Categories: Safety precautions
Number of views: 25246
Comments on the article: 0
What is touch voltage?
Touch voltage is the voltage that occurs on the body of a person or animal at the time of its simultaneous contact with a pair of points of a live conductor or with a pair of conductive parts of electrical equipment, for example, a wire in damaged insulation.
In general, the concept of “touch voltage” refers to two conductive parts that are open for contact, or to an open conductive part and a place on the surface of the earth or floor on which a person or animal stands. If even a person or animal is not currently at the indicated place, one can at least judge the expected touch voltage, that is, its estimated value.

Danger of contact stress
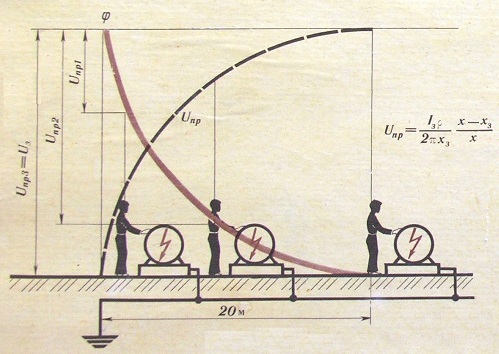
If the insulation of electrical equipment, or the insulation of supply wires, lines, is at least partially damaged, then there is a high probability that a certain voltage will appear on the housings of such equipment and on structures with which this equipment is in contact.
For example, a person standing on the ground touches the frame of some installation, which (the frame) for some reason turned out to be energized, although it is grounded at the same time. In this case, the potential difference between the points on the ground where the human foot is located and the body, in the place where the contact occurs, will be the numerical value of the touch voltage.
If this voltage is safe (within 2 volts of alternating voltage), then there is no reason for excitement, but if it is much higher (if at least exceeds 36 volts of alternating voltage), then this can be dangerous.
As a person moves away from the ground of the installation, the magnitude of the touch voltage for him increases. Outside the current spreading zone from the installation, the touch voltage will be equal to the voltage directly on the equipment casing relative to the ground. Here, the spreading zone is that part of the earth beyond which the potential when the parts of the installation are closed under voltage to earth is assumed to be zero.

The main way to protect against electric shock is reliable insulation.
The main ways to protect people from contact with voltage are isolation of live parts of electrical equipment, location of hazardous parts at heights that are unattainable without special equipment, installation of guards and hazardous proximity alarms, the presence of posters and signs warning of danger, and of course dielectric personal protective equipment. Meanwhile, none of the listed methods of protection is universal, therefore it is better to apply several at once.
So, the availability of reliable insulation of live parts is the main condition for safety in the operation of electrical installations. The most important characteristic of insulation is its resistance.
According to the PUE, cable insulation resistance, even those operating at voltages below 1000 volts, should not be lower than 0.5 MΩ for the wire of each phase, and for the windings of the stators of electric motors the regulated value reaches 1 MΩ at room temperature!
The bottom line is that when a person touches, for example, a bare wire, the current through his body is determined by the resistance of the body itself and the voltage of touch under current conditions. But when a person touches an insulated wire, the insulation resistance is connected in series with the body of the person, and the voltage drop, as well as the current through the body, are much less, and the person in these conditions is more protected from electric shock.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
: