Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 3537
Comments on the article: 0
Wattmeters - types and application, connection diagram, features of use
Each consumer, powered by an electric network, consumes some power. Power characterizes in this case the speed of the electrical network performing the work necessary for the operation of a particular device or circuit, which is powered from this network. Of course, the network must be able to provide this power and not be overloaded at the same time, otherwise an accident can occur.
To measure power consumption in alternating current circuits, special devices are used - wattmeters. Wattmeters show the current power consumption, and some of them are even able to calculate the amount of energy in kilowatt hours consumed in a certain time while the consumer was working. In this article, we will consider several main types of power meters.

Wattmeters are used in a variety of industries and households, especially in the electric power industry and in mechanical engineering. In addition, power meters are often useful in everyday life.
They are used to determine the power of various household appliances, to calculate the approximate cost of electricity per month, to diagnose devices, to test networks, and simply as visual indicators. There are panel wattmeters, wattmeters in the form of network adapters, digital and analog wattmeters.
The principle of operation of these devices in general is simple: the supply voltage and current consumption are measured, and power is defined as the product of these values, taking into account the power factor of the circuit under study. The power factor is determined by the phase difference between current and voltage. Digital wattmeters display readings on the display or record them in digital form, and analog ones are indicated by an arrow on the scale.

Analog wattmeters
Analog devices include wattmeters of an electrodynamic system. Their work is based on the interaction of a pair of coils, the first of which is stationary, and the second is mobile, that is, it can deviate to the side. A fixed coil is connected to a current, and a moving coil is connected to a voltage.

A fixed coil has a small number of turns and is connected in series to the power measurement circuit, while a moving coil has a much larger number of turns and is connected through a resistor parallel to the instrument under study.
The greater the current flowing through the fixed coil, the stronger its magnetic field deflects the moving coil associated with the arrow. The scale is calibrated in watts. As you already understood, here the current, voltage, and power factor of the circuit are automatically taken into account.
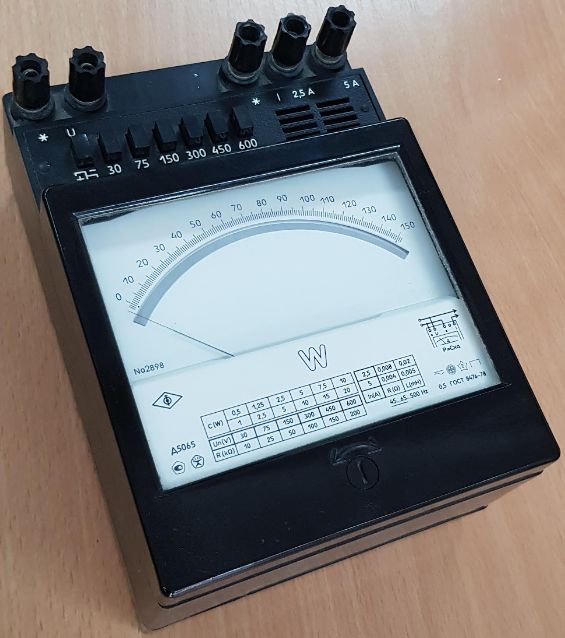
Power meter device:
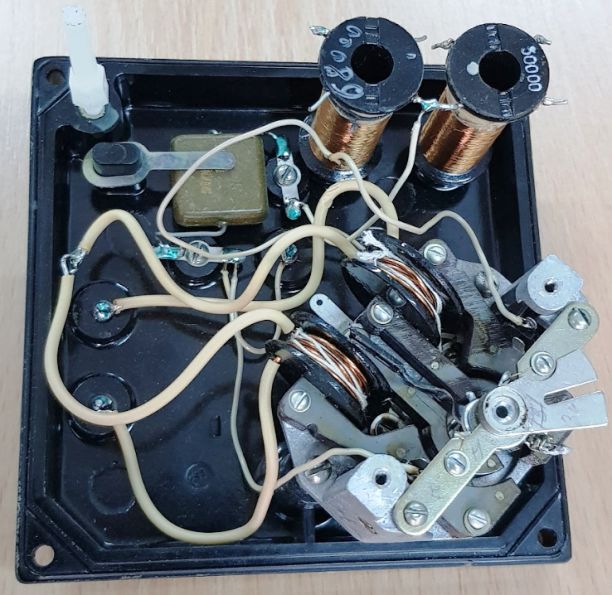

Wattmeter connection diagram:
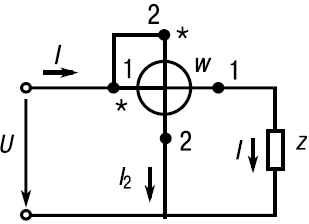
Wattmeter connection diagram from the cover of the D5065 device:
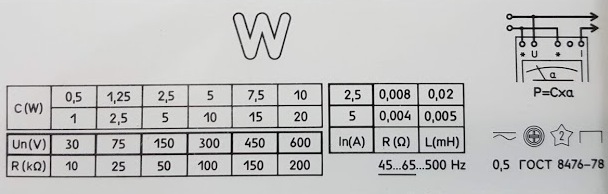
Digital wattmeters
A digital power meter works completely differently. The current is measured indirectly according to Ohm's law by estimating the voltage drop across a calibrated shunt, and the voltage is measured using a digital voltmeter. Current sensor maybe not necessarily a shunt, but also a current transformer.
The instantaneous current and voltage parameters measured by the circuit are processed by a microprocessor, which calculates the consumed power on the basis of these data, as well as the total amount of electricity that was consumed by the consumer during the measurements. The result is displayed on the digital display of the device.

Analog devices can often be found in the form of panel, modular products, and digital - in the form of professional equipment and portable devices.
Household power meter
A very common example of a simple digital wattmeter is household wattmeter in the form of a network adapter - an adapter.It is designed to monitor power consumption, as well as to quickly evaluate the cost of electricity at home. The power meter is inserted into the outlet from which the device is usually powered, the consumption of which must be known. Then, the plug of the device itself is inserted into the socket of the wattmeter.
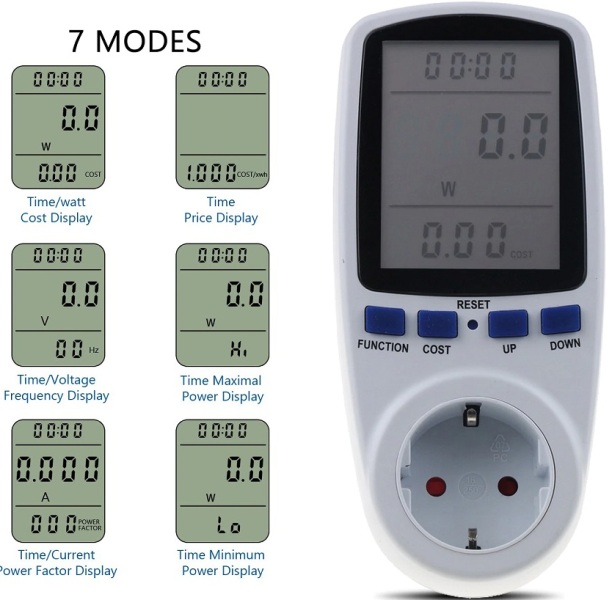
By pressing the appropriate button, the wattmeter starts counting the time and records the amount of electricity consumed from that moment, that is, the energy that was given through its outlet. The cost of electricity is immediately considered if the price of kilowatt hours is pre-set. While the device is working and the power meter measures power, the cost on the display is periodically updated. This type of wattmeter is capable of measuring powers up to 3600 watts.
It is necessary to insert the device into a power outlet and insert a plug into it - the display immediately starts the countdown and in real time the power consumption is displayed. Using the buttons, you can switch the displayed parameter from power - to current, voltage, see peak power, minimum power, etc.
In addition, the display shows the AC frequency at the outlet. By setting the cost of a kilowatt-hour of electricity, using a household wattmeter, you can estimate the cost of electricity consumed by a refrigerator, computer, fan, air conditioning, heater, water heater, etc.
Professional power meters
Professional power meters feature advanced functionality and increased accuracy class. These devices allow testing simpler measuring devices, and they themselves are able to measure power in a much wider range of currents, voltages and frequencies than household ones.
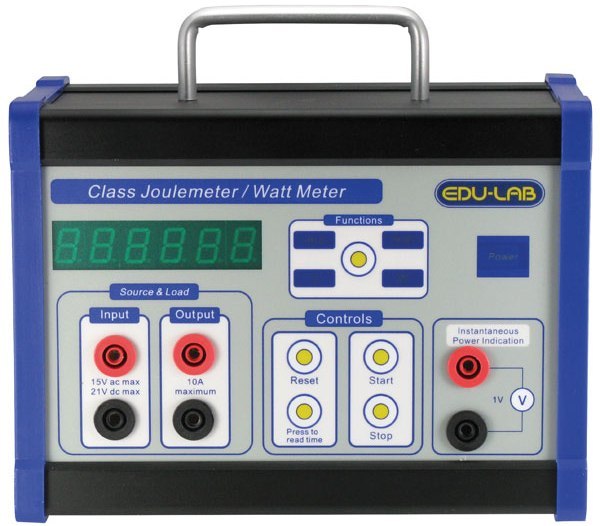

A professional wattmeter costs more than any stationary device of this class, simply because of the increased requirements for accuracy and quality of measurements. Professional wattmeters are often not critical to the shape of the current; they can measure alternating and constant, sinusoidal, rectangular, pulsating and sawtooth currents, while calculating the power consumption with an indication of the power factor and nature of the load (active, inductive, capacitive, mixed). Available for both single-phase and three-phase circuits.
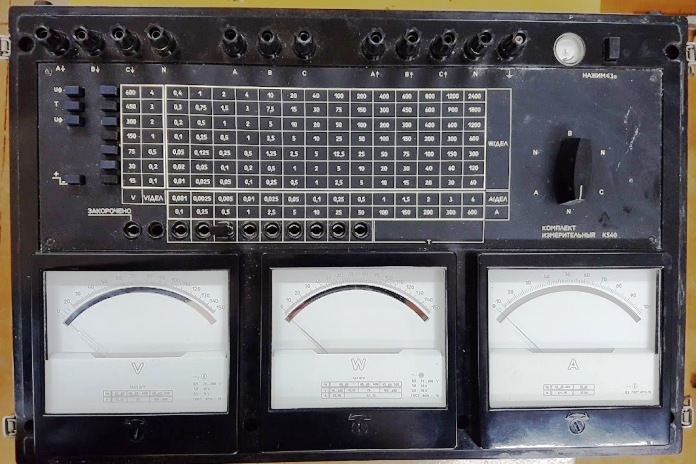
Analog wattmeter as part of a professional laboratory measuring kit K540:

Panel wattmeters
For making measurements and indicating active and reactive power in networks of three-phase or single-phase alternating current, switchboard built-in wattmeters are useful. The indicator displays the current power value in the form of numbers on its display, which can usually have up to four digits to ensure sufficiently high accuracy. The device has the form of a kind of measuring head mounted in a housing.
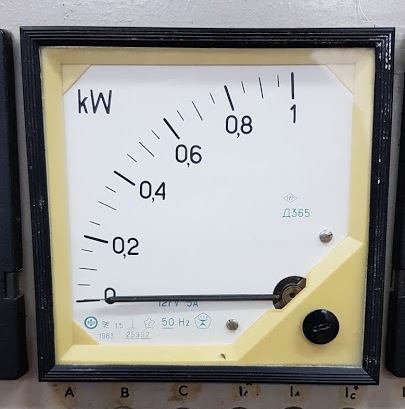

The usual use of wattmeters of this type is the indicator panels of various electrical devices operating in networks with a frequency of 50 Hz, that is, those where the wattmeter is installed permanently and can no longer be removed. It is possible to pair the wattmeter with electronic circuits that adjust the operation of the circuit in which it is installed depending on the dynamics of the active or reactive power consumption.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
