Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 21604
Comments on the article: 1
Electrical cables, wires and cords - what is the difference
In fact, all these electrical products are designed to perform a common task: the transmission of electricity from a voltage source to a consumer. They must perform their functions for a long time and reliably without creating emergency situations and malfunctions.
Wires and cables work in all fields of human practice, when it is necessary to create a closed loop for the passage of electric current, to eliminate its loss through unforeseen leaks.
Due to the similarity of the issues being addressed, many ordinary people do not distinguish their differences, they belong to one category.
However, cables, wires and cords operate in different operating conditions, are used on different sections of electric current mains, and differ in purpose. Therefore, they have a different internal structure and design.
On electric transmission lines, there are cases when electricity is sequentially transmitted through overhead wires and cable, as shown in the photo below.

A cable branch on an overhead power line is created to perform specific tasks required by local conditions.
Electric wire
Composition
It has the simplest construction, consisting of two parts:
1. a metal core that serves to create an electric current path;
2. insulation layer, eliminating the drainage of currents in an undesirable direction.
The insulation functions can be assigned to the air surrounding the metal, and not to a special shell made of polymers and dielectrics. In this case, the core of the wire is exposed, and the contact points of the wires with the fastening elements to the supporting structures are created with dielectric properties. They are called insulators.
Materials for a conductive core are most often created on the basis of:
-
copper and its alloys;
-
aluminum.
A promising design is considered composite aluminum coppercreated for the effective use of the best performance characteristics of the above metals.
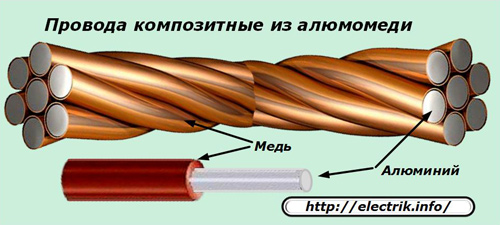
To solve specific problems, conductive conductors made of steel alloys, nichrome, other metals and even silver or gold can be used.
Core construction
It can be created from:
1. a solid conductor of a certain length;
2. or twist from thin wires working in parallel. Single wire wires are easier to manufacture. They are the most rigid, they are used for the transmission of electrical energy during stationary fixing, they transmit DC and low-frequency currents well.
Stranded cores are more flexible, work better at high frequencies.
Types of wires
Usually, the term wire refers to a single-wire product. In fact, they can be twisted or mounted with several wires. Examples include PUNP, PPV, APPV brands, dual telephone wires such as "noodles" and other designs.
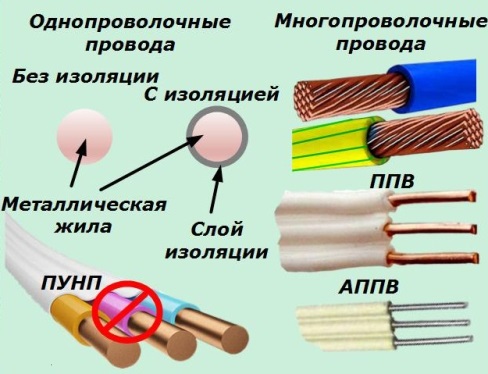
All of them are designed to work in light operating conditions and in most cases require additional mechanical protection from external influences.
Electrical cable
Its more complex design is created to ensure reliable operation under the influence of destructive environmental factors.

The number of conductors is determined by the operating conditions. They are isolated among themselves by various dielectric layers. Additional cable elements may include:
-
protective outer shell made of plastic, steel or wire armor;
-
aggregate;
-
core;
-
screen.
Each of these parts performs protective functions for specific conditions.

The main groups of cables for electricians are:
-
power, working in electrical installations up to and more than 1000 volts;
-
control, transmitting information about the state of various elements of the system;
-
controls used to transmit commands entered manually or by automatic systems;
-
communications based on the exchange of signals of different frequencies.

A special group includes cables for special purposes:
-
radiating, used to transmit high-frequency radio signals;
-
heating, turning electrical energy into heat.
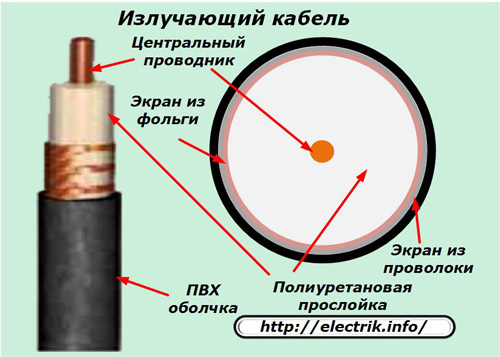
Conductors
They are made according to the same principles as for wires. They can be created from different materials with a multi-wire or solid conductor. Covered with a dielectric layer.
According to the degree of flexibility, cable designs are divided into seven groups. The category # 1 is classified as a rigid core. The most flexible and accordingly expensive is No. 7.
Stranded wires of flexible cables during installation are connected through special tubular lugs called terminators. There is no need to install them on a mono core.

Shell
Protects conductive cores and their insulation from mechanical damage, seals them from moisture, foreign impurities. May contain reinforcing and shielding layers.
Shell materials most often serve:
-
plastics
-
tissue;
-
reinforced grades of rubber;
-
metals.
Plastic materials can perform the following tasks:
1. provide an insulating layer with high dielectric properties;
2. create a sealed hose that protects the structure placed in it;
3. serve as a shield through the use of semiconductor properties.
Impregnated cable paper is used in high-voltage products up to and including 35 kV.
Cross-linked polyethylene is used to ensure the dielectric properties of cables operating in electrical installations with voltage up to 500 kV with high reliability and durability.
For high-voltage circuits of 110 ÷ 500 kV, inclusive, until 2005 oil-filled cables were manufactured, consisting of shielded cores mounted inside an airtight enclosure with oil. With the mass introduction of insulation based on cross-linked polyethylene, their design has lost its relevance.

Safe Working Conditions
All cable products are rated for:
1. short circuit behavior in the cable channel;
2. The ability to withstand prolonged overload;
3. the spread of open flame with high heat;
4. the release of toxins during combustion.
Hazard KZ
When the circuit between the veins creates a temperature of up to a thousand degrees. It is transmitted to nearby cables with small losses, heats them, is able to draw them into combustion. The resulting gases create high pressure, which depressures the cable channel, provides an influx of fresh air with oxygen, which supports the development of the fire.
Long overload
Excessive currents heat the metal of the conductive core and the insulation layer with a sheath. Under the action of the temperature limit, chemical reactions of decomposition of the insulation layer occur, gases are released. Mixing with air and ignition begin.
Combustion spread
The usual shell of PVC plastic compounds and individual grades of polyethylene is able to transfer the combustion process further, which contributes to the development of fires. Particular danger is created with vertical cables.
According to this indicator, cable products are divided into:
-
regular;
-
not spreading combustion in a single gasket: vertically and horizontally;
-
not spreading combustion in group laying: vertically and horizontally;
-
fire resistant.
The main indicator of this process is the specific heat of combustion of the electrical wiring or cable line, determined experimentally.
Ability to release toxic substances
It takes into account the reaction of the cable sheath to an external fire affecting its structure. Insulation compounds that do not even spread combustion can release dangerous toxins with significant heating.
Such cables are not allowed to be used in places with a mass concentration of people in the transport of subways and similar objects.
Cable Product Requirements
To increase operational reliability and safety, modern cables are evaluated by:
-
fire resistance;
-
resistance to heating of the dielectric and fire resistance;
-
ways of cutting ends - ending;
-
protection against moisture penetration.
Each of these parameters has analysis methods and evaluation criteria for the results.
Electric cord
Its design takes something in between an electric wire in insulation of several cores and a cable. It is created by special technological methods to impart increased flexibility properties, which ensures long-term operation when creating frequent, numerous bends.
Appointment of an electric cord: providing connections of a voltage source with mobile electrical appliances.
At home electric cord installed on table lamps and sconces, irons, kettles, and other similar consumers.

A household and professional power tool is also connected in the same way.

But, in the technical literature it is customary to call such a design a power cable, which more accurately reflects the principle of its operation.
Labeling Methods
Cables and wires must be distinguished when buying or selling and during operation. To this end, they are labeled:
-
at the factory;
-
during installation in an electrical installation.
Factory marking includes:
-
color marking of the insulating layer of conductive wires;
-
drawing inscriptions on shells with letters and numbers;
-
hanging tags or labels.
It allows you to:
-
determine the purpose and design features of cable products;
-
analyze the technical characteristics of a particular model;
-
evaluate the possibility of using it in the specific conditions of the electrical installation.
Operational marking supplements the factory information and is carried out by applying inscriptions and tags indicating circuit designations and laying routes of both the entire cable and a separate core between electrical elements. It can be supplemented by the inclusion of electronic markers that provide information about its characteristics. This allows you to reliably calculate it even in a filled cable channel among similar models.
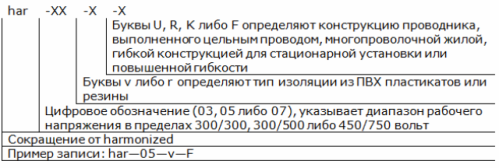
European power cable labeling
Color identification of insulation of conductors in Russia
The dielectric sheath of the wire can be painted:
-
solid color along the entire length;
-
drawing color tags.
GOST 28763 defines the rule to use markup only in the following colors: white, turquoise, yellow, green, brown, red, orange, pink, light blue, gray, purple and black.
Moreover, for yellow and green colors, only their combined combination on one shell is allowed. Using them separately is prohibited. This color is intended for protective conductor designations.
To highlight the neutral or middle conductor, a light blue color is used. Phase conductors are usually indicated in black, brown and gray.
Alphanumeric identification of conductor insulation in Russia
Exemplary labeling methods reflect the principles for determining the design of cables and wires. But, they do not contain a complete list of all information about them, which are published in detail in special directories.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
: