Categories: Featured Articles » Practical Electronics
Number of views: 40341
Comments on the article: 1
Quartz resonator - structure, principle of operation, how to check
 Modern digital technology requires high accuracy, so it is not surprising that almost any digital device, which would not catch the attention of the average man today, contains a quartz resonator inside.
Modern digital technology requires high accuracy, so it is not surprising that almost any digital device, which would not catch the attention of the average man today, contains a quartz resonator inside.
Quartz resonators for various frequencies are necessary as reliable and stable sources of harmonic oscillations, so that the digital microcontroller could rely on the reference frequency and operate with it in the future, during the operation of the digital device. Thus, a quartz resonator is a reliable replacement for an oscillatory LC circuit.
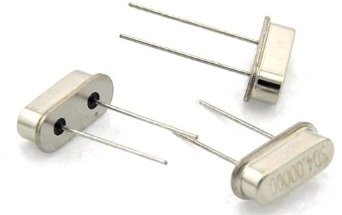
If we consider a simple oscillatory circuit, consisting of capacitor and inductor, it quickly becomes clear that the quality factor of such a circuit in the circuit will not exceed 300, in addition, the capacitor capacitance will float depending on the ambient temperature, the same will happen with inductance.
It is not for nothing that capacitors and coils have such parameters as TKE - temperature coefficient of capacitance and TKI - temperature coefficient of inductance, showing how much the main parameters of these components change with their temperature.
Unlike oscillatory circuits, quartz-based resonators have a Q factor unattainable for oscillatory circuits, which can be measured with values from 10,000 to 10,000,000, and the temperature stability of quartz resonators is out of the question, because the frequency remains constant at any temperature, usually from the range from - 40 ° C to + 70 ° C.
So, due to the high temperature stability and quality factor, quartz resonators are used everywhere in radio engineering and digital electronics.
For assignment microcontroller or processor clock frequency, he always needs a clock generator, on which he could reliably rely on, and this generator always needs a high-frequency and high-precision one. Here the quartz resonator comes to the rescue. Of course, in some applications, piezoelectric resonators with a quality factor of 1000 can be dispensed with, and such resonators are sufficient for electronic toys and household radios, but quartz is needed for more accurate devices.
The basis of the quartz resonator is piezoelectric effectarising on a quartz plate. Quartz is a polymorphic modification of silicon dioxide SiO2, and is found in nature in the form of crystals and pebbles. Free form in the earth's quartz crust is about 12%, in addition, in the form of mixtures, other minerals also contain quartz, and in general more than 60% quartz in the earth's crust (mass fraction).
To create resonators, low-temperature quartz, which has pronounced piezoelectric properties, is suitable. Chemically, quartz is very stable, and it can only be dissolved in hydrofluoride acid. Quartz is superior in hardness to opal, but does not reach diamond.
In the manufacture of a quartz plate, a piece is cut from a quartz crystal at a strictly specified angle. Depending on the cutting angle, the resulting quartz plate will differ in its electromechanical properties.
Much depends on the type of cut: frequency, temperature stability, resonance stability, and the absence or presence of spurious resonant frequencies. Then, a layer of metal is applied to the plate on both sides, which can be nickel, platinum, silver or gold, after which the plate is fixed with hard wires to the base of the quartz resonator case. The last step - the case is hermetically assembled.
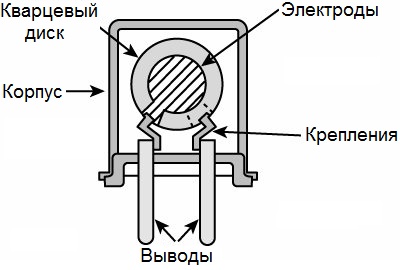
Thus, an oscillatory system with its own resonant frequency is obtained, and the quartz resonator obtained in this way has its own resonant frequency determined by electromechanical parameters.
Now, if an alternating voltage of a given resonant frequency is applied to the metal electrodes of the plastic, a resonance phenomenon will appear, and the amplitude of harmonic oscillations of the plate will increase very significantly. In this case, the resonator resistance decreases significantly, that is, the process is similar to what is happening in a sequential oscillatory circuit. Due to the high quality factor of such an "oscillatory circuit", the energy loss during its excitation at the resonant frequency is negligible.
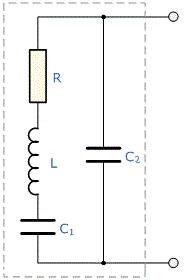
On the equivalent circuit: C2 is the static electric capacity of the plates with holders, L is the inductance, C1 is the capacitance, R is the resistance, reflecting the electromechanical properties of the installed quartz plate. If you remove the mounting elements, a consistent LC circuit remains.
During installation on a printed circuit board, a quartz resonator cannot be overheated, because its design is quite fragile, and overheating can lead to deformation of the electrodes and holder, which will certainly affect the operation of the resonator in the finished device. If quartz is heated to 5730 ° C, it will completely lose its piezoelectric properties, but, fortunately, it is impossible to heat an element with a soldering iron to such a temperature.
The designation of the quartz resonator in the diagram is similar to the designation of a capacitor with a rectangle between the plates (quartz plate), and with the inscription "ZQ" or "Z".
Often the cause of damage to the quartz resonator is a fall or a strong impact of the device in which it is installed, and then it is necessary to replace the resonator with a new one with the same resonant frequency. Such damage is inherent in small-sized devices that are easy to drop. However, according to statistics, such damage to quartz resonators is extremely rare, and more often the malfunction of the device is caused by a different reason.
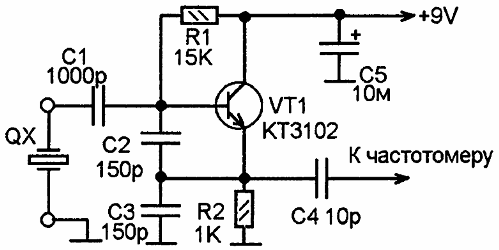
To check the quartz resonator for serviceability, you can assemble a small probe that will help not only to verify the operability of the resonator, but also to see its resonant frequency. The probe circuit is a typical crystal oscillator circuit using a single transistor.
By turning on the resonator between the base and the minus (it is possible through a protective capacitor in case of a short circuit in the resonator), it remains to measure the resonant frequency with a frequency meter. This circuit is also suitable for pre-setting the oscillatory circuits.
When the circuit is turned on, a healthy resonator will contribute to the generation of oscillations, and an alternating voltage can be observed on the emitter of the transistor, the frequency of which will correspond to the fundamental resonant frequency of the tested quartz resonator.
By connecting a frequency meter to the probe output, the user will be able to observe this resonant frequency. If the frequency is stable, if a slight heating of the resonator with a raised soldering iron does not lead to a strong drift of the frequency, then the resonator is in good condition. If there is no generation, or the frequency will float, or it will turn out to be completely different than it should be for the tested component, then the resonator is faulty and should be replaced.
This probe is also convenient for pre-setting the oscillatory circuits, in this case the capacitor C1 is required, although it can be excluded from the circuit when checking the resonators. The circuit is simply connected instead of the resonator, and the circuit begins to generate oscillations in a similar way.
The sampler assembled according to the given circuit works wonderfully at frequencies from 15 to 20 MHz. For other ranges, you can always search for circuits on the Internet, since there are many of them, both on discrete components and on a microcircuit.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
