Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 2846
Comments on the article: 0
The most popular electrical devices in electrical installations
All electrical devices used in production can be divided into 3 groups: control, monitoring and protection devices. The devices of the first group are divided into manual and remote control devices. The second group includes various sensors and relays that perform the functions of sensors. The devices of the third group protect electrical installations from various emergency operation modes (short circuits, current overloads, increase and decrease voltage, etc.).
The most common electrical devices in electrical installations are electromagnetic starters, electromagnetic relays, control buttons, circuit breakers and thermal relays.
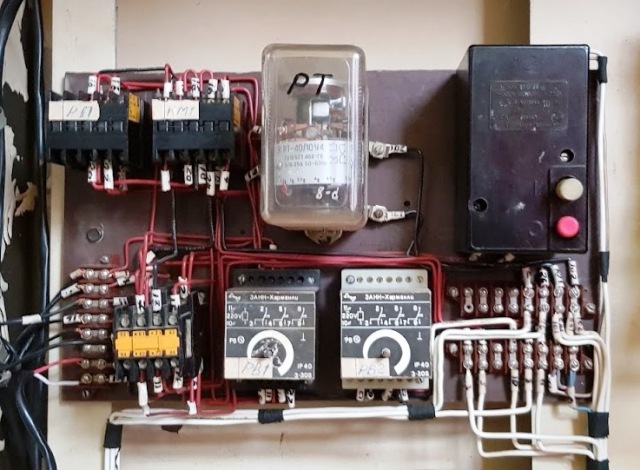

Electromagnetic starters
These are the most popular electrical appliances. Around the world, a huge number of them are produced. They are designed for remote control of various power loads, most often electric motors, but are also used to control other powerful consumers - heating elements, powerful spotlight lamps, etc.

The term "remote control" means that to turn on the starter directly with him, no action is taken. In the circuit of its control coil, buttons are usually used, with which they give a signal to turn on and off. The control and power circuits of the starter are not electrically connected.
The starter can be used as a power amplifier, as it allows a relatively low-power control circuit (coil) to control powerful power circuits. So, for example, the power consumption of the starter coil of the 1st magnitude is 8 VA, and it can control a current of 10A and a power of up to 4 kW. For starters of other sizes, the power gain is even greater.
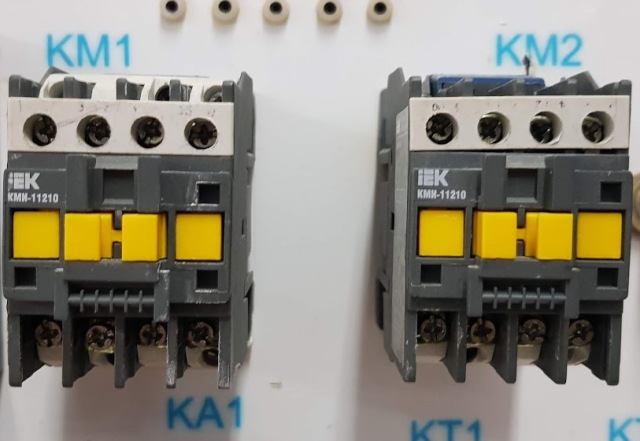

There are a large number of different series of electromagnetic starters: PML, PM12, KMI, PME, PMA, PAE, starters of foreign manufacturers. All of them are arranged and work on the same principle.
When voltage is applied to the starter coil, it flows around with a current, a magnetic flux is created, which closes through the magnetic circuit and causes the movable part of the magnetic circuit to be attracted to the stationary one. The bridge type contacts are connected to the moving part of the magnetic circuit.
When voltage is removed from the starter coil, for example, by pressing the "Stop" button in its control circuit, the starter is switched off and the movable part of the magnetic circuit returns to its original position due to the counteracting spring.
Very clearly, the design and principle of operation of the electromagnetic starter is shown in the form of animation on the YouTube channel of the Cable.RF company.
The device of the electromagnetic starter:
All starters have 3 power contacts and at least 1 additional (interlock). There are starters with a lot of additional contacts. In most series, to increase the number of contacts, it is possible to use special contact attachments in conjunction with the starter.
All power contacts are normally open (closing), additional contacts can be either normally open or normally closed (closing). You can determine the type of contact by the inscription next to it.
So, for example, in the popular PML electromagnetic starters, power contacts are indicated on the edges between them by the numbers "1 - 2", "3 - 4" and "5 - 6", and additional "13-14". The last two digits of the additional contacts indicate their type - "1 - 2" - normally closed,"3 - 4" - normally open.Power contacts are always rated for current, according to the size of the starter (1 - 10 A, 2 - 25 A, 3 - 40 A, 4 - 63 A, etc.), additional contacts for a maximum current of 10 A.
The "elder brother" of the starter is a Soviet electromagnetic contactor capable of switching currents of 100 or more amperes 3600 times per hour (once per second):
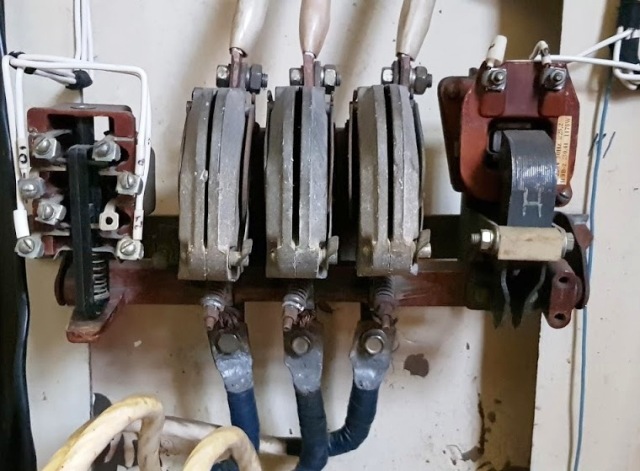
Currently, in the literature and in catalogs, starters are often called contactors. In the last century, these were different devices, but the terminology has changed and now under the contactors and fuses often mean the same electrical device.
This question turned out to be very debatable, therefore, if desired, here you can argue about it:
What is the difference between a contactor and a starter
Motor start-up circuit using an electromagnetic starter:
For more information about starters, see here:
The device and principle of operation of the starter
Features of modern starters and their application
Service and repair of starters
Electromagnetic control relays
Unlike electromagnetic starters, relays do not have power contacts. We can assume that all the contacts of conventional relays are additional and intended for switching only control and signaling circuits.
There are a large number of different relays, especially there are many different types of them in such areas as relay protection and automation. The most common electrical apparatuses in production in terms of the number of apparatuses sold by all manufacturers a year after starters are conventional electromagnetic control relays.
For a long time, automation of all machine tools, installations and machines was built on these devices. They provided the necessary logic for controlling the operation of the circuit. Currently, their scope is narrowing, because most automatic circuits now work using programmable logic controllers (PLC) and the entire logic of the circuits is now described in software.
A popular option for using electromagnetic control relays in our time is signal amplification by power. So the outputs of the controllers are not designed for switching high currents, so often relays with shunted coils with diodes are placed in the output circuits of the controllers.
True, various semiconductor (solid-state) relays have already begun to supplant them here, the main advantage of which is the lack of contacts (there is nothing to burn and oxidize). Semi-conductor relays are considered more reliable electrical devices.
Electromagnetic relays are capable of controlling currents of 6 - 10 A. Coils of electromagnetic starters switch their relay contacts, and they already control electric motors and other actuators of automatic control systems.
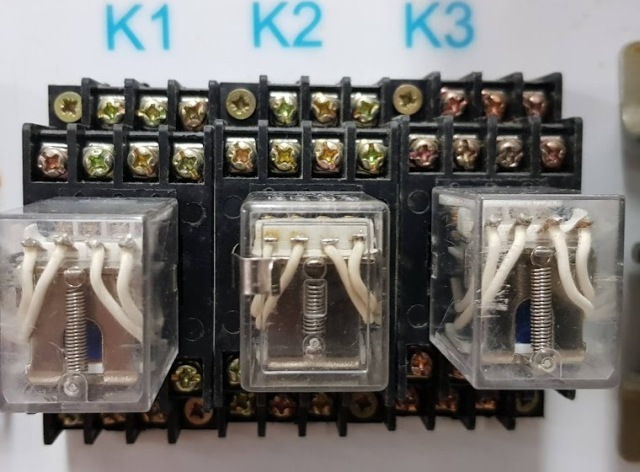
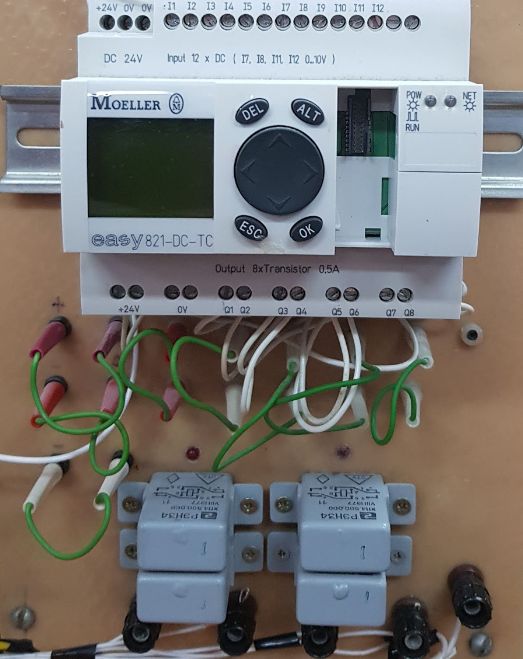
Case study: four REN34 relays are connected to the outputs of the Easy Moeller PLC in the training laboratory:

It is often difficult to quickly understand where starters and relays are located on old machine circuits made according to ancient GOSTs. To deal with this issue, you can be guided by the following rule: if there is a coil in the circuit and it has contacts in the power part of the circuit, for example, in the circuit where the electric motor is located, then this is an electromagnetic starter, and if there is no contact in the power part of the circuit, then this is an electromagnetic relay management. In this case, the relay must have contacts in the control circuit. Contactless coil - electromagnet.
More about the relay:
Device and relay application examples, how to select and connect
Operation and repair of electromagnetic relays
Control buttons
These are manual control devices. They are designed to supply signals to the circuit by directly clicking on them. The main feature of all control buttons is the presence of the self-return function, i.e. after releasing the button, its pusher returns due to the opposing spring to its original state.
This ensures the so-called "zero protection" of the electric motor.After disconnecting the supply voltage for any reason, the button in the starter coil circuit will not allow it to turn on spontaneously after the voltage appears. The electromagnetic starter can only be turned on again by consciously pressing the "Start" button.
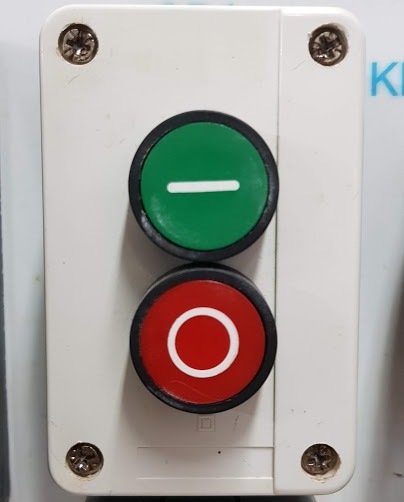

Buttons in the form of separate electrical devices are most often used on various remotes and control panels. Also, they are assembled in several pieces in one case and are issued in the form of complete products - button posts.
The control panel of the woodworking machine with buttons, switches and switches:
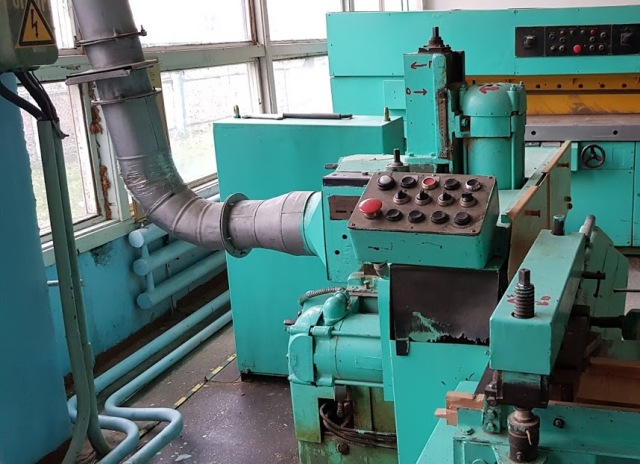

The buttons are designed for switching small currents of 6 - 10 A, mainly for controlling the chains of coils of electromagnetic starters and relays.
In the electrical circuits of machine tools, installations and machines for these purposes, switches (latched buttons), toggle switches, and various switches are also used. All of them are also intended for switching exclusively control circuit currents.
Electromagnetic starter with integrated Start and Stop buttons:
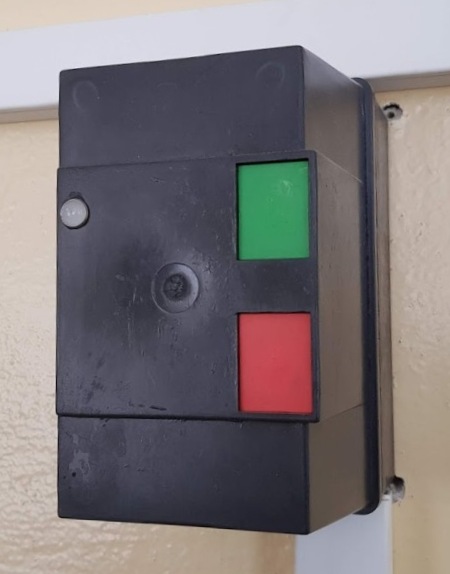

Miniature control button:

Laboratory toggle switches:

If there is a need to manually turn the power circuits on and off, then batch switches and knife switches are most often used for this.
Batch switch:

Circuit breakers
These are the most popular devices that protect various electrical circuits from emergency operation. All electrical installations must be protected from short circuits, and the electric motors of machines from current overloads.
The circuit breaker has in its design the so-called releases that respond to changes in the monitored parameters in the circuit and trip the circuit breaker when the monitored parameter exceeds the set value.
Single pole circuit breaker:

The device and principle of operation of the circuit breaker:
The electromagnetic release operates instantly when the current flowing through the circuit breaker is exceeded. Different circuit breakers have a different value - 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13 with respect to the rated current.
The thermal release is a bimetallic plate, which bends when heated and turns off the machine during current overload according to the principle "the greater the current, the faster it will work."
On the protective characteristic of a circuit-breaker with a combined release, on the left side there is a zone of action of a thermal release, and on the right - a zone of operation of an electromagnetic release.
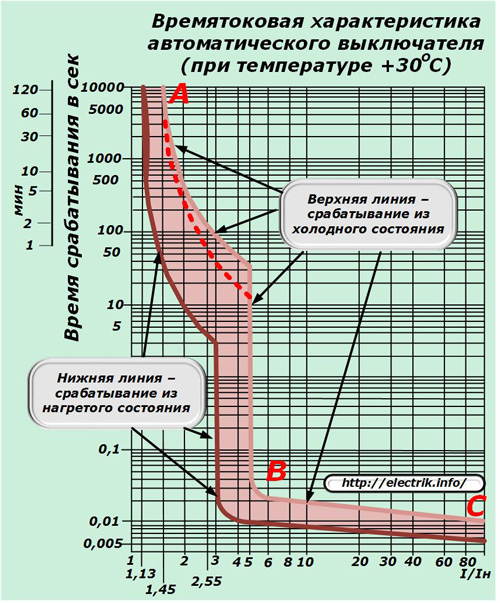
Circuit breakers can also be used.additional releases - independent, allowing to disconnect the circuit breaker from an external signal, minimum and maximum voltage.
How to choose a starter and circuit breaker for an induction motor
Legendary Soviet automatic switch AP50:
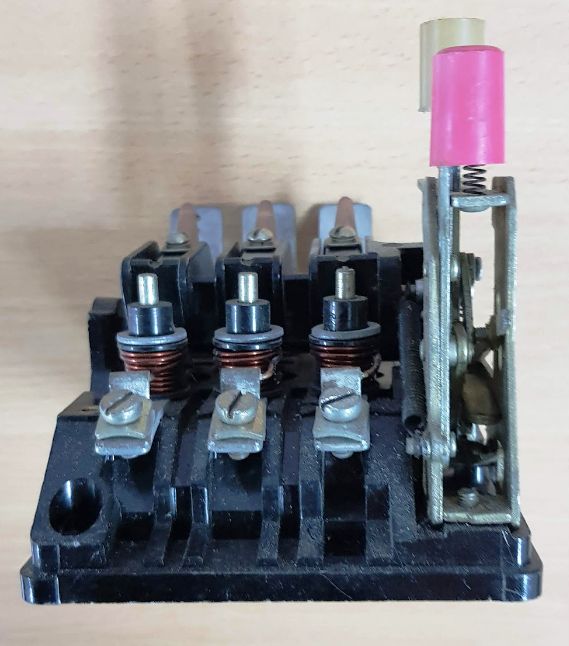

The past and present of circuit breakers (the second is 30 years older):
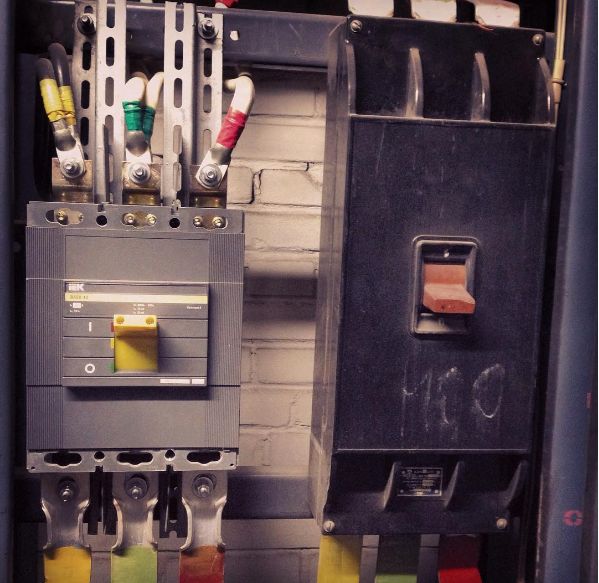

In older circuits, the function of short circuit protection was performed by fuses. Now in all modern installations and machines fuses are replaced by circuit breakers, as thanks to them, operational efficiency is increased and there is no opportunity to interfere in the work of the electrical installation by unqualified personnel by installing uncalibrated melt inserts, which for a long time in the case of fuses was very common.
Thermal relays
On the same principle as the thermal release of the circuit breaker, the popular electrical devices work -thermal relays. They also use bimetallic plates, which are made of two materials with different temperature expansion coefficients and bend when heated.Bimetal plates are included in the electric motor circuit and protect it from current overloads by bending and opening the relay contact in the coil circuit of the electromagnetic starter.
Thermal relay TRN10 with two bimetallic plates and a cover removed:
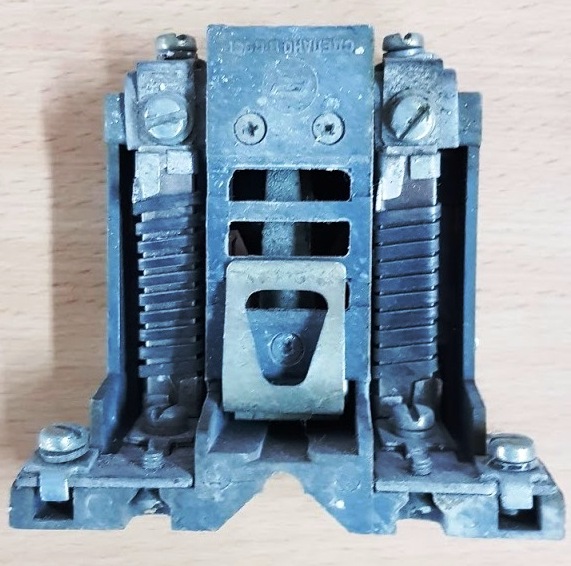


Often in the schemes of machines there are several motors and one circuit breaker at the input. The switch bulges out according to the total current of the motors and protects the electrical installation from short-circuit currents, and each electric motor is individually protected by its own separate thermal relay, which is selected according to the current of a particular electric motor.
Read more about these electrical devices here:
All the electrical apparatuses described above play a very important role in electrical installations, and even the complete replacement of relay-contactor control systems with systems using computer technology and various semiconductor devices will not displace them from use. The trend will continue to miniaturize them, improve technical specifications, but for sure, these devices will be used in various electrical installations for a long time.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
