Categories: Featured Articles » Autonomous power supply
Number of views: 4088
Comments on the article: 0
What is an MPPT controller for solar charging
MPPT is one of the ways to use the resources of an energy source, whether it be a solar battery or a wind generator, but in this article we will talk specifically about solar energy. Its main feature is to increase the efficiency of an alternative source by “pulling” the maximum amount of energy by choosing a specific voltage and current.
The choice of these parameters is reduced to the analysis of the current-voltage characteristics of the source and determining at what voltage and current consumption the maximum power will be consumed. That is how the abbreviation stands for MPPT - Maximum Power Point Tracking (tracking the point of maximum power).

General Principles of MPPT Controllers
At first glance at the question, you might think: “Well, use the maximum voltage possible, so there will be a maximum load current (battery charge).” This is logical, but in reality it is not. This is primarily due to the current-voltage characteristic of the solar cell.
In the operating (useful) mode, the solar cell (horizontal portion of the I – V characteristic) is a current source, that is, its output current depends only slightly on the voltage at its terminals. The output voltage (Uoutc) depends on the resistance of the connected load. This we can see on the CVC.
In the right part, where the voltage is maximum, you see the open circuit voltage Uхх, which is limited by the number of elements in the battery and their internal device. The current in this case tends to 0. And vice versa, on the left side, where the voltage tends to 0 - short circuit voltage Uкз, and the current is limited by the power of the elements.
If we take the current strength of the solar battery in the useful area for a constant value, then the voltage will be determined by the load resistance, if it is infinity, then we will observe the idle mode (at Rн = ∞ ⇒ Uoutc = Uр.хх), respectively, with a short circuit, the load resistance will tend to zero, like the output voltage (at Rн = ∞ ⇒ Uoutc = Ucz). The maximum power will come at a certain ratio of load resistance, voltage and current.

What does all this mean? We pass from batteries to controllers!
The controller is an intermediate link between the solar battery and the battery, it regulates the charge current through a PWM, for example, or any other that the designer has chosen. But just applying voltage directly from the battery does not mean ensuring maximum power transfer from the panels to the battery.
For an effective charge, the controller monitors the current received from the battery and its output voltage, as well as the current supplied by the battery and the voltage on it. To make sure of this, we select 2 arbitrary points on the I – V characteristic (we give it here again) and compare the power in them with the maximum power point (TMM) indicated in the figure, in which the current seems to be not maximum ...
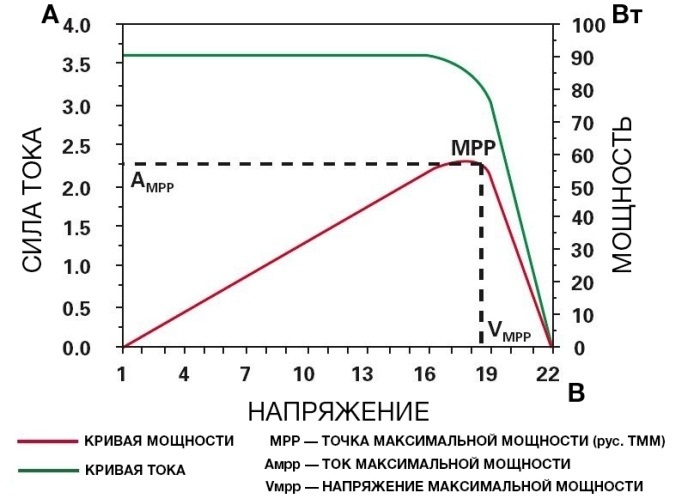
Let's say we have a battery with a rated voltage of 12V, which means that in the charged state we get about 14.2-14.5 V at the terminals, and about 11V in the discharged state, even if in one case we have 13V and in the other - 12V. We will choose such voltages with the I – V characteristic for an approximate analysis of power with a direct connection “solar panel - battery”.
According to the CVC, in both cases, the battery will give a current of about 3.6A, we get the following power transmitted during the charge:
1) 13 * 3.6 = 46.8 W
2) 12 * 3.6 = 43.2 W
And at the point of maximum power marked on the I – V characteristic:
3) 18.5 * 3.25 = 60.125W
The result is obvious - the power in the TMM is approximately 25-35% more, depending on the charge of the battery. But how to make the battery give off current at a voltage of 18.5V, instead of the one that is present on the terminals of the battery?
Everything is simple and complex at the same time - search for the maximum power point
As noted earlier, the controller is installed between the solar panels (battery) and the batteries, it turns out that it serves as the load of the panels, and the battery as the load of the controller, it is also a secondary power source. Any power source, and any device in electrical engineering can be represented in the form of resistance. This is called "equivalent" or "reduced" resistance (depending on the specific case), which is determined by the same Ohm law, that is, we can say that the input resistance of the controller is:
Rcont = Uinput / Iin. Cons.
The voltage of the maximum power point of solar panels depends on a number of factors:
-
Illumination
-
Temperature (the dependence of the CVC and the position of the TMM on temperature is shown in the figure below);
-
Age of elements, etc.
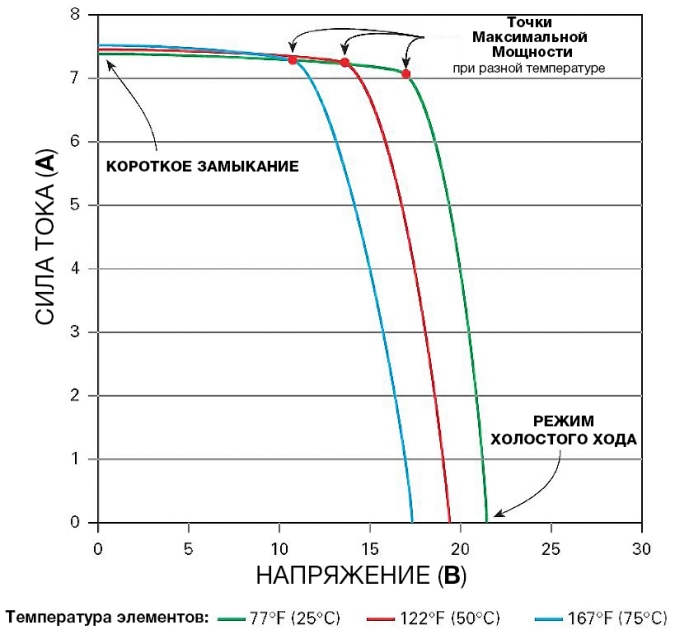
Therefore, it will not work to set it fixed and universal, plus it changes in accordance with the load resistance and current consumption (the idealized CVC is given above, in practice there will still be some slope in the work area).
There are many methods for finding this “magic” one. In one embodiment, the MPPT controller scans the current-voltage characteristics of solar cells, determining the optimal parameters for current operating conditions, for example, by changing the input current, its input resistance accordingly changes. Using current and voltage sensors, the control system calculates the power value and compares it with the previous one until it reaches its maximum value. This is called the "perturbation and observation method."
Depending on the specific method for determining TMM and the internal device of the controller, incl. its firmware, the search for TMM occurs with a certain frequency. However, in practice, most methods are similar and are based on the principle of "deviate and observe." In some models, it is possible to configure this period in the range from 1 time in several minutes to 1 time in several hours. Depending on the frequency of the search, the overall performance of the system is determined.
Since as a result of changing the input parameters we get the maximum possible power from specific elements, the next task is to give it to the load, that is, use the battery to charge. In the end, it all comes down to controlling an electronic power converter, let's say we got a TMM current of 5A at a voltage of 17.5V, this is:
17.5 * 5 = 87.5 W
So it is possible to give the battery with a voltage of 12 V at the terminals the following current:
87.5 / 12 = 7.3A
In most cases, the conversion is performed using a buck (buck) or a buck-boost converter. Typical structures of converters we considered in the article earlier.
Whereas when using ON / OFF or PWM controllers input and output current would be equal. Which leads to a less efficient disposal of available power, for example, since the input current was 5A, with this output current, the power spent on charging the batteries would be equal to:
12 * 5 = 60 watts.
This once again illustrates the calculations presented in the discussion of the current – voltage characteristics.
However, you should not consider MPPT technology a panacea for solar energy. The difference in battery charge efficiency using MPPT and PWM controller is the smaller, the more the battery is charged. When the voltage at its terminals (Uakb) rises, and the difference between Umm decreases, then a large power of the solar panel is used.
Similarly to the above example, suppose that the voltage on the battery is not 12, but 13.5V, provided that the solar panel works with the same parameters, it will look like this:
13.5 * 5 = 67.5W
If at 12V 68% of the maximum power was used, then at 13.5V 77% is already used. Also note that your batteries will not be constantly charged, and they will not receive current of the same power constantly.Therefore, in MPRT controllers, several stages of charge are usually implemented, for example: MPPT (with maximum power) - equalizing - fast (forced) - supporting. Among other things, it is worth remembering that the current of the solar battery should not exceed the rated current of the controller, otherwise the maximum use of power is not realized.
But all this does not tell us that MPPT controllers do not need to be used, but only that they should not be overestimated.
The fact remains that in the lower price segment devices with MPPT technology are more expensive than PWM, but not always ... For example, there is an MPPT controller "EPSolar MPPT TRACER-2210A", the cost of which is in the range of $ 180, and a similarly priced ($ 180-200) PWM controller with an output current of 20A STECA PR2020.
At the same time, there is another PWM device with the same output current - "SRNE SR-HP2420" costing a little over $ 20, while MPPT from the same manufacturer "SRNE SR-ML2420" with the same output current, it costs $ 85.
Prices for some models of controllers, we will consider below.
Overview of the modern market for MPPT controllers
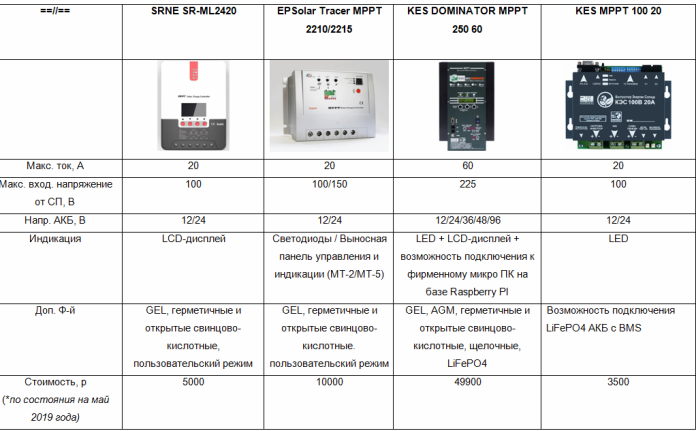
See the table in a separate file
The table does not provide a complete list of functions and protections, since it occupies a large amount. For information, a typical set of functions looks something like this:
-
from the wrong polarity of the connection of the joint venture and battery;
-
from short circuit at the entrance of the solar panel;
-
from short circuit in the load;
-
from overheating;
-
turning off the solar panel after reaching the end of the battery charge;
-
load shedding when the voltage on the battery is too low;
-
from a break in the battery circuit;
-
preventing battery discharge through the solar panel at night;
-
control of current consumption by load.
The table reflects the fact that the cost of the MPPT controller depends not only on its maximum current (power), but also on the range of output voltages, the list of supported batteries, the ability to connect display, display and monitoring tools, and a number of other factors. The choice of a controller is complicated and very individual, so it’s at least pointless to make any comparisons and ratings.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
