Categories: Novice electricians, About electricians and not only
Number of views: 59395
Comments on the article: 3
How relay protection and automation work
 The first human experiments with electricity and the creation of circuits for the passage of current were accompanied by short circuits and malfunctions, during which experience and knowledge were acquired, regularities of the proceeding processes were revealed, and operating rules were developed.
The first human experiments with electricity and the creation of circuits for the passage of current were accompanied by short circuits and malfunctions, during which experience and knowledge were acquired, regularities of the proceeding processes were revealed, and operating rules were developed.
Based on the analysis of the mistakes made, devices began to be created that protect equipment and people from electrical effects. The first such devices were fuses, which burned out when critical loads were created, breaking the electric current circuit.
More complex protective structures began to be massively introduced after 1891, when in Russia, according to the project of Mikhail Osipovich Dolivo-Dobrovolsky, 220 kW of electric energy per 175 km was successfully transported with an efficiency of 77% based on a three-phase voltage system developed by the same scientist.
The protection principle was based on the principle of relays - devices that constantly monitor any electrical parameter of the network, and when they reach critical values, they trigger: they sharply change their initial state by switching the electrical circuit.
The first protection devices were made on the basis of electromechanical relay designs, and the specialists involved in their operation began to be called the term "relay", which is valid to date.
The relay protection and automation service (RPA) created in the power system on the basis of constantly gained experience is simultaneously involved in other complex processes:
-
control systems, including local, remote and remote methods;
-
device locks;
-
signaling circuits, allowing to analyze events occurring in the network;
-
measurements of various electrical quantities in existing circuits;
-
analysis of the quality of measurements based on metrological standards;
-
some other features.
Principles of constructing a circuit of protective devices
A rather cumbersome and complex initial base based on electromechanical structures is constantly being improved and modified. For the protection work, new technical developments are introduced. In modern energy complexes, electromagnetic, induction, static - semiconductor and microprocessor devices are successfully combined.
They are united by a practically unchanging basic algorithm of processes, which is modernized for each specific case. The main protection functions are demonstrated by the structural diagram.
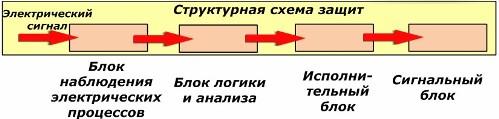
The main functions of protective devices
Observation unit
Its main function is to monitor the ongoing electrical processes in the system based on measurements from current and / or voltage measuring transformers.
The output signals taken from the unit can be directly transmitted to the logic circuit for comparison with the user-defined deviations from the nominal values, called settings, or initially converted to digital form.
Logic block
Here, the input signals are compared with the boundary characteristics of the settings. The slightest match between them leads to the issuance of a command to operate the defenses.
Executive unit
It is constantly maintained in readiness for response to logical unit commands. In this case, switching occurs in the wiring diagram according to a predetermined algorithm that excludes equipment damage and personal injury.
Alarm unit
The processes occurring in the system are carried out so quickly that a person is not able to perceive them with their organs.To fix the perfect events, alarm devices are installed that use visual, sound exposure methods with saving the changes that have occurred in the memory.
In all alarm constructions, the transfer of its state after operation to its initial position is performed once by the operator manually, which eliminates the loss of information about the operation of protection by automation.
Principles of protection
A very serious attitude to the reliability and safety of electricity use has determined the basic requirements that relay protection systems must meet. However, they are also technical devices, which means: they have the ability to disrupt the proper performance.
Failure of relay protection systems is possible with:
-
faults inside the protections;
-
excessive responses when the action of the executive body is not required;
-
false work in the absence of damage to the electrical system.
To exclude failures during operation, a project is developed, installed, commissioned with commissioning and maintenance of relay protection devices taking into account the developed requirements for relay protection and automation devices for:
-
selectivity based on the hierarchy of the scheme;
-
speed determined by the response time;
-
sensitivity to starting factors;
-
reliability of work.
Principle of selectivity
Another common name for it is selectivity. This characteristic allows you to accurately identify and localize the place of the manifested malfunction in a structured network with any hierarchy.
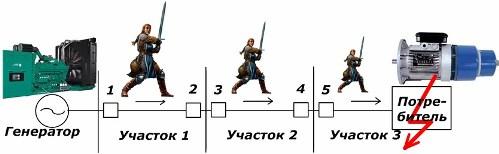
For example, a generator transmits electric energy to many consumers located in sections No. 1, 2 and 3, equipped with their own protections 1-2, 3-4 and 5, respectively. In the event of a short circuit inside the end user at site No. 3, the fault currents will pass through all the protection circuits from the source.
However, in this situation, it makes sense to disconnect the final section with a damaged electric motor, leaving all operating devices in operation. For this purpose, different relay protection settings are introduced for each circuit at the design stage of the circuit.
The protective devices of section 5 must feel the fault currents earlier and ensure their emergency disconnection from the generator faster. Therefore, in the above scheme, the values of the current and time settings in each section are reduced from the generator to the consumer, following the principle: the closer to the place of damage, the higher the sensitivity.
At the same time, the redundancy principle is fulfilled, taking into account the possibility of failure of any technical devices, including protective systems of a lower level. This means: if the protection of section 5 of section 3 is malfunctioning, a short circuit should disconnect the relay protection devices No. 4 or 5 of line No. 2, which, in turn, are insured by the protection of section No. 1.
Performance principle
Damage shutdown time consists of at least two factors:
1. triggered protection;
2. operation of the circuit breaker drive.
The first parameter can be adjusted from the minimum value due to the design of the protection and the number of elements used. Such methods create a delay time for the inclusion of special adjustable relays in the circuit. It is used for further protection.
Devices close to the place of damage must be configured to operate with the shortest possible time intervals for operation.
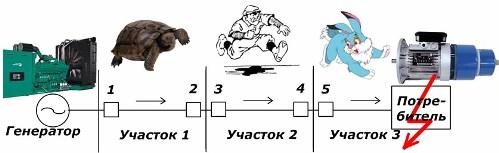
Principle of sensitivity
This characteristic allows you to determine the types of calculated damage and abnormal situations of the power system inside the current protection zone.
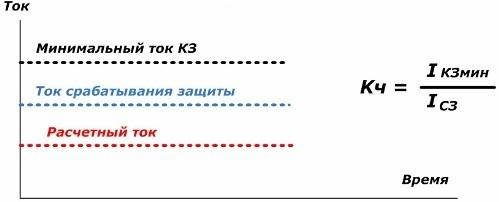
Sensitivity of relay protection and automation devices
To determine its numerical expression, the coefficient Кч is introduced, calculated by the ratio of the minimum value of the short-circuit current for the section to the value of the tripping current.
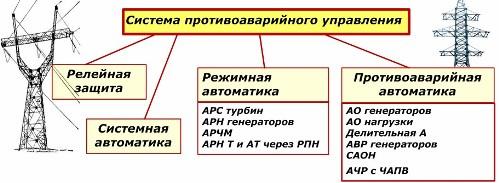
At the same time, relay protection and automation devices work correctly at Icz The optimal value of the sensitivity coefficient lies in the range of 1.5-2. Reliability principle To define it, the terms are introduced: uptime maintainability; longevity; persistence. Each of them has its own evaluation criteria. Reliability of relay protection and automation devices Operation and maintenance of relay protection devices consider three options for reliability in response functions: 1. with internal short circuits in the protected zone; 2. during the passage of external short-circuit outside the work area; 3. in modes without damage. At the same time, reliability is divided into: operational; hardware room. Emergency control Any relay protection unit is not only an independent circuit, but is combined into higher-level complexes, which ultimately constitute the emergency control system of the power system. She has every element interconnected with other components and comprehensively performs its tasks. A shortened list of protection and automation functions is demonstrated by a simplified block diagram. Grid Emergency Management A brief summary of the features of the operation of relay protection and automation allows us to conclude that the profession of a relay operator requires constant study of the equipment coming into operation, improvement of knowledge and the formation of strong practical skills. More information about the profession of a relay operator: Profession Electrician relay protection and automation Read about modern relay protection devices here: Microprocessor-based relay protection devices: an overview of capabilities and controversial issues
See also at i.electricianexp.com
: