Categories: Automata and RCD
Number of views: 26261
Comments on the article: 6
Automatic steam fuses - device and features of use
 Since the beginning of mass electrification of the country, the issue of ensuring the protection of electrical equipment and people from electric shock has been an acute issue. For this purpose, the industry launched a mass production of fuses with fusible inserts equipped with a thin wire thread. It burned out during increased load or short circuit in a controlled circuit.
Since the beginning of mass electrification of the country, the issue of ensuring the protection of electrical equipment and people from electric shock has been an acute issue. For this purpose, the industry launched a mass production of fuses with fusible inserts equipped with a thin wire thread. It burned out during increased load or short circuit in a controlled circuit.
Their design included a permanently installed dielectric block with two contacts, into which a porcelain body with a replaceable fusible insert was screwed. Such fuses were installed in pairs in the phase and neutral wires of the supply network.
After a short operation, the disadvantages of this design were identified:
-
frequent burnout of calibrated insert threads, caused by poor stability of the electrical characteristics of the power supply system and low technical literacy of the population;
-
the need to have a large supply of replaceable fuses in home use;
-
the massive use of homemade "bugs" instead of fuses with significantly higher current ratings, due not only to a shortage of fuses on sale, but also to the reluctance of people to buy them.

After that, the industry mastered the production of an automatic device for protecting home electrical wiring 220 volts based on the pads already in use.
According to the existing tradition, they were also called fuses. Only along the way added the terms:
-
automatic, which determines the possibility of an autonomous shutdown of faults and subsequent manual switching on by a person without replacing any parts;
-
threaded, indicating the principle of attachment to a dielectric block.
As a result, this defense received the short name PAR, consisting of the abbreviation of these three words.

The principle of formation of protective characteristics
The basis of the PAR operation is the simultaneous monitoring of the load currents flowing through it with two devices based on:
1. thermal releases operating with a delay time for shutdown;
2. current cut-off, quick-acting when critical network loads occur.
A summary time profile of these SAF defenses is shown in the current schedule.

The basis of the scale is the excess of loads of nominal values along the abscissa axis and the duration of its action in seconds on the ordinate axis.
Two lines of this characteristic are clearly visible on the chart:
1. a drop-down section in hyperbolic dependence formed by the operation of a thermal release;
2. Strictly straight vertical line showing the operation of the current cutoff.
The operating characteristic of an automatic threaded fuse clearly demonstrates two principles underlying the design of this device:
1. reliable transmission of the rated load current without false responses (the curve is slightly shifted to the right of the ratio I / In = 1);
2. shutdown at excess of nominal values.
The operation area of the thermal release provides acceleration of shutdowns of very high loads and at the same time maintains a voltage supply to the home network with insignificant short-term inrush currents.
For example, when the nominal value is tripled, caused by the start of the electric motor and its output to the mode, the PAR controls the situation and does not disconnect the voltage for 8 seconds, which is enough to turn on and accelerate the rotor together with the connected kinematic circuit.
If the excess reaches six times, then the protection will work in a little more than one second.
At nine overstating currents, a current cut-off is activated, which relieves voltage from the equipment in 0.1 second or even faster.
How to choose the optimal steam design for home use
Automatic fuses are designed specifically for domestic use with a voltage of 220 and a little less often - 380 volts. For this purpose, on their case and in the documentation the technical characteristics implemented by the manufacturer are indicated.

Devices designed for two-wire networks 220 are produced for rated currents of 6.3 and 10 amperes, and for circuits 380 - 10, 16 or 20. These indicators should be used when choosing protection.
To do this, calculate the power of all electrical consumers of the apartment, which can be simultaneously turned on, and divide its expression in watts by current voltage in volts. It turns out the load current in amperes. It remains to compare it with the rated current of the steam and select the most suitable model from the line manufactured by the manufacturer.
It should be noted that the creation of a small margin of protection current will provide a reserve of power consumption for connecting additional devices, and the absence of it will cause redundant, knowingly false shutdowns.
PAR operation modes
Based on the patterns shown using the time schedule, four main stages of the protection state can be distinguished:
1. rated mode;
2. operation of the thermal release;
3. current cutoff;
4. Manual shutdown and on.
Let's consider them in more detail.
Steam Optimum Load Mode
The design of the main protection elements is shown in the figure below.
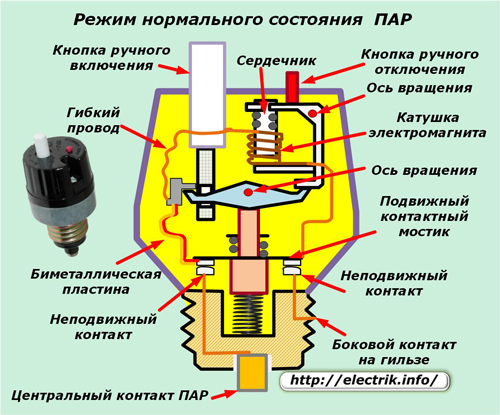
The load current is supplied to the central contact of the protection and removed from the side, located on a threaded metal insert. Inside the case, a movable anchor moves, which has two fixed positions:
1. lower worker when the power contacts are closed;
2. top protective, providing a break in the electrical circuit.
When located below, the force of the compressed spring acts on the anchor, the upward direction of which is blocked by the fixation of the upper contact pads of the pivoting lever. Its position is limited on the left side by a pin of a bimetallic plate (some manufacturers install twisted wire), and on the other, by a continuation of the shutdown electromagnet housing.
In this state, the rated load current passes through the PAIR along the path:
-
central contact of the housing;
-
connection wire with fixed contact;
-
the left contact of the movable bridge, connected due to the force of spring compression;
-
bimetallic plate with a persistent pin;
-
a flexible wire connected to an electromagnet winding;
-
a conductor connecting a trip coil to a second movable contact;
-
a contact pad between the right side of the bridge and the stationary part;
-
a wire providing connection with a threaded tip.
A current of a nominal value passing through the bimetal and the coil of the coil induces working heat and an electromagnetic field in them, which only prepare the disconnecting elements for operation, but are not able to relieve voltage from the working circuit.
Emergency shutdown occurs when the setpoint values are exceeded.
Network congestion mode
When the load current becomes greater than the nominal value, then its thermal effect on the bimetal gradually leads to the bending of the plate and the removal of the pin fixed on it from engagement with the movable arm of the armature.
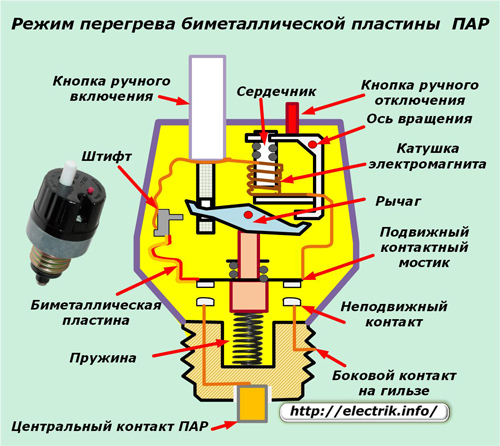
The left end of the lever disengages and rotates around its axis of rotation. The released energy of the compressed spring pushes the anchor up together with the movable bridge attached to it. The left and right power contacts reliably provide two-sided breaking of the current circuit, which appeared under the influence of emergency mode.
After current interruption, the bimetallic plate begins to cool and return to its original position. But, for this it is necessary to withstand some time.
After the bimetal returns to its cooled state, you can press the large white manual button on the STOP end. This action lowers the entire anchor and engages the left part of the rocker arm with a pin that has returned to its original position.
The fuse turns out to be in working position and begins to control the processes of current flowing through it. If the cause of the PAR shutdown remains unresolved, then it will be triggered again.
Network short circuit mode
When between phase and neutral wires If a small electrical resistance occurs or they are short-circuited, then a short-circuit current is generated, passing through both disconnecting systems. Only an electromagnet coil is faster than bimetal bends.
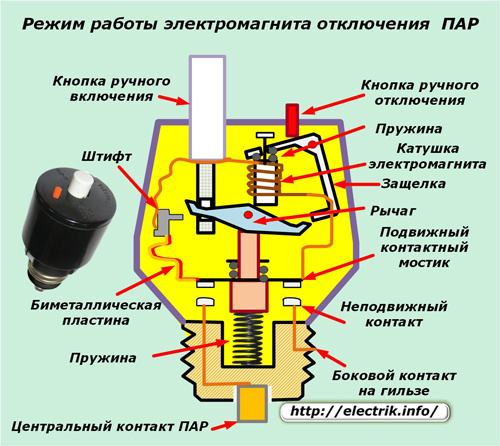
Under the influence of the generated magnetic field, the core of the coil is sharply pulled down and strikes the lever, and the latch of the electromagnet simultaneously rotates about its axis, removing the anchor retention.
The lower spring with its force, as in the previous case, throws up the movable system together with the fixed power contacts. As a result, they relieve tension from the protected zone.
Since a large current flow is necessary for such a shutdown, it manages to heat up the bimetallic element, which is deformed and prohibits rapid manual switching on before cooling and returning its restrictive pin to its original position.
The fuse can be returned to ON after cooling the thermal release. But, for this, the cause of the triggering of the PAR should be eliminated. Otherwise, there will be a repeated release of voltage from the circuit with sensitive protection.
Steam Manual Off Mode
Sometimes, to carry out repair work, for example, periodically removing the meter for verification, it is necessary to disconnect the voltage from the electrical wiring of the apartment. For these purposes, a small red button for manual shutdown is mounted on the fuse box.
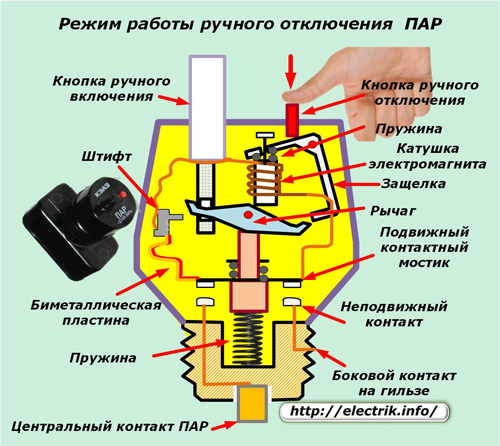
When pressed, the body of the latch of the electromagnet rotates around its axis, freeing the engagement of the right side of the pivot arm, as when triggered by the electromagnet. The anchor is released from hold and under the force of the spring opens its contacts.
We remind you that for safe work in electrical installations it is necessary to visually verify the creation of an open circuit. It can only be seen with the protection housing turned out of the dielectric block.
During the operation of steam, special attention is paid to:
-
the state of the pads and the force of their squeeze;
-
the compression ratio of the spring, affecting the speed of emergency shutdowns.
Conclusion
Threaded automatic fuses meet the requirements of safety and reliability in their characteristics. However, due to the rapid increase in the load on the home network and mass production for them various circuit breakershaving smaller dimensions and the ability Din rail mounts, SAR protections are less and less installed in new buildings and continue to operate in old buildings located mainly in rural areas.
Read also:Which protection devices are better: fuses or circuit breakers?
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
