Categories: How does it work
Number of views: 3249
Comments on the article: 0
The device and principle of operation of the 3D printer, the main methods and types of 3D printing
Currently, 3D printing technology is increasingly being used to create decorative elements, machine parts and apparatus, and various functional units. And the most relevant developments allow you to print entire buildings and even organs and prostheses for humans. At the same time, on the market you can find printers starting at several hundred dollars, for domestic use and tens of thousands of dollars - for industrial use. In this article, we will cover basic information about the types and design of a 3D printer.
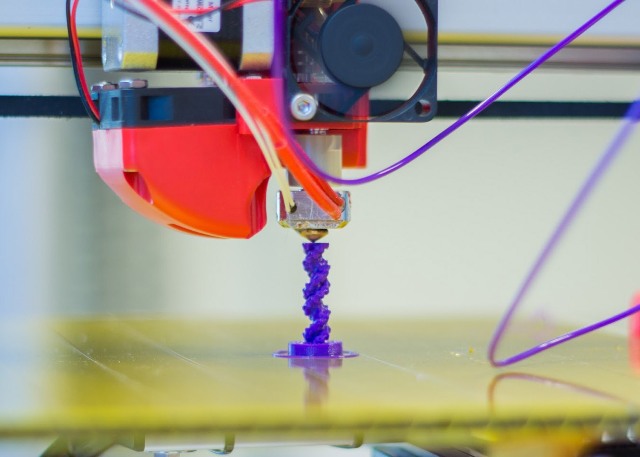

Kinds
The concept of 3D printing is not so clear. It is divided into many types, differing on the principle of forming a printable object and the materials used for this. What are they like?
FDM printing (Fused Deposition Modeling) - This is the most common way to obtain volumetric objects in everyday life, respectively, and the cheapest option for volumetric printing. In this case, the 3D printer prints the part with molten plastic. The most commonly used plastics are PLA and ABS. The thickness of 1 printing layer is on average between 50-100 microns (in most models). What this printer consists of we will consider later.
SLA Printing (Laser Stereolithography) - sounds like "stereo lithography." The installation for this type of 3D printing consists of a laser (this is a fixing body that moves along the rods with the help of engines) of the base on which the part and bathtubs with liquid photopolymers are printed. The principle of operation is the use of photopolymer words as a material.
The laser draws on resin each layer of the future object. After each layer, the working platform is immersed in a bath with a photopolymer to a depth equal to the thickness of the next layer. The interaction of the laser beam and the photopolymer hardens in the places where the laser beam hit its surface.
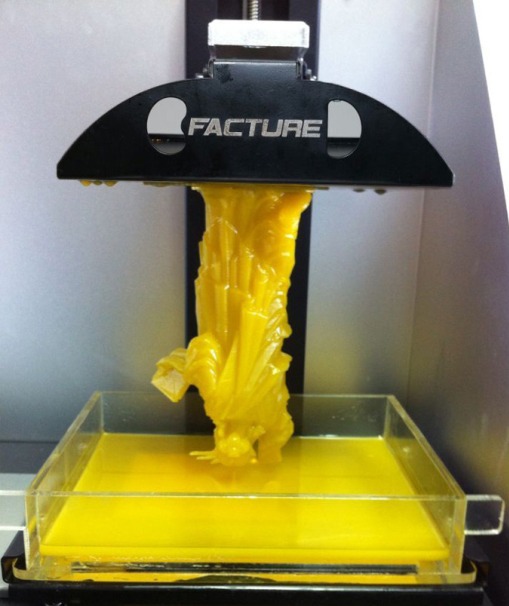

This method allows you to achieve accurate results, and the layer thickness can reach as little as 15 microns. This allows the use of stereolithography for medical purposes (dentistry) and jewelry. SLA technology does not require the printing of supporting elements, and after printing the product is immersed in a bath with solutions to clean the model. The final stage is ultraviolet irradiation for the complete fixation of photopolymers. The main disadvantage is the high cost of printers and supplies, which makes it inappropriate to use it at home.
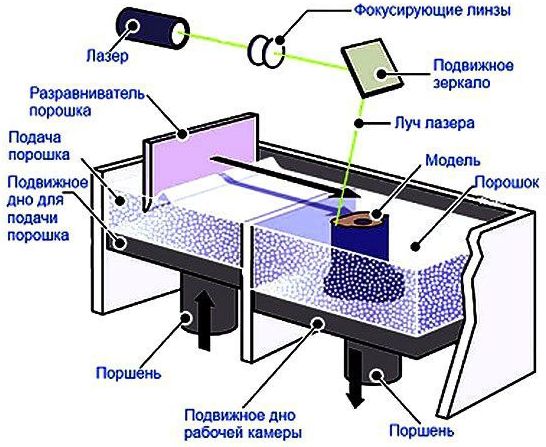
SLS technology - Selective laser sintering. A powder layer is fed to the working surface, depending on the task - it can be metal, plastic, and even ceramics and glass, after which the layer area of the future part is processed with a laser, then the platform is lowered, and the process is repeated. Reminds SLA, by the principle of action. At the end of the process, heat treatment of the element is required. Also not suitable for domestic use and is expensive.
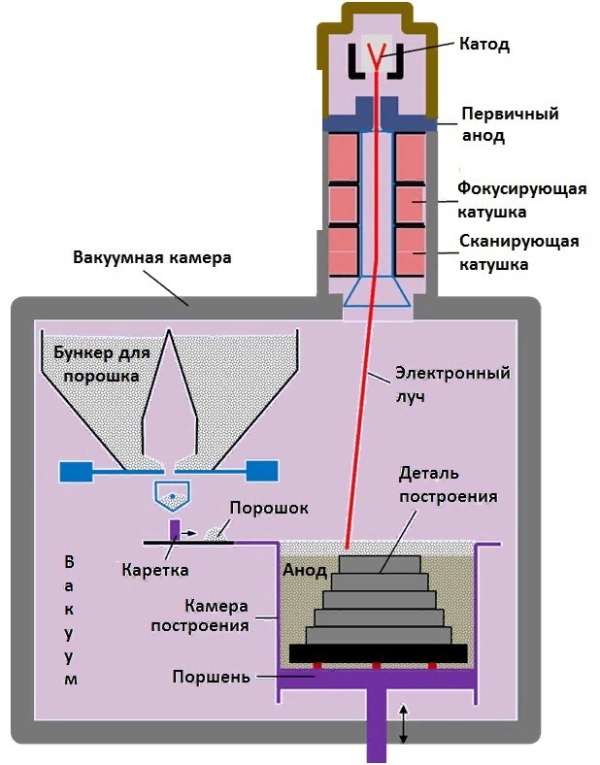
Electron beam melting or EBM technology. It differs from the previous technology in that the metal powder is melted by an electron beam in a vacuum, and the result does not require heat treatment.
SLM - selective laser melting, works only with metal powders, according to the principle of operation it is similar to SLS, but, like in EBM, final heat treatment is not required.
3Dp - the difference from the previous ones is that the working material is not melted, but layers of glue are applied using inkjet printing. In this way, color 3D printing is possible.
FDM 3D Printer
Printing using FDM technology is the most common among both amateurs and for solving many professional tasks. The same method is one of the oldest. Therefore, we will examine in more detail exactly the type of volumetric printing that is well suited for the home and workshop.
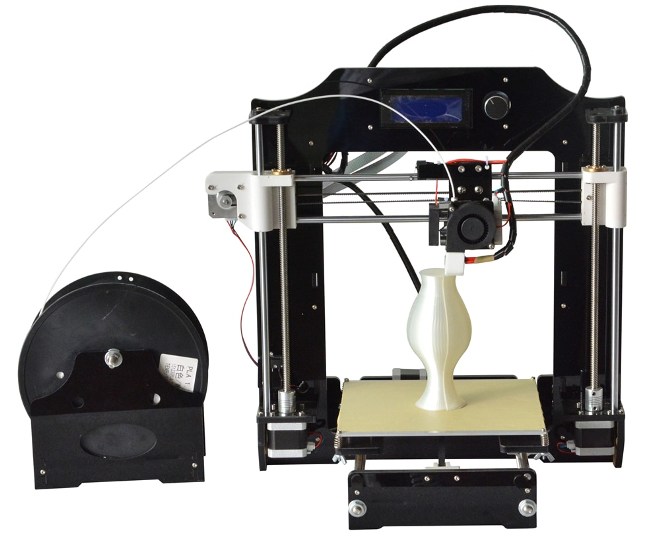

Device and features
A 3D printer that prints with plastic using FDM technology consists of:
1. The working surface, often called the platform. It can be heated.
2. An extruder, in simple terms, is a print head.It has a plastic filing mechanism, heaters and print nozzles.
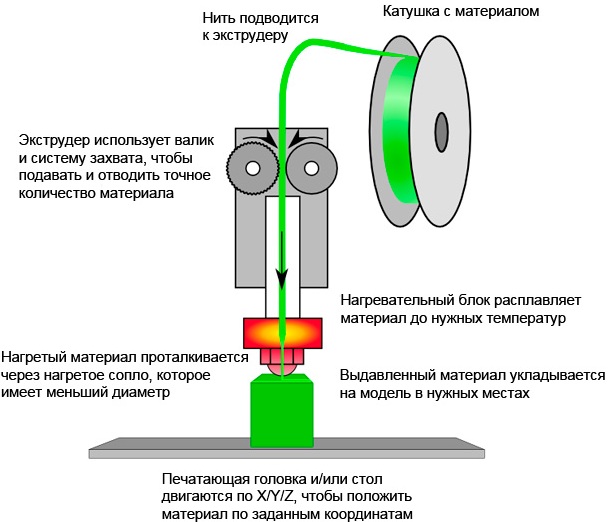
3. The mechanism of movement of the extruder along the axes. Consists of rods, a helical shaft and motors, for example, stepping.
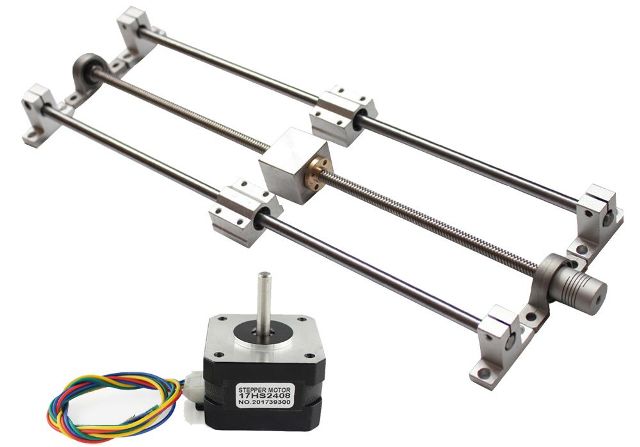

Depending on the design of the printer, both the extruder and the working surface can move along the vertical axis (Z axis), and it can also move along the Y axis. The extruder moves along the horizontal axes.
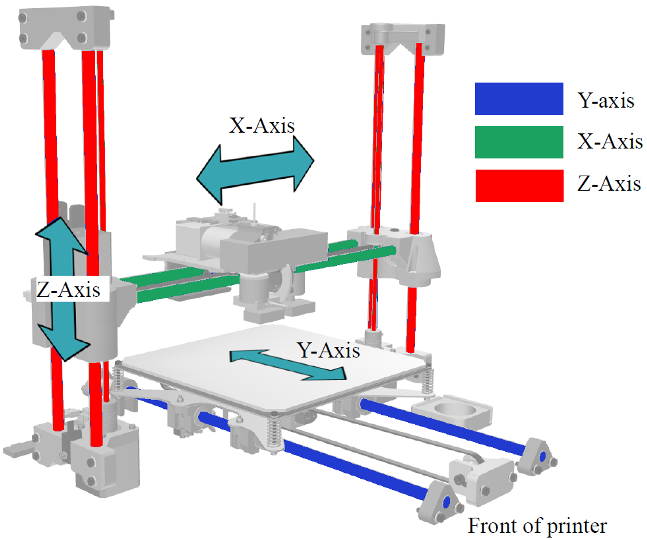
Note:
A 3D model is created for printing using any type of 3D printer, but it cannot be loaded into the printer for printing. Before this, the model is processed, the so-called G code. The meaning of this action is to divide the model into layers and form trajectories along which the extruder will move (or another printing element, depending on the technology).
When printing, ABS and PLA plastics are used. Depending on the complexity of the device, the extruder may contain two nozzles and more - one for printing parts with basic material, and the other for printing supporting supports (supports).

Supports are needed to support parts hanging in the air so that they do not sag during cooling and solidification. After printing is completed, the support legs are removed.
A simplified version of the 3D printer is 3D pen. In fact, it is an extruder that you yourself move your hand. Although it’s a children's toy, it’s just a wonderful product for entertainment and acquaintance with technology, and if you have artistic skills, you will surely be able to create beautiful home decor.
Specifications
When choosing a 3D printer, you need to consider several characteristics, among them:
-
What materials the device prints, although the most common models support printing with two types of plastics - ABS and PLA, but still pay attention to this issue when buying.
-
Print Resolution - The quality and accuracy of the part depends on the thickness of the layer. A layer thickness of 50 microns is considered excellent, and at 100 - more than good.
-
Print speed - more dependent on print resolution.
Important:
Since the part is printed in layers, remember that its surface will be rough and dull, and its fracture strength will be much lower than that of solid products. The height (thickness, as you prefer) of the layer depends on how rough the part will turn out. On the other hand, the thinner the layer - the more time will be spent on printing and the more passes the extruder will make, the load on all elements of the printer will increase.
-
Dimensions of the print area - this issue can become a stumbling block in the choice of a particular model. You cannot print the product more than the printable area. It is limited by width, depth, and height, in other words, the X, Y, and Z axes.
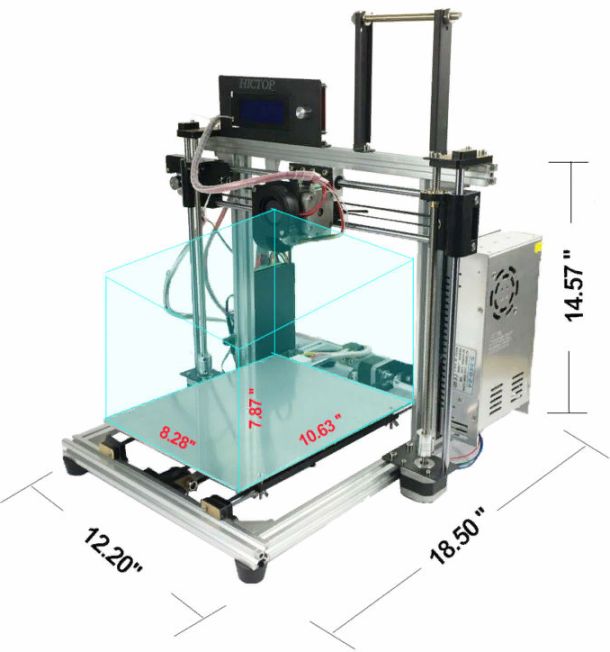
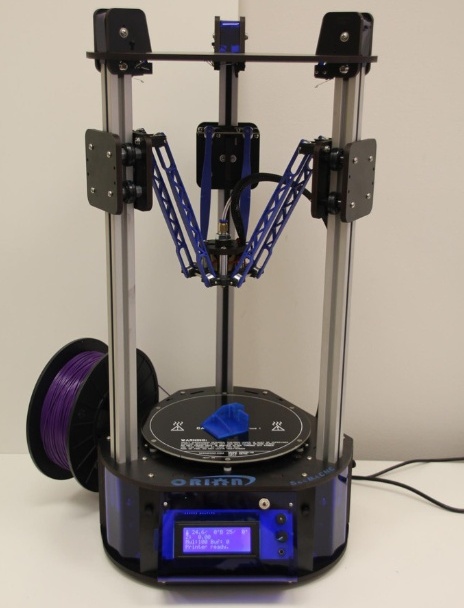
In some cases, for example, for delta printers, the diameter and height of the print area are indicated, since it has a cylindrical shape (see the figure below).

Conclusion
In this article, we touched on general questions about 3D printers and printing in general, if you are interested in any specific topics in more detail - write about this in the comments and we will tell you about them.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
