Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 355101
Comments on the article: 16
Digital and analogue signal: what are the similarities and differences, advantages and disadvantages?
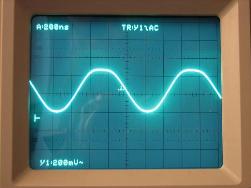 When dealing with television and radio broadcasting, as well as modern forms of communication, very often you come across terms such as "Analog signal" and "Digital signal". For experts, there is no secret in these words, but for people ignorant the difference between the “digit” and the “analogue” may be completely unknown. And yet there is a very significant difference.
When dealing with television and radio broadcasting, as well as modern forms of communication, very often you come across terms such as "Analog signal" and "Digital signal". For experts, there is no secret in these words, but for people ignorant the difference between the “digit” and the “analogue” may be completely unknown. And yet there is a very significant difference.
When we talk about a signal, we usually mean electromagnetic oscillations that induce EMF and cause current fluctuations in the receiver antenna. Based on these vibrations, the receiving device — a television, radio, walkie-talkie or cell phone — makes up the “idea” about which image to display (if there is a video signal) and what sounds this video signal should accompany.
In any case, the signal of a radio station or a mobile communication tower can appear both in digital and in analog form. After all, for example, sound itself is an analog signal. At a radio station, the sound perceived by the microphone is converted to the electromagnetic waves already mentioned. The higher the frequency of sound, the higher the frequency of oscillations at the output, and the louder the speaker speaks, the greater the amplitude.
The resulting electromagnetic waves, or waves, propagate in space using a transmission antenna. So that the air does not get clogged with low-frequency noise, and so that different radio stations have the opportunity to work in parallel, without interfering with each other, the vibrations resulting from the influence of sound are summed, that is, “superimposed” on other vibrations having a constant frequency. The last frequency is called the “carrier”, and it is precisely on its perception that we tune our radio receiver to “catch” the analog signal of the radio station.
The reverse process takes place in the receiver: the carrier frequency is separated, and the electromagnetic waves received by the antenna are converted into sound waves, and the speaker’s familiar voice is heard from the speaker.
In the process of transmitting an audio signal from a radio station to a receiver, anything can happen. Third-party interference may occur, the frequency and amplitude may change, which, of course, will affect the sounds emitted by the radio. Finally, the transmitter and receiver themselves introduce some error during signal conversion. Therefore, the sound reproduced by an analog radio receiver always has some distortion. The voice can be fully reproduced, despite the changes, but the background will be hissing or even some kind of wheezing caused by interference. The less confident the reception, the louder and more distinct these external noise effects will be.
In addition, the terrestrial analog signal has a very low degree of protection against unauthorized access. For public radio stations, this, of course, does not matter. But while using the first mobile phones, there was one unpleasant moment related to the fact that almost any extraneous radio receiver could be easily tuned to the desired wave to eavesdrop on your telephone conversation.
Analogue broadcasting has such disadvantages. Because of them, for example, television in the near future promises to become fully digital.
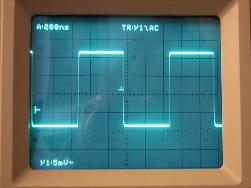 Digital communications and broadcasts are considered more protected from interference and external influences. The thing is that when using the “numbers”, the analog signal from the microphone at the transmitting station is encrypted into a digital code. No, of course, the flow of numbers and numbers does not extend into the surrounding space. Just a sound of a certain frequency and volume is assigned a code from radio pulses. The duration and frequency of the pulses is predetermined - it is the same for both the transmitter and the receiver.The presence of an impulse corresponds to unity, the absence to zero. Therefore, such a connection was called “digital”.
Digital communications and broadcasts are considered more protected from interference and external influences. The thing is that when using the “numbers”, the analog signal from the microphone at the transmitting station is encrypted into a digital code. No, of course, the flow of numbers and numbers does not extend into the surrounding space. Just a sound of a certain frequency and volume is assigned a code from radio pulses. The duration and frequency of the pulses is predetermined - it is the same for both the transmitter and the receiver.The presence of an impulse corresponds to unity, the absence to zero. Therefore, such a connection was called “digital”.
A device that converts an analog signal into a digital code is called analog-to-digital converter (ADC). And the device installed in the receiver, and converting the code into an analog signal, corresponding to the voice of your friend in the dynamics of a GSM standard cell phone, is called a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
Errors and distortions are virtually eliminated during the transmission of a digital signal. If the impulse becomes a little stronger, longer, or vice versa, then it will still be recognized by the system as a unit. And zero will remain zero, even if some random weak signal appears in its place. There are no other values for the ADC and DAC, like 0.2 or 0.9 - only zero and one. Therefore, interference with digital communications and broadcasting has almost no effect.
Moreover, the “figure” is also more protected from unauthorized access. Indeed, for the DAC of the device to be able to decrypt the signal, it is necessary that it “knows” the decryption code. The ADC along with the signal can also transmit the digital address of the device selected as the receiver. Thus, even if the radio signal is intercepted, it cannot be recognized due to the absence of at least part of the code. This is especially true. for mobile cellular.
So here differences between digital and analog signals:
1) An analog signal can be distorted by noise, and a digital signal can either be clogged with noise at all, or come without distortion. The digital signal is either definitely there or completely absent (either zero or one).
2) An analog signal is available for perception by all devices operating on the same principle as the transmitter. The digital signal is reliably protected by a code; it is difficult to intercept it if it is not intended for you.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
