Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 4409
Comments on the article: 0
How to calculate the filament temperature of a filament lamp in nominal mode
As you know, with increasing temperature of the metal, its electrical resistance increases. For various metals, in connection with this phenomenon, its own temperature coefficient of resistance α is characteristic, which can be easily found in the reference book.
The reason for this phenomenon is that the thermal vibrations of the metal crystal lattice ions become more intense with increasing temperature, and the conduction electrons that form the current collide with them more often, spending more energy on these collisions. And since the current itself (according to the Joule-Lenz law) leads to heating of the conductor, then as soon as the current begins to flow through the conductor, the resistance of this conductor immediately begins to increase.
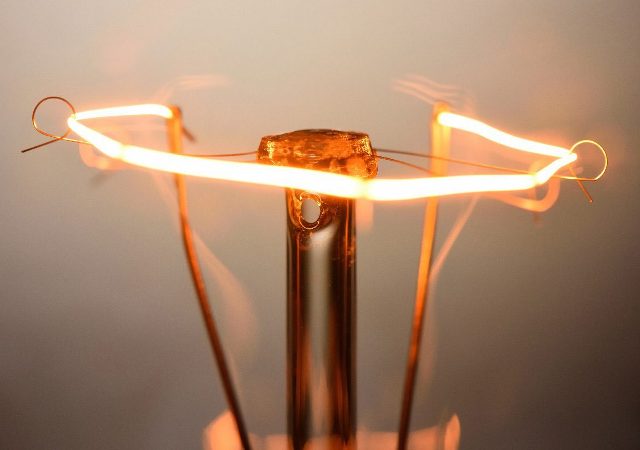
Similarly, the resistance of the filament of the lamp increases when it is connected to a power source. Let's find the temperature of the filament of the lamp in the nominal mode of its operation.

The temperature coefficient of resistance of tungsten (from which the filament of an incandescent lamp is made) is α = 0.0045 / K, and it is associated with a change in resistance (together with a change in temperature) by the following relation:
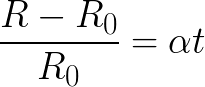
Here:
R0-resistance of the filament at 0 ° C;
R-resistance of the filament at the current temperature t.
The resistance R0 of the incandescent filament at 0 ° C is not known to us, it now needs to be determined indirectly. To do this, first with a multimeter we measure the resistance of the lamp at room temperature.
Next, take a look at the room thermometer, and thus find out the air temperature in the room.
If we assume that the cold filament of the lamp has exactly the same temperature as the air in the room, then the resistance of the lamp at 0 ° C is easily determined by the formula:
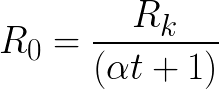
It is necessary to substitute here:
t-temperature in the room (by thermometer);
Rk-resistance of the lamp filament at the current temperature in the room (measurable with a multimeter).
So, now we know the resistance R0 of the filament of our lamp at 0 ° C. Now, knowing the nominal lamp power and its rated voltage, we determine purely mathematically its nominal resistance Rn according to the following well-known formula:
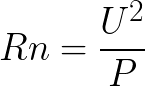
We substitute here the data indicated directly on the lamp:
U-rated voltage of the lamp;
P-rated lamp power.
Now we bring the very first formula to the following form, and substitute the nominal resistance Rn just found, and the resistance R0 at 0 ° С, which was found above, as well as the temperature coefficient of resistance α = 0.0045 / K for tungsten (taken from the reference book):
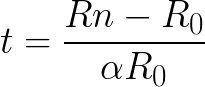
So we found the actual temperature of the filament of the lamp in working condition, not measuring it directly, but only knowing the rated power P, the rated voltage of the network U, the cold resistance Rk, the room temperature t and the temperature coefficient of tungsten resistance α.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
