Categories: How does it work
Number of views: 38105
Comments on the article: 0
Types of electric generators and the principles of their work
An electric generator is a machine or installation designed to convert non-electric energy into electrical energy: mechanical energy into electrical energy, chemical energy into electrical energy, thermal energy into electrical energy, etc. Today, basically, when we use the word “generator”, we mean a mechanical converter energy into electrical energy.
It can be a diesel or gasoline portable generator, a nuclear power plant generator, a car generator, a homemade generator from an asynchronous electric motor, or a low-speed generator for a low-power wind turbine. At the end of the article, we will take as an example the two most common generators, but first we’ll talk about how they work.

One way or another, from a physical point of view, the principle of operation of each of the mechanical generators is one and the same: electromagnetic induction phenomenonwhen, when the magnetic field crosses the conductor, the induction emf arises in this conductor. The sources of the force leading to the mutual movement of the conductor and the magnetic field can be various processes, however, as a result, the emf and current must always be obtained from the generator to power the load.
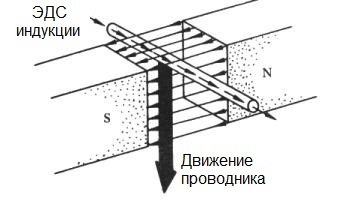
The principle of operation of the electric generator - Faraday Law
The principle of the electric generator was discovered back in 1831 by the English physicist Michael Faraday. Later, this principle was called the law of Faraday. It lies in the fact that when the conductor crosses perpendicular to the magnetic field, a potential difference occurs at the ends of this conductor.
The first generator was built by Faraday himself according to the principle he discovered, it was a “Faraday disk” - a unipolar generator in which a copper disk rotated between the poles of a horseshoe-shaped magnet. The device produced significant current with a slight voltage.
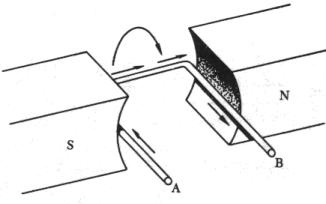
It was later found that individual insulated conductors in generators are much more efficient from a practical point of view than a solid conductive disk. And in modern generators, it is now the stator wire windings that are used (in the simplest case, a coil of wire).
Alternator
The vast majority of modern generators are synchronous alternators. They have an anchor winding on the stator, from which the generated electrical energy is diverted. An excitation winding is located on the rotor, to which a constant current is supplied through a pair of contact rings in order to obtain a rotating magnetic field from a rotating rotor.
Due to the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction, when the rotor rotates from an external drive (for example, from an internal combustion engine), its magnetic flux intersects each of the phases of the stator winding in turn, and thus induces an emf in them.
Most often there are three phases, they are physically displaced at anchor relative to each other by 120 degrees, so a three-phase sinusoidal current is obtained. Phases can be connected in a “star” or “triangle” pattern to obtain standard mains voltage.
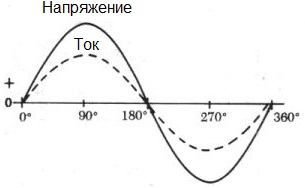
The frequency of the sinusoidal EMF f is proportional to the rotor speed: f = np / 60, where - p is the number of pairs of magnetic pluses of the rotor, n is the number of revolutions of the rotor per minute. Typically, the maximum rotor speed is 3000 rpm. If you connect a three-phase rectifier to the stator windings of such a synchronous generator, you will get a direct current generator (this is, by the way, all automobile generators work).
Three-machine synchronous generator
Of course, the classic synchronous generator has one serious minus - on the rotor there are contact rings and brushes adjacent to them. Brushes spark and wear out due to friction and electrical erosion. In an explosive atmosphere this is not permissible. Therefore, in aviation and in diesel generators, contactless synchronous generators, in particular three-machine ones, are more common.
Three machines have three machines in one housing: a pre-exciter, an exciter and a generator on a common shaft. The pre-exciter is a synchronous generator, it is excited from permanent magnets on the shaft, the voltage it generates is supplied to the stator winding of the exciter.
The stator of the pathogen acts on the winding on the rotor connected to a three-phase rectifier fixed to it, from which the main excitation winding of the generator is fed. The generator generates current in its stator.
Gas, diesel and gasoline portable generators

Today very common in households diesel, gas and gasoline generatorswhich use ICE as an internal combustion engine - an internal combustion engine that transmits mechanical rotation to the generator rotor.
Liquid fuel generators have fuel tanks, for gas generators - it is necessary to supply fuel through the pipeline, so that then the gas is fed into the carburetor, where it will turn into an integral part of the fuel mixture.
In all cases, the fuel mixture is burned in the piston system, causing the crankshaft to rotate. This is similar to a car engine. The crankshaft rotates the rotor of a contactless synchronous generator (alternator).
The best inverter generators of home power plants have a built-in battery to compensate for differences and a double conversion system, in such devices the alternating voltage is more stable.
Car Generators

Another example of an alternator - the most common type of generator in the world - car generator. This generator traditionally contains an excitation winding with slip rings on the rotor and a three-phase stator winding with a rectifier.
The built-in electronic regulator keeps the voltage within the acceptable range for a car battery. A car generator is a high-speed generator, its speeds can reach 9000 per minute.
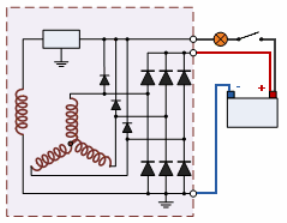
Although initially the current is obtained alternating (the pole tips of the rotor alternately and in different polarity intersect the three phases of the stator winding with their magnetic fluxes), then it is rectified by diodes and turns into a constant one suitable for charging the battery.
Unusual designs of electric generators:
Robert Alexander’s super-efficient motor generator
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
