Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 14602
Comments on the article: 0
How short circuit differs from overload
If the phase and zero of the electric network are connected to each other under voltage, not directly through the consumer, but directly, then a short circuit will occur, short for short circuit.
Short circuit is the connection of the conductors of the individual phases to each other or to the ground through a relatively low resistance, which is assumed to be zero with a dead metal short circuit.
No network is designed for continuous operation in this mode. However, this emergency mode sometimes occurs. So, a short circuit can occur due to a violation of the insulation of the wiring or due to an accidental short circuit of unlike conductors by the conductive parts of the electrical equipment. Normal operation of the electrical network will be disrupted. To prevent this undesirable phenomenon, electricians use terminal blocks or simply isolate the connections.
The problem of the short circuit mode is that at the time of its occurrence in the network, the current increases many times (up to 20 times the nominal), which leads to the release of a huge amount of Joule heat (up to 400 times higher than normal), since the amount of heat released is proportional to the square of the current and the resistance consumer.
Now imagine: the consumer resistance here is the ohm fraction of the wiring, and the current, as you know, the higher, the lower the resistance. As a result, if the protective device does not instantly work, excessive overheating of the wiring will occur, the wires will melt, the insulation will ignite, and a fire may occur in the room. In neighboring rooms, powered by the same network, the voltage will drop, and some electrical appliances may fail.
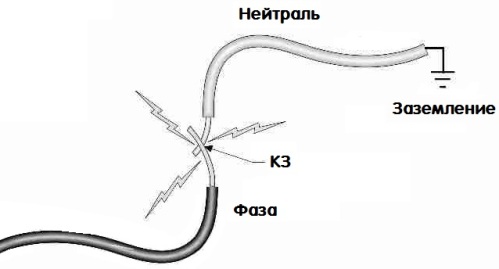
A typical type of short circuit for residential apartments is a single-phase short circuit when the phase closes to zero. For three-phase networks, for example in a workshop or in a garage, a three-phase or two-phase short circuit is possible (two phases to each other, three phases to each other, or several phases to zero).
Short circuit on video:
Three-phase equipment, such as an asynchronous motor or a three-phase transformer, is characterized by inter-turn short circuit, when the turns are short-circuited inside the stator winding or inside the transformer winding, bypassing the remaining working turns and thus causing the device to fail.
Or a short circuit may occur through the conductive housing of the device. Generally conductive enclosures should be groundedin order to protect personnel from accidental electric shock, and use wires in non-combustible insulation in apartments.
There is another type of emergency load mode of the electrical network associated with exceeding the normal current. This is the so-called overload. Overloads sometimes occur in apartments, in houses, in enterprises. This is a dangerous mode, sometimes more dangerous than a short circuit. After all, a short circuit in the apartment can be stopped in the bud instantly triggered circuit breaker in the shield. But current overload is a trickier case.

Imagine that in one single outlet you decided to push a lot of electrical appliances through a tee and through extension cords. What junk can happen in this case? If the core of the wiring connected to the outlet is not designed for a current of more than 16 amperes, then when a load of more than 3500 watts is included in such an outlet, overheating of the wiring fraught with fire will begin.
In general, the thermal effect on the insulation of wires sharply reduces its mechanical and dielectric properties. For example, if the conductivity of an electric cardboard (as an insulating material) at 20 ° C is taken as unity, then at temperatures of 30, 40 and 50 ° C it will increase 4, 13 and 37 times, respectively.
And thermal aging of insulation most often occurs precisely due to overload of electric networks by currents that exceed long-term allowable for a given type and cross-section of conductors. Also, it is impossible to include consumers with more than 2500 W into the outlet on which 250 V 10 A is indicated, because overheating of the contacts may begin, leading to their accelerated oxidation.
To protect against overload in the apartment, as well as for instant relief of short-circuit mode, use circuit breakers.
See also on our website: How to calculate the short circuit current
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
