What can be done with an oscilloscope
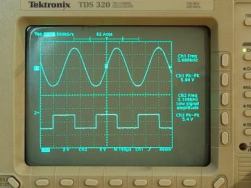 In the workshop of an electronic engineer and electrician, if not necessary, then at least the presence of an oscilloscope is highly desirable. It is used along with simple measuring instruments: an ammeter, voltmeter, ohmmeter, and finally a multimeter. In this article, you will learn about the oscilloscope - what it is and why it is needed.
In the workshop of an electronic engineer and electrician, if not necessary, then at least the presence of an oscilloscope is highly desirable. It is used along with simple measuring instruments: an ammeter, voltmeter, ohmmeter, and finally a multimeter. In this article, you will learn about the oscilloscope - what it is and why it is needed.
Everyone who works with electricity knows that voltage is measured with a voltmeter, and current with an ammeter. But these devices show only the current value that is at the time of measurement. Even when measuring variables by value and sign of values, you get some value averaged over certain algorithms or laws. But with the help of a voltmeter, you can monitor how the value is measured, however, with errors. For dial gauges, they are due to design features, and for digital ones as well, but the sampling frequency and other problems are also added ...
How does the conversion of the analog signal to digital
 In electronics, signals are divided into: analog, discrete and digital. To begin with, all that we feel, see, hear, for the most part, is an analog signal, and what a computer processor sees is a digital signal. It doesn’t sound very clear, so let's deal with these definitions and how one type of signal is converted to another.
In electronics, signals are divided into: analog, discrete and digital. To begin with, all that we feel, see, hear, for the most part, is an analog signal, and what a computer processor sees is a digital signal. It doesn’t sound very clear, so let's deal with these definitions and how one type of signal is converted to another.
In electrical representation, an analog signal, judging by its name, is an analog of a real value. For example, you feel the temperature of the environment constantly, throughout your life. There are no breaks. At the same time, you feel not only two levels of “hot” and “cold”, but an infinite number of sensations that describe this value.For a person, “cold” can be different, this is autumn coolness and winter frost, and light frosts, but not always “cold” is a negative temperature, like “heat” ...
The whole truth about dimming LED lights: dimmers, drivers, and theory
 Adjusting the brightness of light sources is used to create comfortable illumination of a room or workplace. Adjusting the brightness, it is possible to arrange several circuits that are switched on by individual switches. In this case, you will get a stepwise change in illumination, as well as separate luminous and off lamps, which can cause inconvenience. Stylish and relevant design solutions include a smooth adjustment of the overall illumination, provided all the lamps are lit. This allows you to create both an intimate setting for relaxation, and bright for celebrations or working with small details.
Adjusting the brightness of light sources is used to create comfortable illumination of a room or workplace. Adjusting the brightness, it is possible to arrange several circuits that are switched on by individual switches. In this case, you will get a stepwise change in illumination, as well as separate luminous and off lamps, which can cause inconvenience. Stylish and relevant design solutions include a smooth adjustment of the overall illumination, provided all the lamps are lit. This allows you to create both an intimate setting for relaxation, and bright for celebrations or working with small details.
Earlier, when the main light sources were incandescent lamps and spotlights with halogen lamps, there were no problems with adjustment. The usual 220V dimmer was used on the triac (or thyristors). Which was usually in the form of a switch, with a rotary knob instead of keys ...
How is a computer power supply and how to start it without a computer
 All modern computers use ATX power supplies. Previously, AT standard power supplies were used, they did not have the ability to remotely start a computer and some circuitry solutions. The introduction of the new standard was associated with the release of new motherboards. Computer technology is rapidly developing and developing, so there was a need to improve and expand motherboards. Since 2001, this standard was introduced. Let's look at how the ATX computer power supply works.
All modern computers use ATX power supplies. Previously, AT standard power supplies were used, they did not have the ability to remotely start a computer and some circuitry solutions. The introduction of the new standard was associated with the release of new motherboards. Computer technology is rapidly developing and developing, so there was a need to improve and expand motherboards. Since 2001, this standard was introduced. Let's look at how the ATX computer power supply works.
First, take a look at the picture, all the nodes of the power supply are signed on it, then we will briefly consider their purpose. At the input of the power supply there is an electromagnetic interference filter from the inductor and capacitance.In cheap power supplies it may not be. The filter is needed to suppress interference in the power network resulting from the operation of a switching power supply.All switching power supplies can degrade the power supply ...
Field effect transistors: principle of operation, circuits, operating modes and modeling
 We have already examined the device of bipolar transistors and their operation, now let's find out what field-effect transistors are. Field effect transistors are very common in both old circuitry and modern. Nowadays, devices with an insulated gate are used to a greater extent, we will talk about the types of field-effect transistors and their features today. In the article, I will make comparisons with bipolar transistors in separate places.
We have already examined the device of bipolar transistors and their operation, now let's find out what field-effect transistors are. Field effect transistors are very common in both old circuitry and modern. Nowadays, devices with an insulated gate are used to a greater extent, we will talk about the types of field-effect transistors and their features today. In the article, I will make comparisons with bipolar transistors in separate places.
A field effect transistor is a semiconductor fully controllable key controlled by an electric field. This is the main difference from the point of view of practice from bipolar transistors, which are controlled by current. An electric field is created by a voltage applied to the gate relative to the source. The polarity of the control voltage depends on the type of transistor channel. There is a good analogy with electronic vacuum tubes ...
Bipolar transistors: circuits, modes, modeling
 The transistor appeared in 1948 (1947), thanks to the work of three engineers and Shockley, Bradstein, Bardin. In those days, their rapid development and popularization were not yet anticipated. In the Soviet Union in 1949, the prototype of the transistor was presented to the scientific world by the Krasilov laboratory, it was a C1-C4 triode (germanium). The term transistor appeared later, in the 50s or 60s.
The transistor appeared in 1948 (1947), thanks to the work of three engineers and Shockley, Bradstein, Bardin. In those days, their rapid development and popularization were not yet anticipated. In the Soviet Union in 1949, the prototype of the transistor was presented to the scientific world by the Krasilov laboratory, it was a C1-C4 triode (germanium). The term transistor appeared later, in the 50s or 60s.
However, they found widespread use in the late 60s, early 70s, when portable radios came into fashion. By the way, they have long been called the "transistor". This name stuck due to the fact that they replaced electronic tubes with semiconductor elements, which caused a revolution in radio engineering. Transistors are made of semiconductor materials, for example, silicon, germanium was previously popular, but now it is rarely found, due to its high cost and worse parameters, in terms of temperature and other things ...
Single-phase rectifiers: typical circuits, waveforms and modeling
 A rectifier is used in an AC circuit to convert it to DC. The most common is a rectifier assembled from semiconductor diodes. At the same time, it can be assembled from discrete (separate) diodes, or it can be in one housing (diode assembly).
A rectifier is used in an AC circuit to convert it to DC. The most common is a rectifier assembled from semiconductor diodes. At the same time, it can be assembled from discrete (separate) diodes, or it can be in one housing (diode assembly).
Let's look at what a rectifier is, what they are, and at the end of the article we will conduct simulation in a Multisim environment. Modeling helps to consolidate the theory in practice, without assembly and real components, view the forms of voltages and currents in the circuit. For single-phase voltage, there are three common rectification schemes.The simplest circuit consists of only one diode, which gives a constant unstabilized ripple voltage at the output. Diodes are connected to the power circuit by a phase wire, or by one of the terminals of the transformer winding, the second end to the load, the second pole of the load ...
Quick assembly of circuits on solderless breadboards
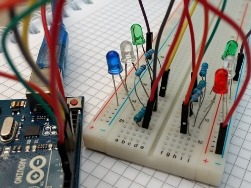 Let's look at the design and purpose of solderless breadboards. What is their advantage over other types of assembly, and how to work with them, as well as what schemes you can quickly assemble for a beginner.
Let's look at the design and purpose of solderless breadboards. What is their advantage over other types of assembly, and how to work with them, as well as what schemes you can quickly assemble for a beginner.
The first problem that a radio amateur faces is not even the lack of theoretical knowledge, but the lack of tools and knowledge about how to install electronic devices. If you do not know how this or that part works, this will not prevent you from connecting it according to the circuit diagram, but in order to clearly and efficiently assemble the circuit, you need a printed circuit board.Most often they are made according to the LUT method, but not everyone has a laser printer. Our fathers and grandfathers painted boards manually with nail polish or paint, and then they were etched. Here the novice is overtaken by a second problem - the lack of etching reagents ...
