Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 35312
Comments on the article: 0
What is cable insulation resistance and its norms
Insulation resistance is one of the most important parameters of cables and wires, because during operation, power and signal cables are always subject to various external influences. In addition, in addition to external influences, the influence of the cores inside the cable on each other, their electrical interaction, which inevitably leads to leaks, is constantly present. Adding factors that affect the quality of insulation here, we get a more complete picture.
For these reasons, the cables are always protected by dielectric insulation, which include: rubber, pvc, paper, oil, etc. - depending on the purpose of the cable, on the operating voltage, on the type of current, etc. For example, underground distribution Telephone lines are made with an armored tape cable, and some telecommunication cables are enclosed in an aluminum sheath to protect against external current interference.

As for the dielectric properties of insulation, it is not only they that affect the choice of a particular material for a particular cable. No less important is heat resistance: rubber is more resistant to high temperatures than plastic, plastic is better than paper, etc.
So, cable insulation is a protection of cores from their influence on each other, from short circuit, from leaks, and from external influences from the environment. And the insulation resistance is determined by the value between the cores and between the core and the outer surface of the insulating shell (or between the core and the screen).
Of course, the insulation material during the operation of the cable loses its former qualities, ages, collapses. And one of the indicators of these adverse changes is a decrease in the insulation resistance to direct current.
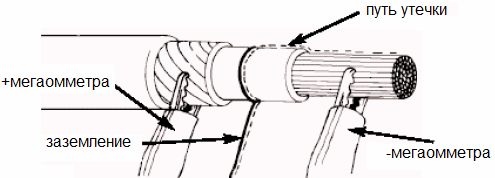
The insulation resistance to direct current for various cables and wires is normalized according to their GOST, which is indicated in the passport for a specific cable product: in laboratory conditions, the normal insulation resistance is fixed at an ambient temperature of + 20 ° C, after which the resistance is reduced to a cable length of 1 km , which is indicated in the technical documentation.
So, low-frequency communication cables have a minimum normalized resistance of 5 GΩ / km, and coaxial cables up to 10 GΩ / km. When measuring, take into account that this is the reduced length for 1 km of cable, respectively, a piece twice as long will have half the insulation resistance, and a piece twice as short as a widow will be larger. In addition, temperature and humidity during measurements have a significant impact on the current value, so it is necessary to introduce corrections, experts know this.
Speaking of power cables, take into account the provisions of the PUE p. 1.8.40. Thus, a norm of 0.5 MΩ for each core between phase conductors and between phase and neutral wires and protective earth wires is assigned to power cables of secondary switching circuits and lighting wiring with voltages up to 1000 V. And for lines with a voltage of 1000 V and higher, the resistance norm is not indicated, but the leakage current is indicated in mA.

Special tests are carried out in which the test voltage is normalized. In accordance with the type of current of the test equipment and the purpose of the cable being tested, taking into account the material with its insulation - set the test voltage on a megohmmeter. So with the help of a megaohmmeter, they evaluate the quality of insulation of high-voltage cables.
An insulation resistance of 1 megohm per kilovolt of operating cable voltage is considered acceptable, that is, for a cable operating at a voltage of 10 kV, a resistance of 10 megohms will be assumed normal by the results of tests with a megohmmeter with a test voltage of 2.5 kV.
Insulation resistance measurements are carried out regularly by a megohmmeter: on mobile installations - once every six months, at hazardous facilities - once a year, at other facilities - once every three years. These measurements are carried out by qualified specialists. As a result of measurements, a specialist draws up a document - an act of a sample established by Rostekhnadzor.
Based on the results of the inspection, a conclusion is made about whether the object needs repair or if its operability complies with the verification requirements. If repair is required - carry out repairs in order to restore the insulation resistance to normal. The protocol is also compiled based on the results of the repair, after the next measurements with a megohmmeter.
See also with us:
Resistance measuring devices - types, device and principle of operation
How to measure resistance with a multimeter
How to measure grounding resistance at home
The method of measuring the resistance of the loop phase-zero
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
