Categories: Electrical Reviews
Number of views: 4918
Comments on the article: 2
Modern portable oscilloscopes - types, characteristics, capabilities and features of use
The oscilloscope is the eyes of a master repairing electronics and a radio amateur. But the cost of advanced models is incomprehensible for beginners and even for many experienced craftsmen. For example, not the coolest digital oscilloscope UNI-T UTD2025CL with two channels with the ability to transmit signals with a frequency of up to 25 MHz costs more than $ 200, and some RIGOL MSO2302A-S is a powerful two-channel oscilloscope with two channels and a bandwidth of 300 MHz with a recorder function costs almost $ 4,000.
But where to go to the simple peasant? For starters, you can turn to the products of manufacturers from the Middle Kingdom. There are a lot of portable oscilloscopes on Aliexpress with different characteristics and capabilities, we will consider some of them in this article.
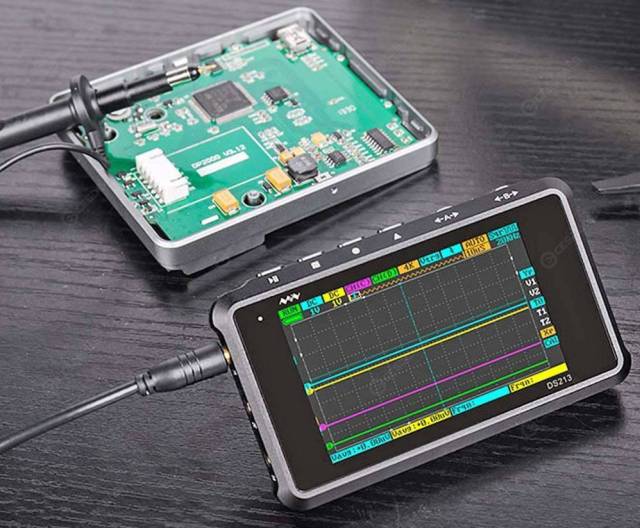

Specifications
To begin with, if we talk about portable oscilloscopes, then in almost all cases these are digital devices. You should not expect special accuracy in measuring voltage, but to check for the presence and approximate level of various signals, for an approximate measurement of the ripple level, for checking distortions in cascades.
Like any measuring device at oscilloscopes There are a number of characteristics, first of all, in the budget segment, you should pay attention to two main:
-
The sampling rate is the number of samples that the oscilloscope can produce in a second. In simple terms, this parameter reflects how many times per second the “brains” of the oscilloscope “measure” or, if you like, “read” the signal from the input. The more often this happens, the higher the frequency the signal can be measured. It is measured in the number of samples (samples) per second, although it is usually indicated in millions of samples per second. In the specifications you can find the abbreviation "MSa / s" - this is it.
-
Bandwidth. This is a frequency band at the upper boundary of which the level of the measured signal decreases by 3 dB. This parameter tells us about the maximum signal frequency that can be measured. This parameter is measured in hertz, or rather, in kilo or megahertz. It is desirable that the bandwidth be 3 ... 5 times the frequency of the measured signal in order to carry out measurements without distortion in amplitude.
For a normal signal display, the sampling frequency should be an order of magnitude (at least) greater than the frequency of the measured signal. It’s easy to understand, just look at the illustration below. Green dots conditionally depict “reading” the signal level with a certain frequency, and the line that connects them is the appearance of the waveform that will be built on them.
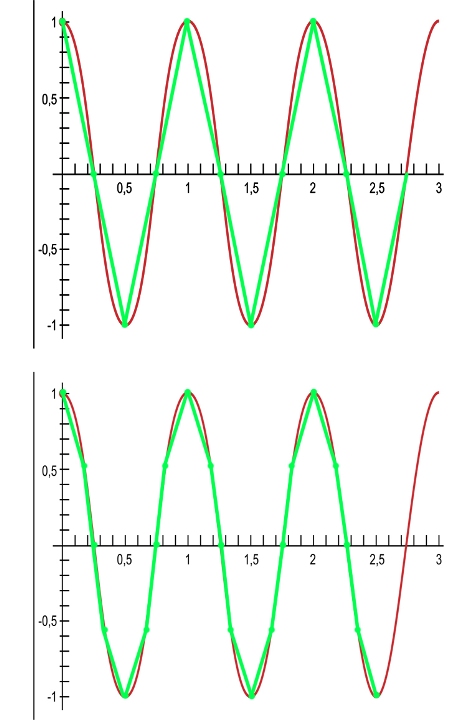
In the upper part, there are 4 points for the period of the sinusoid, and in the lower part of the figure there are 8 points and a line is drawn already between them. As you can see, the higher the sampling frequency, the smoother and more accurate the waveform will be relative to the measured signal. It should be borne in mind that digital oscilloscopes can smooth (and smooth) the resulting image, and the oscillogram is smooth.
For analog oscilloscopes, such a concept as “sampling frequency” does not exist, where the ability to measure a signal is determined to a greater extent by the bandwidth of the device.
Accordingly, if the oscilloscope is not designed for the frequency of the measured signal, you will get either a distorted similarity, or an incomprehensible curve that is completely untrue.
It is also worth noting that the oscilloscopes are single-channel and with a large number of channels. Among the budget, single-channel and two-channel models are common. Several channels allow you to compare signals or simultaneously observe several signals, which may be necessary when repairing or adjusting the circuit.
Since the oscilloscope is a complex measuring device, it has a number of other parameters on which the accuracy of measurements and functions depend, but we will not mention them in this article, since we will focus on budget solutions for amateurs and beginners.
Overview of Budget Oscilloscopes
So, let's move on to the reviews. All the models considered are powered by low DC voltage, which means that they can work either from batteries or accumulators, or from a power supply with the corresponding output voltage. But keep in mind that if there are strong ripples at the output of the power supply, then on the oscilloscope screen you will see a lot of noise and interference. Therefore, the ripple must be smoothed out using capacitors (both electrolytic high-capacity and ceramic).
Perhaps the cheapest and most popular oscilloscope from China is single channel 200 kHz oscilloscope DSO138. The model is sold as an assembly kit or as an assembled device ready for use. The first option is somewhat cheaper and will be interesting for fans to collect something with their own hands. It costs about 1000 rubles for the assembled version, it comes in the form of a printed circuit board with connectors, controls and a display. Also found in a transparent case (or case sold separately.
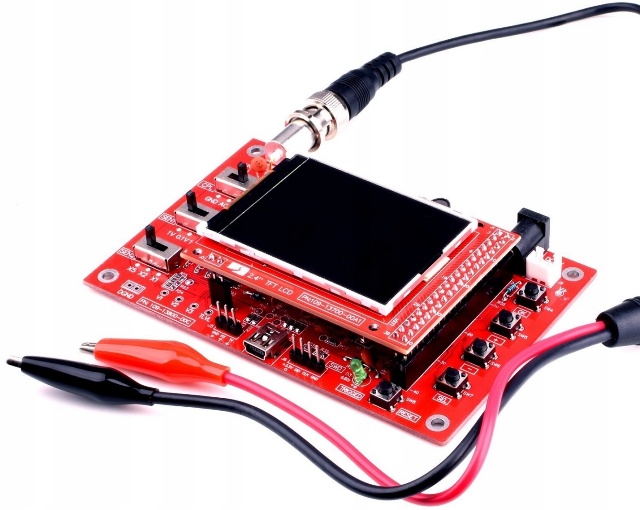

Included is a probe with crocodiles at the ends. Such a probe, in principle, allows you to measure low-frequency signals, but can not compete with the "real" probes for oscilloscopes.
There is a version of “DSO138 mini”, which differs only in the shape of the printed circuit board and the location of the controls. The oscilloscope has a rectangular signal output for tuning the probe, in the photo below you can see it in the upper right corner - a small jumper, and a rectangular pulse is drawn on the board.
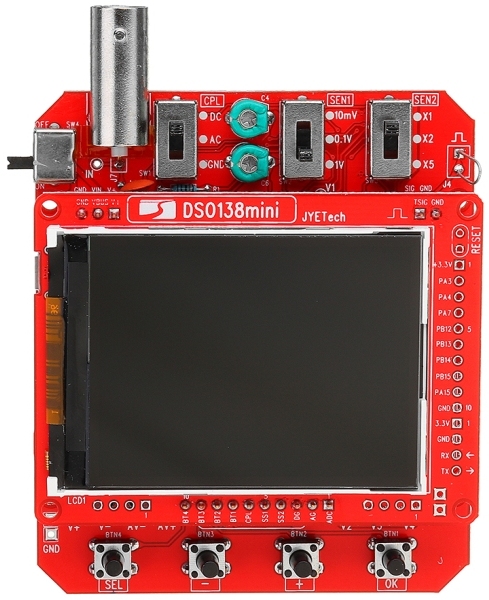
The device is based on the ARM microcontroller STM32F103C8T6 (32-bit based on the Cortex M3 core) and has the following characteristics:
-
number of channels - 1;
-
bandwidth - 0-200 kHz;
-
sampling rate 1 MSa / s;
-
input impedance: 1MOhm / 20pF;
-
maximum input voltage: 50 V with a 1: 1 probe and 400 V, if the probe with a 1:10 divider;
-
communication modes: DC / AC / GND;
-
supply voltage - 9 volts;
-
current consumption - about 100 mA;
-
sensitivity - 10 mV / div - 5 V / div with an accuracy of 5%;
-
ADC - 12 bits;
-
sweep range from 10 μs / div to 500 sec / div;
-
display - color, 2.4 inches with a resolution of 320x240;
-
PCB size - 117 * 76 mm.
The oscilloscope measures the amplitude of the signal, its frequency and period, duty cycle, considers the voltage - maximum, minimum, RMS. It is also possible to set up on which front to synchronize (rising or falling). There is no recording function in it. Sensitivity is regulated by the position of two sliders SEN1 and SEN2 - multiplier and order (10 mV, 0.1V, 1V).

A bandwidth of 200 kHz may even seem quite enough, but do not rush to draw conclusions. Note that the sampling rate is only 1 million samples per second. This is 5 times the frequency of 200 kHz, which by definition does not allow high-quality to shoot such signals.
This oscilloscope feels good in the sound range, when it goes beyond 20 kHz, the signal starts to distort, but still remains digestible, and above 50-70 kHz the distortions become quite strong. Sweeps of 10 μs / div are also not very special and allow you to roam at high frequencies, because the signal period with a period of 100 kHz is already 10 μs.
That is, even if he could adequately display the waveform of the signal with a frequency equal to the declared 200 kHz, then in one cell of the coordinate axis on the screen there would be 2 periods. Moreover, the screen diagonal is 2.4 inches, and the resolution is 320x240 pixels - even if you want, you will not be able to see this signal normally. In principle, you can "watch" simple switching power supplies, the PWM frequency does not exceed 50-100 kHz, below you will see why.
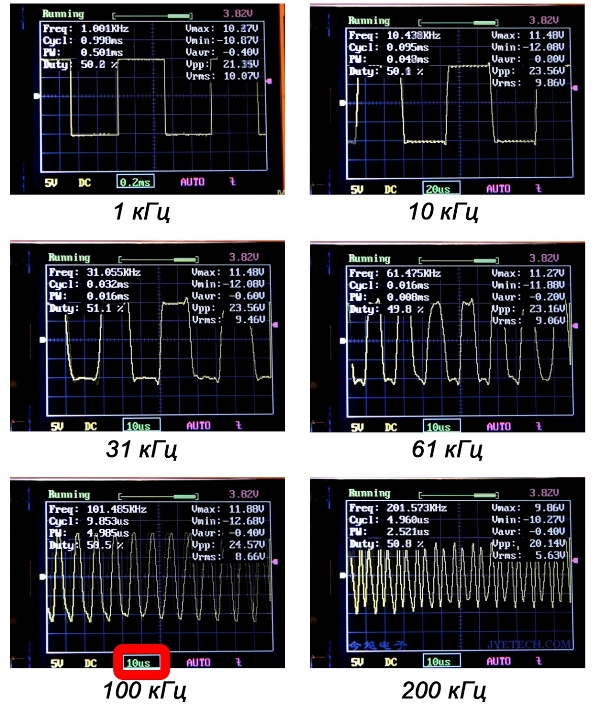
In the illustration above, you can observe how it looks, or rather, how this device sees a rectangular signal at different frequencies, as well as how the waveform changes at high frequencies (a signal from a rectangular turns into a distorted sinusoid). I note that a rectangular signal is considered to be very complex, so the estimation of the frequency with its help is very fair.
Pay attention to what is highlighted in red. This is the division price of the horizontal axis, i.e. each cell is 10 microseconds. This means that it is no longer possible to stretch the signal on the screen for a more detailed study, this is what I said above. If at 60 kHz there are still outlines of rectangular pulses, then at 100, and even more so at 200 kHz, it is no longer clear what.
Nevertheless, such characteristics are at the very least, but they even allow the use of this device in the repair of computer equipment, for example, laptops, as the authors of the following videos.
There are a number of models that, to some extent, are a logical continuation of the DSO138, but differ in appearance and layout, so DSO150 for 1700 rubles, in the kit of which there is already a good probe with a divider (photo above) functionally repeats the previous device, but outwardly it is already more attractive and looks like a finished device. It is controlled not with a set of sliders, as in the previous case, but with 4 buttons and an encoder. No more differences are observed, so we will not dwell on it.
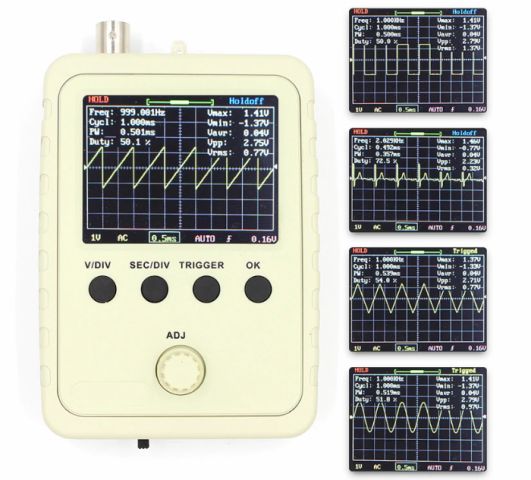
DSO188 - more advanced oscilloscope on 1 MHz, but also like the previous one does not have memory and single-channel. Its cost is 1600-1900 rubles. Compact (a little more than a matchbox) and portable, since it is already powered by a battery - you don’t have to worry about issues of galvanic isolation with the devices in which the measurements are made. The case is assembled from textolite panels, but its side faces are not protected from foreign objects and moisture.
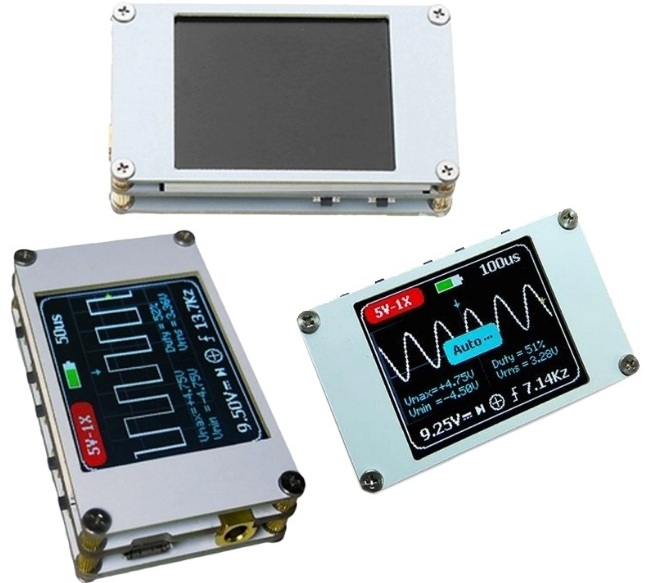

Probes with MMCX connectors are used, in the previous ones there were standard BNC connectors. This is not a problem because it usually comes with the MMCX-BNC adapter. The probe is in the kit, as in the first model - with two crocodiles and without a divider.
Its technical characteristics are slightly superior to previous options:
-
number of channels - 1;
-
bandwidth - 0-1 MHz;
-
sampling rate 5 MSa / s;
-
ADC - 12 bits;
-
input impedance: 1MOhm;
-
maximum input voltage: 40 V with probe 1: 1 and 800 V, if the probe with a divider of 1:10;
-
power source - built-in 230 mAh battery;
-
sensitivity - 50 mV / div - 200 V / div;
-
sweep range from 2 μs / div to 100 ms / div;
-
display - color, 1.8 inches with a resolution of 320x240;
-
device dimensions - 57 * 34 * 11 mm.
It is logical that you should not hope to measure signals at a frequency of 1 MHz, however, a sampling frequency of 5 million selections per second will allow you to easily measure signals at 300-500 kHz, which is already enough for repair and any adjustment of most switching power supplies. This instrument is not suitable for fine tuning and laboratory testing.
There is a useful function "freeze frame". In general, the set of parameters displayed on the screen (frequency, voltage, etc.) matches the previous models. Below is a video with an overview and testing of this model. In addition, this video will be of interest to you if you do not know what bandwidth and sample rate you need, the author talks about this in detail.
For 1600 rubles it is less convenient (because of the dimensions, but it’s a matter of taste), but a more functional oscilloscope than the same DSO150 or 138.
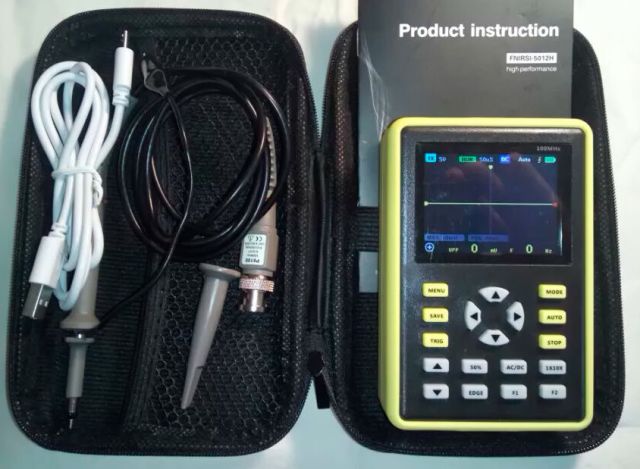
If the above are some fairly old models, then the next one at the time of writing can even be called a novelty. it 100 MHz oscilloscope Fnirsi 5012hIt costs about 4600 rubles. It is single-channel, the connectors for the probes are universal - BNC, and the device itself runs on a battery with a capacity of as much as 5000 mAh (according to other sources - 3000 mAh, it may depend on the configuration or revision). Comes complete with a P6100 probe with a 10x divider and a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz.

The case of the device is plastic in a yellow silicone case, which provides at least some protection against damage.
Specifications:
-
number of channels - 1;
-
bandwidth - 100 MHz;
-
sampling rate 500 MSa / s;
-
ADC - 12 bits;
-
input impedance: 1MOhm / 25pF;
-
communication modes: AC / DC;
-
trigger mode: Single, Normal, Auto;
-
trigger types: Ascending / Descending Breakout;
-
cursor measurements: amplitude, time;
-
maximum input voltage: 80 V with a 1: 1 probe and 800 V, if the probe with a 1:10 divider;
-
power source - 5000 mAh built-in battery;
-
sensitivity - 50 mV / div - 200 V / div;
-
sweep range from 6 ns / div to 50 s / div;
-
display - color, 2.4 inches with a resolution of 320x240;
-
dimensions: 114 x 74 x 33 mm, weight: 300 gr.
Such an oscilloscope is a relatively inexpensive solution for the workshop, in reality it can measure signals with a frequency of 20-30 MHz (and higher - but there will be more distortion), which is a couple of orders of magnitude more than the previous model in the review.
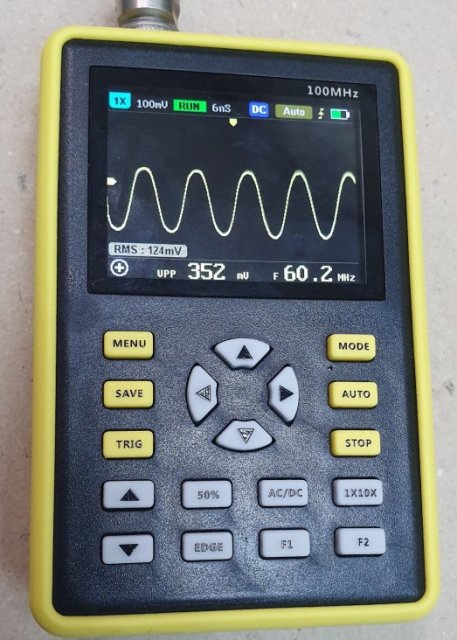
If the probe is with a divider, then such an oscilloscope is enough for most tasks in an electronics repair workshop, for whom it might not be enough, it's radio station lovers. Thanks to the built-in battery, you can use it if you often have to work on the road.

By the way, from the same manufacturer there are other models of oscilloscopes that are cheaper, for example, FNIRSI PRO with a bandwidth of 5 MHz and a sampling frequency of 20 million samples. But it costs not much cheaper, namely 2500-2600 rubles, so there is no particular sense in such savings.
In fact, the model is very good, but there are a couple of drawbacks:
-
there is no output with a calibration signal (needed to adjust the probe);
-
only one channel (although the presence of two channels is not critical for everyone);
-
no connectivity to the computer.
Below is a video where they compare:
JINHAN JDS2022A - this is a two-channel oscilloscope with a passband in 20 MHz, its cost is in the range of 8000-9000 rubles. This device looks like a multimeter, larger than the previous one. It is powered by replaceable batteries of type 18650. This is more convenient than the built-in battery, since being at work outside the workshop, if they are discharged, you can quickly replace them and continue working. It is also possible to charge via a standard micro-USB connector, that is, without removing the batteries from the connector.
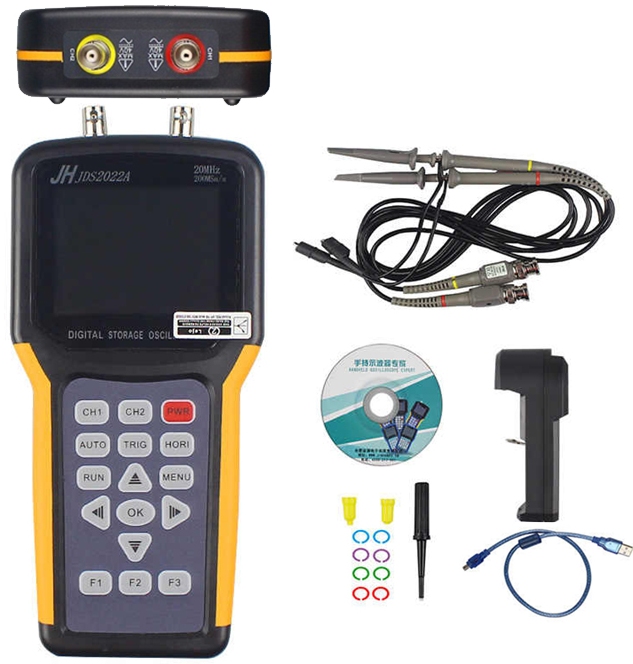

Specifications:
-
number of channels - 2;
-
bandwidth - 20 MHz;
-
sampling rate 200 MSa / s;
-
ADC - 8 bits;
-
input impedance: 1MOhm / 25pF;
-
communication modes: AC / DC;
-
trigger mode: Single, Normal, Auto;
-
trigger types: Ascending / Descending Breakout;
-
maximum input voltage: 40 V with probe 1: 1 and 400 V; if the probe with a divider of 1:10; 2000 volts, if the probe is 1: 100;
-
power source - 2 replaceable 18650 batteries (included, but it may not be - it depends on the seller);
-
sensitivity - 10 mV / div - 5 V / div (if the probe is 1: 1, if there is a divider, multiply by the division factor);
-
sweep range from 10 ns / div to 5 s / div;
-
display - color, 3.2 inches with a resolution of 320x240;
-
Dimensions: 19.5cm * 9.5cm 3.7cm.
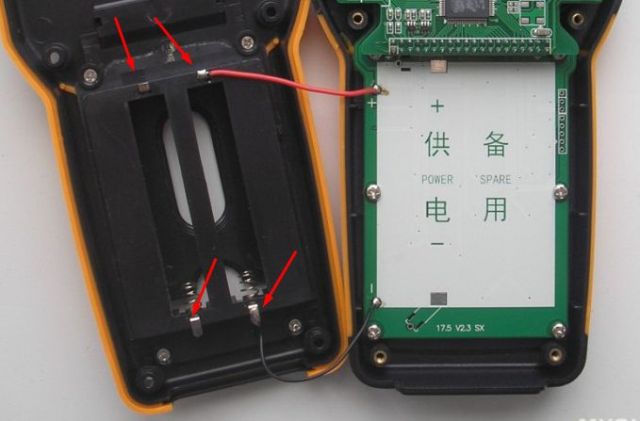
A very strange situation with batteries - there are 2 connectors for them, but 1 is connected to the circuit. When discharging the first one, they need to be interchanged with the second.
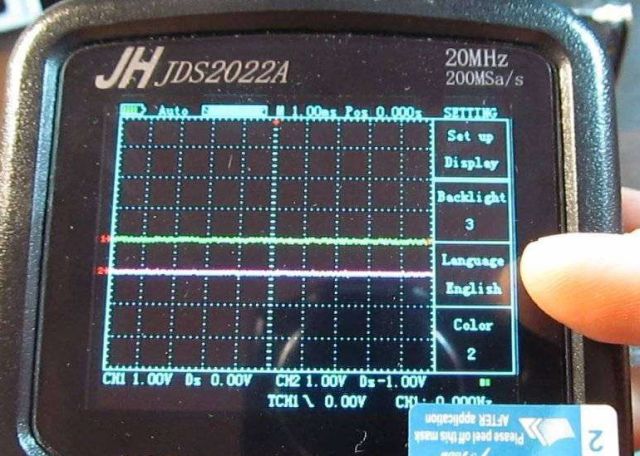
At JINHAN JDS2022A the largest display among competitors from this review, so it will be more convenient both for field work and in the home workshop. It can only measure the amplitude and peak voltage and frequency of the measured signal, but there are modes that allow you to perform mathematical functions with the measured signals on different channels and, for example, depict Lissajous figures. Real tests show that it confidently displays a rectangular signal at frequencies up to 5 MHz, distortions are pretty strong at 10 MHz, but on the whole you can see the presence of a signal.
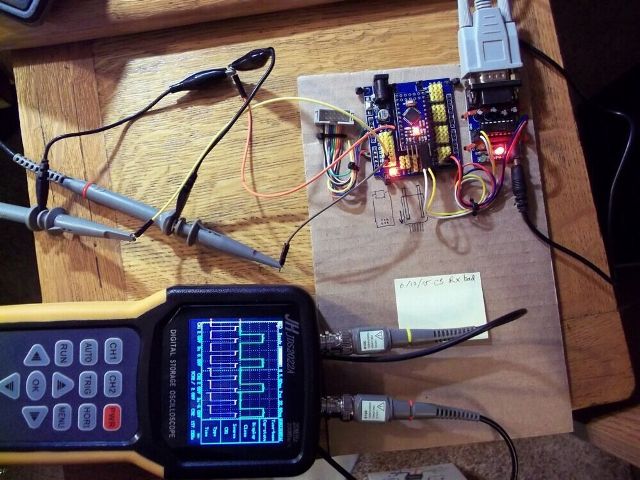

This device also does not have a calibration output, which is inconvenient when working on the road - you need to take a generator with you. This is a convenient and high-quality oscilloscope, and its appearance is already unlike a toy.But it is worth noting that the bandwidth is still lower than on Fnirsi, but it costs almost 2 times more expensive, but it is two-channel.
One of the interesting features is the ability to save an image from the screen. The memory can store up to 6 screenshots that can be downloaded to a computer via micro-USB.
You can watch a more detailed overview of the device in the video below:
There is a single-channel version of this device, as well as a two-channel (one analog and 1 digital channel) with a signal generator - JDS2023 for 7500-8000 rubles and many other models, the main differences of which you see in the table below.
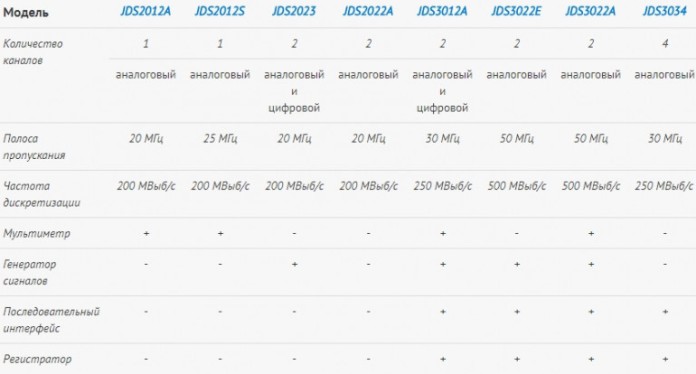
Conclusion
We reviewed several popular models of Chinese oscilloscopes. There are other devices similar in terms of characteristics and price, but it makes absolutely no sense to bring absolutely every one of them. The purpose of this article was to show which models should be paid attention to when choosing the first oscilloscope for a novice master.
The first two models in the review - budget and not too functional, the last two - cover most of the amateur and repair needs. It cannot be said specifically which is better, but personally I like Fnirsi because of the ability to measure relatively high frequencies.
If you need even higher frequencies, but there is no necessary amount of money, look at Soviet analog oscilloscopes. Yes, they do not have the capabilities of digital models, such as recording a signal or the possibility of cursor measurement of a signal at a given point, but they are much cheaper than digital models with a similar frequency range.
The indisputable advantage of portable oscilloscopes is the ability to be powered by a battery, which means that there can be no galvanic connection with the network, so you will not burn the device and you will not be shocked if you get into the mains voltage when taking measurements.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
