Categories: Sharing experience, Auto electrician
Number of views: 31256
Comments on the article: 0
How to measure battery capacity and convert farads to amp hours
What and why battery capacity is measured
Charge Q, as the amount of electricity, is measured in coulomb (C), the electric capacity of capacitors C is in farads, microfarads (microfarads), but battery capacity measured for some reason not in farads, but in ampere-hours (milliampere-hours).
What would that mean? One ampere is a pendant in one second, we know from the course of physics that if an electric charge equal to 1 pendant passes through a conductor in 1 second, then a current of 1 ampere flows through the conductor.

And then what is ampere hour? An ampere-hour (Ah) is considered to be the battery capacity at which, according to a given current of 1 ampere, the battery is discharged 1 hour before the minimum allowable voltage.
for instance for lithium ion battery frame size 18650, with a capacity of 3400 mAh, this means that a battery with a current of 340 mA can give its charge in 10 hours, and a car battery with a capacity of 55 Ah discharges from about 12.8 to 10.8 volts in 2 hours at a discharge current of 27 5 A.
As you probably know, batteries cannot be discharged to zero, and in reality, each type of battery has a minimum voltage that is allowed to discharge the battery without harm.
For example, a lead car battery cannot be discharged lower than 10.5 volts, and a lithium battery can be discharged no lower than 2.75 volts. If these tolerances are violated, the battery life will be depleted much faster than it could be if the recommendations regarding the minimum voltage were observed.
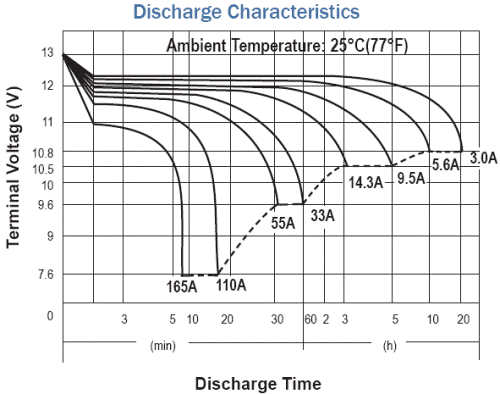
Thus, the battery capacity is estimated based on the regulated norms for various types of batteries: car batteries are tested on a 20 hour discharge cycle, and lithium batteries on a 5 hour one. A fully charged battery is discharged with a pre-selected current I to the minimum allowable discharge voltage, while measuring the discharge time T. At the end of the experiment, multiplying the current and the measured time, the actual battery capacity in ampere-hours is obtained. Q = IT.
The simplest way to experimentally evaluate a known type of battery capacity
So, to measure the capacity of the battery in a simple but painstaking way, without resorting to the use of special devices, it can be fully charged discharged through a resistor of a known acceptable rating.
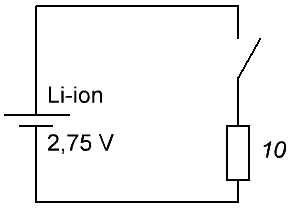
For example, the permissible harmless full discharge voltage of a 18650 lithium cell is 2.75 volts, and its full charge voltage is taken to be 3.75 volts. Remember that such batteries charge no more than 4.35 volts in special chargers!
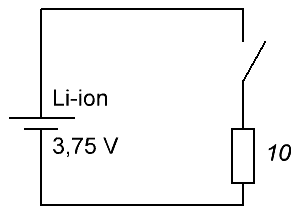
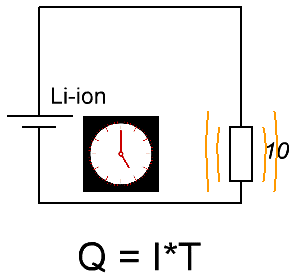
Suppose a fully charged battery is available. Choose an average discharge current of 325 mA, take resistor nominal 10 Ohm, power 2 W - with a margin. We measure the starting voltage at the battery terminals, let's say it turns out to be exactly 3.75 volts, and attach a resistor to the terminals, while simultaneously detecting the time on the clock. Next, we will monitor the voltmeter - after how many hours the voltage will drop to the level of 2.75 volts.
For example, after 10 hours 27 minutes, the voltage on the battery became 2.75 volts, and at the start it was 3.75 volts, and this when discharged through a 10 ohm resistor. So, the capacity can already be estimated with good accuracy: starting current 3.75 / 10 = 375 mA, final current 2.75 / 10 = 275 mA, average current (375 + 275) / 2 = 325 mA. So, within 10.45 hours, the battery gave an average current of 0.325 A, therefore, the capacity is Q = 10.45 * 0.325 = 3400 mAh. This is a crude but reliable way to measure battery capacity.
Car battery
To measure the capacity of a car battery, it is convenient to use a conventional 60-watt incandescent lamp. It will provide an average current of 5 amperes.A lamp and a voltmeter are connected to a fully charged battery (up to about 12.5–12.8 volts), while noting time. When the voltage drops to 10.8 volts - turn off the lamp and record the elapsed time. For example, if 9 hours have passed, then the real capacity of this car battery is Q = 9 * 5 = 45 Ah.
Convert farads to ampere hours
A battery, unlike a capacitor, has a very large portion of non-linearity in the discharge curve. But still, some experiment lovers try, and they succeed in it, in some applications replace the battery supercapacitors.

1 ampere hour is 3600 pendant. Suppose we want to get a capacitor bank that is equivalent in discharge characteristic, albeit in a short section, to a 12 volt battery with a capacity of 55 ampere-hours. 55 amperes per hour is 55 * 3600 pendant.
We take a change in voltage from 13 to 11 volts, then since Q = C (U1-U2), then C = 55 * 3600/2 = 99000 F. Almost 100 kilofarads is the equivalent electric capacity of a car battery if its discharge characteristic were the same as at the capacitor.
There is a video on the Internet where six superconductors of 3000 F each, each 2.7 V connected in series, replace the car’s starter battery. It turns out that 500 F is about 16 V.
Let's estimate what current and for how long such an assembly can give. Let the operating range be adopted again from 13 to 11 volts. How long can I count on a current of 200 A (with a margin)? I = C (U1-U2) / t, then t = C (U1-U2) / I = 500 * 2/200 = 5 seconds. Enough to start the engine.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
