up to 63 amperes;
-
no more than two hours when the rated current exceeds this value of 63 amperes.
The above graph shows that the selected circuit breaker has a shutdown time of the emergency mode from the cold state of 1 hour, and when it is heated, it can decrease up to 40 seconds.
Practical application of the VTX parameters
An analysis of the use of the time-current characteristic of circuit breakers for the currents of conditionally tripping power contacts allows you to take into account the duration of the overload in the connected electrical circuit. This is important because they can damage the equipment.
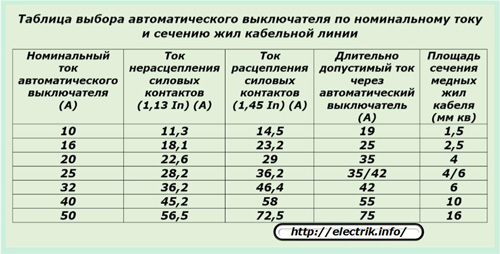
For example, when choosing an automatic machine with a nominal value of 16 amperes and when it is cold, the conditional trip current of 1.45 ∙ 16 = 23.2 amperes will act on the connected wiring for one hour. This time is enough to overheat the insulation of copper wires with a cross section of 1.5 mm square and disable it, create the conditions for a fire. And the cases of protection of such conductors, and aluminum 2.5 mm square, with such automatic machines are still often found in practice.
To exclude such situations, it is recommended to carefully analyze the time-current characteristic of circuit breakers in relation to the load connected to them. To facilitate their selection, a correspondence table has been created for the rated currents and cross-sectional areas of copper conductors of cables and wires.
Manufacturers of circuit breakers check all their products for compliance with accepted standards. The basic requirements for machines are set out in GOST R 50345—2010. However, in some areas, the time-current characteristics of each plant may vary slightly. This feature must be considered when choosing a particular model and its checks.
Types of time-current characteristics of circuit breakers
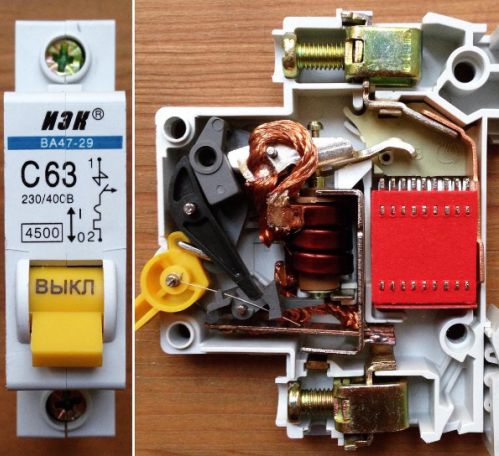
Circuit breakers can be created for various purposes for operating conditions. According to these indicators, their VTX graphs have different time response limits. This allows them to rebuild on selectivity, to avoid false shutdowns of equipment.
Circuit breakers are available for domestic or industrial use.
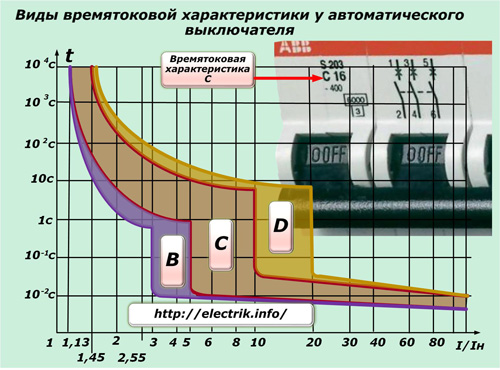
Household machines are classified in three groups B, C and D:
1. Class B is designed to protect long lines and lighting systems. The multiplicity of currents for its operation lies within 3 ÷ 5 In;
2. Class C protects outlet groups or equipment that generates moderate inrush currents. The multiplicity of currents 5 ÷ 10 In;
3. Class D is used to protect consumers with high inrush currents, for example, transformers or machines with powerful asynchronous electric motors. Multiplicity of currents 10 ÷ 20 Inom.
Type B circuit breakers are more sensitive. They decided to protect end consumers inside apartments and houses. And as an introductory automaton, it is better to install those that belong to type C.
The quality of the wiring condition and the magnitude of the resistance of the phase-zero loop can affect the choice of a circuit breaker. Old insulation with a high content of leakage currents and overestimated loop performance can worsen the operation conditions of a type C machine or bring it to failure. In such situations, class B is used.
Industrial machines are classified in three groups:
1. class L - more than 8 In;
2. class Z - more than 4 Inom;
3. class K - more than 12 Inom.
Among manufacturers in Europe there are models of machines with class A, which has a current multiplicity boundary of 2 ÷ 3 Inom.
All these features must be taken into account when choosing the design of the circuit breaker and its checks. Automatons marked with the same rating, depending on the type of time-current characteristic, have different response times.
More on this topic: Main parameters of circuit breakers
See also at i.electricianexp.com
: