Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 301970
Comments on the article: 17
Types of cables and their differences

The modern cable industry has an extensive assortment of various wires. And each type of wire is designed to solve a certain range of problems.
Having contacted the electrical installation at your own site or in your own apartment, you can very soon notice that the cables and wires used in the installation are mainly copper, less often aluminum. With all the variety, there are simply no other materials. Further, you can notice that the structure of the cores of these cables also varies: the core can consist of many wires, but it can be whole. The core structure affects the flexibility of the cable, but does not affect its conductivity.
It seems that on that spectrum cable specifications and ends. But where then is such a variety of brands? VVG, NYM, SIW, PVA, ball screw - how do they differ from each other? For the most part, insulation properties.
In this article, we will consider the main common types of electrical wires, dwell on their characteristics, and note their areas of application.
1. VVG cable
For the electrification of residential buildings use different, mainly copper, cables, but in recent years, most often you can find VVG cable, including its modified versions.
VVG cable marking means: external insulation from polyvinyl chloride, core insulation - also from polyvinyl chloride, flexible cable conductors. Although the flexibility of the VVG cable is relative, after all, up to a cross section of 25 square meters. mm inclusive, his conductors are solid, not multi-wire.
Cable insulation is resistant to aggressive environments, while it is quite durable and does not support combustion. The cores can be either single-wire or multi-wire, depending on the modification of the VVG cable.
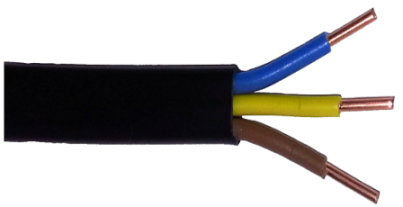
The main purpose of this cable is the transmission and distribution of electricity in networks with voltages up to 1000 volts at an industrial frequency of alternating current of 50 Hz. For laying home networks use VVG cable with a cross section of up to 6 sq. Mm, for the electrification of private houses - up to 16 sq. Mm. During installation, bending along a minimum radius of 10 wire sizes in width is allowed. The cable is supplied in bays of 100 meters.
Among the varieties of VVG cable are: AVVG - with an aluminum core, VVGG - with a refractory sheath, VVGp - a flat section, VVGz - with the addition of PVC or in rubber insulation, also between individual conductors.
VVG is the most common copper cable for indoor installation. It is laid openly, in boxes, laid in strobes. The isolation of VVG provides him with a long service life of 30 years. The number of wires of the VVG cable can meet the needs of both a three-phase and a single-phase network: from two to five.
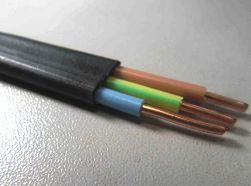 The most common color of the external insulation of VVG cables is black, but recently, white VVG has completely ceased to be a rarity. The insulation color of individual VVG cores corresponds to the standard marking: for the PE conductor - yellow-green, for the N conductor - blue or white with a blue stripe, and the insulation of phase conductors is most often done in pure white.
The most common color of the external insulation of VVG cables is black, but recently, white VVG has completely ceased to be a rarity. The insulation color of individual VVG cores corresponds to the standard marking: for the PE conductor - yellow-green, for the N conductor - blue or white with a blue stripe, and the insulation of phase conductors is most often done in pure white.
Modifications of the VVG cable marked “NG” and “LS” are distinguished, respectively, by the inability of the insulation to spread combustion and by a low level of smoke emission when exposed to fire. There is a modification of VVG, characterized by the ability to fully withstand open fire for a certain time in minutes. This modification is indicated by the Latin letters FR.
In everyday life, almost no cable is found that is similar in characteristics to the VVG cable, but having wires made of aluminum - AVVG. Its unpopularity is justified by the restriction on the use of aluminum in distribution networks, as well as by the shortcomings of aluminum cable products.
In addition, there is a foreign analogue of VVG cable manufactured according to the international DIN standard. It's about NYM cable. It differs from VVG in somewhat improved characteristics, in particular, in that it has a special self-extinguishing internal filler, which provides sealing of the compounds.
2. NYM cable
Copper all-wire conductors has PVC insulation, the outer shell is also made of PVC, does not support combustion, and is resistant to aggressive environments. From one to five veins with a section from 1.5 to 35 sq. Mm. located tightly inside the white protective sheath. Between the conductors there is a halogen-free coated rubber seal that provides the cable with heat resistance and durability. This cable is applicable in a wide temperature range from -40 ° C to + 70 ° C, moisture resistant. Core colors: brown, black, gray, blue, yellow-green.
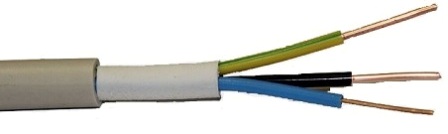
NYM cable is designed for installation of power and lighting networks in industrial and residential buildings with a maximum voltage of up to 660 volts (300/500/660). The cable can be laid both indoors and outdoors, taking into account, however, that sunlight insulating the cable is harmful, therefore, when installing outdoors it must be protected from sunlight, for example by placing it in a corrugation.
During installation, bending along the radius of at least four cable diameters is allowed. It is delivered in bays from 50 meters.
Unlike VVG, NYM cable always has only copper and only all-wire cores (mono-cores). It is quite convenient for ordinary installation, because it has a perfectly round cross section, but for the same reason it is somewhat inconvenient to lay it in plaster or concrete, otherwise it is similar to VVG.
Cable production on video:
How to distinguish a quality cable when buying it:
3. CIP cable (wire)
SIP means "self-supporting insulated wire." This means that the self-supporting insulated wire is able to withstand the effects of significant mechanical loads. If we take into account the fact that the insulation of the self-supporting insulated wire is made of cross-linked polyethylene, which is immune to moisture and direct sunlight, the scope of its use becomes obvious: it is a street cable for power transmission lines and branches for individual inputs. It is slowly replacing the previously uninsulated aluminum wires A and AC, which were widely used for these purposes.

SIP is an aluminum cable whose cores do not have common insulation. The minimum cross-section of CIP conductors is 16 square meters. mm., and the maximum - 150 square meters. mm The number of cores is not directly indicated in the marking of this wire - only the item number is given, in which all data is encrypted.
For example, SIP-1 is a cable of three cores, one of which is a zero carrier. SIP-2 is a cable of four cores, one of which is a zero carrier. And SIP-4 has four current-carrying conductors, the mechanical load on which is distributed evenly.
Since SIP is a very specific cable, for the installation with its use a whole range of special fittings is available: branch and connecting clamps and anchor brackets.
4. Cable (cord) of the PVA
PVA - a copper wire in vinyl insulation connecting. The sheath is made so that it fills the space between the cores, which gives the wire high strength. The number of cores is from two to five, and the cross section of each is from 0.75 to 16 square mm.
Operating temperature range - from -25 ° C to + 40 ° C, resistant to chemical influences, 100% environmental humidity is allowed. The wire withstands multiple bending cycles, up to 3,000 times guaranteed. Shell color is white. Core color: red, black, orange, blue, gray, brown, green, yellow, yellow-green.

The PVA wire is widely used in everyday life as power cords various household appliances, such as electric kettles, as well as extension cords.It is designed to work in alternating current circuits with a frequency of 50 Hz and voltages of up to 380 volts; therefore, PVA wire is also used in networks where a flexible wire is required for wiring lighting systems, sockets, etc. Flexibility is one of the most important advantages of this wire.
PVA insulation, both internal and external, is made of polyvinyl chloride. The inner core insulation, as with VVG, has a standard marking. But PVA conductors are multiwire, so this is a very flexible cable. It is only necessary to take into account that the PVA conductors must be terminated or tinned during installation.
Given that the outer vinyl layer of a round PVA has a thickness of up to several millimeters, this cable is great for cords portable electric power supply. That is, for their "connection" to the network. Therefore, it is called connecting.
PVA can withstand mechanical loads relatively well. The cross section of his veins varies from 0.75 to 16 square meters. mm., therefore, this cable can be used for the manufacture of any extension cords and handles that are not used at low temperatures. Indeed, in the cold PVA shell, unfortunately, just bursts.
5. Cable (cord) ШВВП
ШВВП - cord in a vinyl sheath, with conductors in vinyl insulation, flat. In general, this cable is similar to VVG, but, unlike the latter, the ball screw has flexible multi-wire copper conductors. Therefore, he, like PVA, often used for extension cords. However, the insulation of ball screws does not differ in increased strength, and responsible loaded lines with this cord are not performed.
Accordingly, the cross sections of ball screws are only small: 0.5 or 0.75 square meters. mm with the number of cores equal to two or three.The wire is flat in shape. This wire can be used at temperatures from -25 ° C to + 70 ° C, and can withstand humidity up to 98%. Easily demolishes the effects of chemically aggressive environments. The shell color is white or black. Core color: blue, brown, black, red, yellow.
In addition to weak extension cords (which, by the way, often cause troubles in the economy of people new to electricity), ballscrews are most often used in automation to power low-voltage systems.
It is also used to connect household appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, personal hygiene appliances, etc. to the network. It is capable of working in AC networks with a frequency of 50 Hz at a voltage of up to 380 volts. Very flexible, which is very important in everyday life.
The main function of the ball screw wire is the connecting cord: on one end is the device, on the other is the plug.

6. KG cable
KG is a flexible copper rubber cable with multi-wire cores, the cross section of which varies from 0.5 to 240 square meters. mm The number of cores can be from one to five. Core insulation rubber - based on natural rubbers.

The operating temperature range of the cable is from -60 ° C to + 50 ° C with humidity up to 98%. Insulation of the cable KG allows you to lay it in the open air and even in open sunlight. The wires are always multi-wire, which makes this cable flexible. Color cores: blue, black, brown, yellow-green, gray.
KG is most often used in industrial installations, where it is necessary to provide a flexible movable cable entry.
The KG cable is designed to power portable mobile devices, such as heat guns, welding machines, spotlights, etc., from an alternating current network or from generators with a frequency of up to 400 Hz at a voltage of up to 660 volts, or a constant voltage of up to 1000 volts.
During installation, bending along a radius of at least eight outer diameters is allowed. Usually supplied in bays of 100 meters or more. There is a modification of KGng - in non-combustible isolation.
It is very important that the rubber insulation of this cable, even in severe frost, partially retains its properties, and the KG almost always remains flexible, especially when it comes to the modification of CL. Therefore, it is often used for the manufacture of extension cords operating in a wide variety of harsh conditions.
7. Cable VBBSHv
Armored power cable with copper conductive wires, which can be either single-wire or multi-wire. From one to six veins with a section from 1.5 to 240 sq. Mm. have PVC insulation and PVC sheath. A feature of this cable is the presence of a layer of steel two-tape armor between the cores and the sheath.
The cable easily withstands temperatures from -50 ° C to + 50 ° C with humidity up to 98%. PVC insulation provides resistance to aggressive environments. The color of the shell is black. The insulation color of the cores is either solid or in a combination of the main marking colors with white.

The VBBShv armored cable is intended for laying power supply networks of freestanding buildings and structures, as well as electrical installations, both underground and in pipes in the open air (to protect from sunlight). The maximum AC voltage is up to 6000 volts. For direct current, traditionally single-core modifications of this cable are used.
During installation, bends of a radius of at least ten external cable diameters are allowed. It is delivered traditionally in bays from 100 meters. There are modifications: AVBBSHv - aluminum conductors, VBBSHvng - non-combustible performance, VBBSHvng-LS - non-combustible performance with low gas emission at elevated temperatures.
8. Wire PBPP (PUNP)
Flat mounting wire with copper single-wire conductors in PVC insulation and PVC sheath. The core can be two or three, with a section from 1.5 to 6 sq. Mm. Operating temperature range from -15 ° C to + 50 ° C, permissible humidity 98%. Resistant to aggressive environments. Shell color is white or black, core color: white, blue, yellow-green.

Designed for installation of lighting systems and wiring outlets in buildings, with a maximum AC voltage of industrial frequency of 250 volts. During installation, bends with a radius of at least ten times the width are allowed. It is delivered in bays of 100 and 200 meters.
Modification PBPPg (PUGNP) - stranded wires, during installation, bending along a radius of at least six times the width is allowed. Modification APUNP - aluminum all-wire (only all-wire) conductors.
9. PPV wire
Flat wire with single-wire copper conductors in PVC insulation with dividing inter-core inserts. There may be two or three. Cross section from 0.75 to 6 sq. Mm. The wire may be operated in the temperature range from -50 ° C to + 70 ° C.
The insulation is resistant to aggressive environments and vibrations, does not support combustion, and the permissible ambient humidity is 100%. The insulation color is traditionally white, an additional protective shell is not required.

PPV wire is intended for installation of stationary lighting systems and household electrification networks, which are laid inside buildings. The maximum voltage is 450 volts with alternating current frequency up to 400 Hz. During installation, bending with a radius of at least ten times the width is allowed. It is delivered in bays of 100 meters. APPV modification - with aluminum conductors.
10. AR wire
Aluminum single-core round wire in PVC insulation. It is found both multi-wire and single-wire. A multi-wire conductive core may have a cross section from 25 to 95 square mm, and a single-wire conductor from 2.5 to 16 square mm. The temperature range is quite wide - from -50 ° C to + 70 ° C.
Insulation is resistant to aggressive environments, and the wire itself is resistant to vibration. Humidity up to 100% is allowed. The insulation is white.

The reclosure wire is used in the installation of switchboards, power networks, lighting systems, electrical equipment, such as machine tools. It can operate under voltage up to 750 volts with alternating current up to 400 Hz, or at direct current with voltage up to 1000 volts.
Laying is allowed indoors or outdoors, but with a prerequisite - with protection from direct sunlight, in a pipe, in a corrugation, in a special channel, etc. For installation, bending with a radius of at least ten times the diameter of the wire is permissible.It is delivered in bays from 100 meters.
11. Wire PV1
Round copper single core wire in PVC insulation. The minimum number of wires in the core is one, the minimum cross-section of one wire is 0.5 square mm. A multi-wire core can have a cross section from 16 to 120 square mm, and a single-wire core from 0.5 to 10 square mm.
The range of permissible operating temperatures is from -50 ° C to + 70 ° C, insulation is resistant to chemical influences, the wire is resistant to mechanical vibrations, permissible humidity is up to 100%. The insulation color may be different: red, white, blue, black, yellow-green.

It is used for electrification in various fields, starting from the installation of switchboards and lighting systems, ending with the winding of transformer windings for domestic needs. The wire is designed for voltages up to 750 volts with alternating current with a frequency of up to 400 Hz, and up to 1000 volts with direct current.
They are laid either indoors or under external conditions, but in protective pipes, corrugations, or in cable channels. Open laying is not permissible under conditions of constant presence of the wire under the influence of sunlight.
Bending radius of at least ten times the diameter of the wire. It is delivered in bays from 100 meters. The reclosure wire is a modification of the PV1 wire, but only with aluminum as the core material.
12. Wire PV3
Round copper single core wire in PVC insulation. The multi-wire core of the wire may have a cross section from 0.5 to 400 square mm. The range of safe working temperatures is from -50 ° C to + 70 ° C, insulation is resistant to aggressive environments, permissible humidity is up to 100%. The insulation color may be different: red, blue, white, black, yellow-green.

It is used for electrification in various fields: installation of switchboards, wiring of lighting systems, electrical wiring for powering equipment in industrial shops, etc., that is, where multiple bending is required. The wire is designed for voltages up to 750 volts with alternating current with a frequency of up to 400 Hz, and up to 1000 volts with direct current.
The PV3 wire is laid either indoors or under external conditions, but in protective pipes, corrugations, or in cable channels. Ideal when laying wiring on risers in houses. In addition, this wire is popular in car tuning. Open laying is not permissible under conditions of constant presence of the wire under the influence of sunlight. Bending radius of at least five times the diameter of the wire. It is delivered in bays from 100 meters.
We hope that this article helped you get a general idea of the most common electrical wires, their characteristics and applications, and now you can easily choose the right type of wire for your needs.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
