Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 106788
Comments on the article: 8
Service and repair of magnetic starters
Magnetic starters, as the name implies, were conceived as a switching device for starting electric motors. Therefore, the number of power poles of these devices is almost always equal to three - in terms of the number of network phases. Starters are often equipped with thermal overload relays and a housing with “start” and “stop” buttons.
But the starter turned out to be a very convenient and functional thing. A wide range of rated currents, small dimensions and the possibility of autonomous installation outside any switchgear or switchboard have led to the fact that magnetic starters began to be widely used in everyday life for inclusion in the network of various powerful power consumers, for example, heating boilers.
Like any other electrical device, the magnetic starter periodically also needs repair and maintenance.

How is a magnetic starter arranged?
In general, this is, at a minimum, a coil of thin wire in varnish insulation, placed in one plastic case with contacts. Contacts, as usual, are divided into movable, mechanically connected to the spring-loaded core of the coil, and fixed, stationary located in the upper part of the housing.
At the same time, for starters rated for a current of 20 amperes, one can clearly distinguish between power pairs of contacts in the amount of three pairs, and pairs of contacts of auxiliary control circuits designed for weak currents. The number of low-current contacts is almost unlimited, especially since for many starters it is possible to purchase additional contact boxes, which allow assembling very complex circuits on starters.
Such a design provides the starter with a not very high degree of protection against external influences - at the IP00-IP30 level. If you need to achieve a greater degree of protection, you will have to use starters in an additional protective casing, often equipped with their own buttons for starting, stopping and returning the thermal relay, if any.
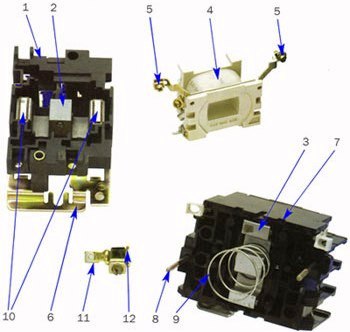
Fig. 1. The device of the magnetic starter PML:
1 - base made of heat-resistant plastic, 2 - the fixed part of the magnetic circuit, 3 - the moving part of the magnetic circuit, 4 - electromagnetic control coil, 5 - contact clamps, 6 - metal platform (for starters with a rating of over 25 A) 7 - traverse with movable contacts, 8 - fixing screw, 9 - return spring, 10 - aluminum rings, 11 - fixed contact, 12 - clamp with a notch for fixing the conductors.
The maintenance program for magnetic starters is simple and includes the following items:
1. External inspection for damage and chips of the case, as well as the removal of contaminants (not only from the surface of the case, but also from the surface of the core of the electromagnet). Chips and damage to the case occur not only due to shocks and falls, but also due to prolonged exposure to vibrations caused by the operation of a worn AC mains and the marriage in the installation of the starter, as well as its own defects.
If damage to the case has led to the fact that the starter cannot be fixed securely, or its contacts cannot be freely closed / opened, then there is simply no other way than replacing the case or starter.
Special attention should be paid to checking the availability of all parts and parts of the starter. For example, a movable contact plate together with its pressing spring can easily “get lost” - a new one will be required.
 2. Revision of the mechanical part. The test is subjected to a working spring, which ensures contact breaking. It should be tight enough, the turns should not come close.The course of the starter armature relative to the housing is checked: it is necessary that there are no any jamming and difficulties during movement.
2. Revision of the mechanical part. The test is subjected to a working spring, which ensures contact breaking. It should be tight enough, the turns should not come close.The course of the starter armature relative to the housing is checked: it is necessary that there are no any jamming and difficulties during movement.
Checking the stroke is carried out by closing the contacts "by hand". In the presence of mechanical jamming, you can resort to lubrication or grinding of the rubbing parts.
3. Cleaning contacts - a measure that it is better to refrain from when servicing serviceable magnetic starters.
The highly conductive layer of movable and fixed contacts is relatively thin, therefore, if you rub a file on it with each maintenance, the starter will very soon fail. A file is needed only if the contacts have obvious traces of carbon deposits or fusion. And sandpaper for stripping contacts is excluded categorically.
When closing, all the contacts of the starter should abut each other tightly over the entire surface, without displacements and inclinations, the presence of which indicates the need to adjust the mechanical part.
4. If the starter contains metal parts in the housing, or is in a metal casing, then make sure that there is no circuit between these parts to be earthed and the power contacts. For all starters in general, it is necessary to check the absence of short circuits between the individual power poles. At the household level, for these purposes it is enough to use a conventional multimeter. A megohmmeter is used in production, and insulation resistance normalized - not less than 0.5 megohms.
5. The starter coil is subjected to a thorough inspection. Cracks in the frame, damage, carbon deposits and melting of insulation - all these are sure signs of significant problems. A coil with such signs is best replaced.
Of course, it is usually possible to determine the inter-turn short circuit in the coil only during operation by indirect signs, such as an increased hum during the operation of the starter. Nevertheless, if you systematically check the active resistance of the coil wire, you can notice a significant and sharp decrease. This symptom speaks quite eloquently of a coil malfunction, which theoretically can be rewound, but in practice it is easier to replace.
 6. However, the increased hum during the operation of the starter can be caused by some other reasons besides defects of the coil itself. For example, a skew may occur during its installation, an insufficient voltage level in the network is possible, a return spring that is too strong can be selected.
6. However, the increased hum during the operation of the starter can be caused by some other reasons besides defects of the coil itself. For example, a skew may occur during its installation, an insufficient voltage level in the network is possible, a return spring that is too strong can be selected.
All these factors lead to the fact that the anchor during closure is not tight enough to the core. The result will be a greater coil current due to its lower inductive resistance (hence the hum), as well as the burning of power contacts.
You can check the tightness of the surfaces of the magnetic circuits of the core and the anchor using an ordinary thin clean sheet of paper laid between these parts. At least 70 percent of the surface should be in contact - then the contact will be reliable.
7. If there is a thermal overload relay, its setting must be checked.. In industrial enterprises, this is done with the help of special test benches. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to load and check the relay at the household level. To do this, you can pass the relay to a special laboratory, or, in extreme cases, test it using a known load of a higher rating.
Magnetic starter repair produced according to the results of maintenance and is usually reduced to the replacement of parts and assemblies that are not subject to restoration and adjustment. Such spare parts can be: a coil, individual contacts and even the contact group as a whole, housing parts, springs, screws and clamping plates.
See also on this topic: How to connect a magnetic starter
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
