Categories: Electrical Reviews
Number of views: 2364
Comments on the article: 0
Types, characteristics and differences of SIP wires
The modern world is so electrified that the number of wired connections and electrical networks can no longer be counted. Consumers of various purposes have not been connected with bare wires for a long time, and even power lines are no exception.
SIP wire (short for "self-supporting insulated wire") successfully applied in many networks, industrial and domestic, which is by no means accidental. The fact is that wires of this type differ in a number of advantages, which we will talk about later.
When compared with other brands of wires, the SIP is truly unique. It is designed to transmit electrical energy, while it is positioned just like a wire, and not like a cable, although it carries itself, has insulation, is multi-core - almost like a cable.
Take for example brand wire SIP-1 3x150 + 1x70. There are three insulated conductors with a cross-section of 150 sq. Mm each, and the zero load core is not insulated and has a cross-section of 70 sq. Mm. This wire is rated for 660 volts.
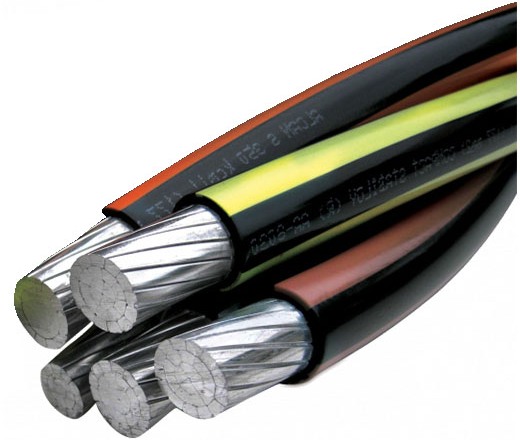

CIP wires are available in different brands and sizes, the main of which are five. The first digit after the letters "SIP" denotes the number of wire variety. Further in the name are data in the form of numbers, reflecting the number of cores and their cross-sectional area, and at the end there may be a letter - an identifier of the distinguishing features of this model.
Basically, all SIP wires contain a certain number of cores in their design, one of which carries a bearing function (mechanical load, weight of the conductive structure).

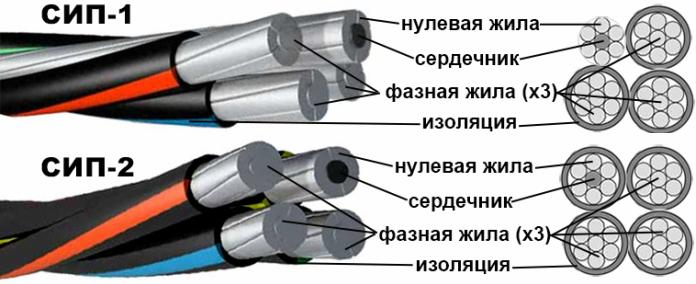
SIP-1
The SIP-1 wire is most often four-wire. All its veins are multi-wire assemblies, in the construction of each of which the conductors are twisted together. In general, the three multi-wire cores are phase-wise for the purpose, they have thermoplastic polyethylene insulation, and the fourth core does not have insulation, and is intended to be a neutral conductor.
The central wire of the neutral conductor is steel, it is the carrier for the entire SIP wire, acts as a kind of core of the neutral conductor.
When the letter “A” follows in the marking after the designation SIP-1, the neutral conductor will also be insulated. SIP-1 wire is designed and used in lines and networks with a voltage of 0.66 / 1kV.

The fundamentally characteristic number of conductive wires for the SIP-1 wire varies from 1 to 4. The cross section of the conductors is from 16 to 120 sq. Mm. The conductive core is always aluminum, the zero core around the steel core is made of aluminum alloy. The voltage class of the SIP-1 wire is from 0.4 to 1 kV.
Its main insulation is thermoplastic polyethylene. The normal operating temperature range of the wire is from -60 to + 50 ° С, and during operation it is allowed to heat up to + 70 ° С. The permissible bending radius during installation is at least 10 diameters. Service life - at least 40 years.
SIP-1 is used for the manufacture of branches from high-voltage lines, for mounting power inlets in residential premises, as well as in outbuildings - for laying electrical networks on the walls.
SIP-2
SIP-2 wire is a four-core self-supporting wire, all four of which are equipped with polyethylene insulation. The usual version of the SIP-2 wire is the same insulation of all four conductors. However, there is a variety of this wire - SIP-2A, characterized in that the fourth, zero conductor with a core, is insulated with cross-linked polyethylene, as are its phase conductors.
A variety of SIP-2A is suitable for applications in more aggressive atmospheric conditions. Like SIP-1, SIP-2 can be used in lines with an alternating voltage of 0.66 / 1kV.

The number of conductive wires for the SIP-2 wire is from 1 to 4. The cross-section of conductors is from 16 to 120 sq. Mm.Conducting vein aluminum, zero - from an aluminum alloy. Voltage class from 0.4 to 1kV. Insulation includes light stabilizer and polyethylene. The normal temperature range is from -60 to + 50 ° C, let's say heating to + 90 ° C.
The maximum bending radius is at least 10 diameters. Service life not less than 40 years. It is used for the manufacture of branches from high-voltage lines, for the installation of power supplies in residential premises, as well as in utility buildings - for laying electrical networks on walls.
SIP-3
SIP-3 wire is a single-core version of the self-supporting SIP wire. In the center of this wire is a steel wire - the core, around which the main aluminum current-carrying conductors are entwined. This type of wire is usually used in high-voltage lines with an operating voltage of 6 to 35 kV, and serves, as a rule, as a phase wire for transmitting electric energy over long distances.

In the SIP-3 wire, there is always only one core with a cross section of 35 to 240 square mm. The conductive core is made of an aluminum alloy. Voltage class from 10 to 35kV. Insulation includes light stabilizer and polyethylene. The normal temperature range of the wire is from -60 to + 50 ° С, heating up to + 70 ° С is permissible.
Allowed bending radius of at least 10 diameters. Service life not less than 40 years. It is used for mounting high-voltage lines with voltage from 6 to 35 kV.

SIP-4
SIP-4 wire is very different from previous models of self-supporting wire. It is essentially an assembly of two (or one!) Pairs of aluminum conductors, and the zero-carrying conductor with a steel core is completely absent here. For this reason, the wire of the SIP-4 brand is not used for laying lines, since there is always the possibility of a wire breaking in case of strong wind.
The insulation of the four cores is made of thermoplastic polyethylene, and the cores themselves are made of aluminum. A variety of SIP-4N has more durable conductors - from aluminum alloy.

The wire SIP-4 (SIP-5) can contain from 2 to 4 cores with a cross section of 16 to 120 sq. Mm. The conductive core is always aluminum (except for modification H). Voltage class from 0.4 to 1kV. Insulation - thermoplastic polyethylene.
The normal temperature range is from -60 to + 50 ° C, let's say heating to + 90 ° C. Permissible bending radius of at least 10 diameters. Service life not less than 40 years.
This wire (like SIP-5) is used when installing branches from high-voltage lines, power inputs to residential premises, for laying networks along the walls of outbuildings.
SIP-5

SIP-5 wire is one pair of insulated aluminum conductors without a zero core and without a steel supporting core. The insulation here is made of cross-linked polyethylene (increases the maximum allowable working temperature by one third compared to ordinary thermoplastic polyethylene), the cores are made of pure aluminum. A variation of SIP-5N is characterized in that the conductors are made of a more durable aluminum alloy.
Wire selection
Choosing a SIP wire for a particular purpose, first of all pay attention to the characteristics of each of its brands. Typically, the number of current-carrying conductors varies from 1 to 4, which provides the ability to solve almost any task for any required modification of the network. The cross-sectional spread characteristic for SIP is from 16 to 240 square mm.
According to the voltage brands SIP-1, SIP-2, SIP-4 and SIP-5 are suitable for networks of class up to 1 kV. And only the SIP-3 wire is suitable for a line up to 35 kV, since it can be laid independently.
Assess the temperature regime with a margin for short-term heating in emergency mode, which is allowed no more than 8 hours for an annual load. Each wire has its own permissible bending radius, which simultaneously determines and limits the possibilities of bending the wire during installation. If you bend the SIP wire more than permissible, its mechanical strength and dielectric properties will be violated.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
