Categories: Featured Articles » Practical Electronics
Number of views: 50067
Comments on the article: 5
How to determine the type of capacitor
There are many different types of capacitors in the electronic components market today, and each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Some are capable of operating at high voltages, others are notable for significant capacitance, others have a low inductance, and some are characterized by an exceptionally low leakage current. All these factors determine the application of specific types of capacitors.
Consider what types of capacitors are. In general, there are a lot of them, but here we will consider the main popular types of capacitors, and we will figure out how to determine this type.

Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors, for example, K50-35 or K50-29, consist of two thin strips of aluminum twisted into a roll, between which electrolyte-impregnated paper is placed as a dielectric. The roll is placed in a sealed aluminum cylinder, on one of the ends of which (radial type of housing) or on two ends of which (axial type of housing) are the contact leads. Conclusions can be soldered or screw.
The capacitance of electrolytic capacitors is measured by microfarads, and can be from 0.1 microfarads to 100,000 microfarads. A significant capacity of electrolytic capacitors, in comparison with other types of capacitors, is their main advantage. The maximum operating voltage of electrolytic capacitors can reach 500 volts. The maximum permissible operating voltage, as well as the capacitance of the capacitor, are indicated on its housing.
This type of capacitors also has disadvantages. The first of which is polarity. On the capacitor case, the negative terminal is marked with a minus sign, this terminal should be present when the capacitor in the circuit operates at a lower potential than the other, or the capacitor will not be able to accumulate charge normally, and will most likely explode, or be damaged in any case if it takes a long time keep it energized with the wrong polarity.
Due to the polarity, electrolytic capacitors are applicable only in direct current or pulsating current circuits, but not directly in alternating current circuits, only rectified voltage can charge electrolytic capacitors.
The second disadvantage of this type of capacitor is the high leakage current. For this reason, it will not be possible to use an electrolytic capacitor for long-term storage of charge, but it is quite suitable as an intermediate filter element in the active circuit.
The third disadvantage is that the capacitance of this type decreases with increasing frequency (ripple current), but this problem is solved by installing on the boards parallel to the electrolytic capacitor a ceramic capacitor of a relatively small capacity, usually 10,000 less than that of the adjacent electrolytic one.
See here for more details: Electrolytic capacitors

Now let's talk about tantalum capacitors. An example is K52-1 or smd A. They are based on tantalum pentoxide. The bottom line is that when tantalum is oxidized, a dense, non-conductive oxide film is formed, the thickness of which can be technologically controlled.
A solid state tantalum capacitor consists of four main parts: anode, dielectric, electrolyte (solid or liquid) and cathode. The production chain is rather complicated. First, an anode is created from pure pressed tantalum powder, which is sintered in high vacuum at a temperature of 1300 to 2000 ° C to obtain a porous structure.
Then, by electrochemical oxidation, a dielectric is formed in the form of a tantalum pentoxide film, the thickness of which is controlled by changing the voltage during electrochemical oxidation, as a result, the film thickness is obtained from hundreds to thousands of angstroms, but the film has such a structure that provides high electrical resistance.
The next stage is the formation of an electrolyte, which is a semiconductor manganese dioxide. The tantalum porous anode is impregnated with manganese salts, then it is heated so that manganese dioxide appears on the surface; the process is repeated several times until full coverage is obtained. The resulting surface is covered with a layer of graphite, then silver is applied - a cathode is obtained. The structure is then placed in a compound.
Tantalum capacitors are similar in properties to aluminum electrolytic, but they have features. Their operating voltage is limited to 100 volts, the capacitance does not exceed 1000 microfarads, their own inductance is less, therefore, tantalum capacitors are also used at high frequencies reaching hundreds of kilohertz.
Their disadvantage is that they are extremely sensitive to exceeding the maximum allowable voltage, for this reason tantalum capacitors fail most often due to breakdown. A line on the body of the tantalum capacitor indicates a positive electrode - anode. Lead or SMD tantalum capacitors can be found on modern printed circuit boards of many electronic devices.

Ceramic Single Layer Disc Capacitors, for example, types K10-7V, K10-19, KD-2, are characterized by a relatively large capacity (from 1 pF to 0.47 microfarads) with small sizes. Their operating voltage ranges from 16 to 50 volts. Their features: low leakage currents, low inductance, which enables them to operate at high frequencies, as well as small size and high temperature stability of the capacitance. Such capacitors successfully operate in DC, AC and ripple current circuits.
The loss tangent tanδ usually does not exceed 0.05, and the maximum leakage current does not exceed 3 μA. Ceramic capacitors are stable in external factors, such as vibration with a frequency of up to 5000 Hz with acceleration up to 40 g, repeated mechanical shocks and linear loads.
Ceramic disk capacitors are widely used in smoothing filters of power supplies, in filtering interference, in inter-stage communication circuits, and in almost all electronic devices.
Marking on the capacitor housing indicates its rating. Three numbers are deciphered as follows. If you multiply the first two digits by 10 to the power of the third digit, you get the value of the capacitance of this capacitor in pf. So, a capacitor labeled 101 has a capacitance of 100 pF, and a capacitor labeled 472 has 4.7 nF.

Ceramic Multilayer Capacitors, for example, K10-17A or K10-17B, unlike single-layer ones, have alternating thin layers of ceramic and metal in their structure. Their capacity is therefore greater than that of single-layer ones, and can easily reach several microfarads. The maximum voltage is also limited here to 50 volts. Capacitors of this type are capable, like single-layer ones, of working properly in DC, AC and pulsating current circuits.

High Voltage Ceramic Capacitors able to work at high voltage from 50 to 15000 volts. Their capacitance lies in the range from 68 to 100 nF, and such capacitors can operate in DC, AC or pulsating current circuits.
They can be found in line filters as X / Y capacitors, as well as in secondary power supply circuits, where they are used to eliminate common-mode interference and noise absorption if the circuit is high-frequency. Sometimes without the use of these capacitors, failure of the device can endanger people's lives.

A special type of high voltage ceramic capacitor is high voltage pulse capacitorused for powerful pulse modes. An example of such high-voltage ceramic capacitors are domestic K15U, KVI and K15-4. These capacitors are capable of operating at voltages up to 30,000 volts, and high voltage pulses can follow at high frequencies, up to 10,000 pulses per second. Ceramics provide reliable dielectric properties, and the special shape of the capacitor and the arrangement of the plates prevents breakdown from the outside.
Such capacitors are very popular as circuit in high-power radio equipment and are very welcome, for example, with teslostroiteley (for design Tesla coils on a spark gap or on lamps - SGTC, VTTC).
Polyester (polyethylene terephthalate, lavsan) capacitors, for example K73-17 or CL21, based on a metallized film are widely used in switching power supplies and electronic ballasts. Their case made of epoxy compound gives the capacitors moisture resistance, heat resistance and makes them resistant to aggressive environments and solvents.
Polyester capacitors are available in capacities from 1 nF to 15 microfarads, and are designed for voltages from 50 to 1500 volts. They are distinguished by high temperature stability with high capacity and small size. The price of polyester capacitors is not high, so they are very popular in many electronic devices, in particular in ballasts of energy-saving lamps.
The capacitor marking contains at the end a letter denoting the tolerance for the deviation of the capacitance from the nominal, as well as a letter and a number at the beginning of the marking, indicating the permissible maximum voltage, for example 2A102J - capacitor for a maximum voltage of 100 volts, 1 nF capacity, permissible capacitance deviation + -5% . Labeling tables can be easily found on the Internet.
A wide range of capacitances and voltages, makes it possible to use polyester capacitors in DC, AC and pulsed current circuits.
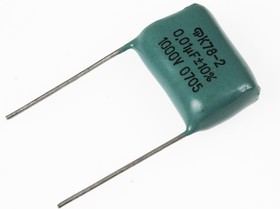
Polypropylene Capacitors, for example, K78-2, unlike polyester, have a polypropylene film as an insulator. Capacitors of this type are available in capacities from 100 pF to 10 microfarads, and the voltage can reach 3000 volts.
The advantage of these capacitors is not only a high voltage, but also an extremely low loss tangent, since tanδ can not exceed 0.001. Such capacitors are widely used, for example, in induction heaters, and can operate at frequencies measured by tens or even hundreds of kilohertz.

Deserve special mention starting polypropylene capacitorssuch as CBB-60. These capacitors are used to start AC induction motors. They are wound with a metallized polypropylene film on a plastic core, then the roll is filled with a compound.
The capacitor housing is made of a material that does not support combustion, that is, the capacitor is completely fireproof and is suitable for use in harsh conditions. The conclusions can be either wired, or under the terminals and under the bolt. Obviously, capacitors of this type are designed to operate at an industrial network frequency.
Starting capacitors are available for alternating voltage from 300 to 600 volts, and the range of typical capacities is from 1 to 1000 microfarads.
See also on this topic: The use of capacitors in electronic circuits
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
