 When replacing halogen lamps with 12V in LED downlights, the question often arises: "Do I need to change the power source?". For halogens, we used electronic transformers with an output voltage of 12 volts, and for LED lamps special power supplies (PSUs) with an output voltage of 12 volts are also sold. What is their difference and are they interchangeable? Let's figure it out!
When replacing halogen lamps with 12V in LED downlights, the question often arises: "Do I need to change the power source?". For halogens, we used electronic transformers with an output voltage of 12 volts, and for LED lamps special power supplies (PSUs) with an output voltage of 12 volts are also sold. What is their difference and are they interchangeable? Let's figure it out!
An electronic transformer is called a switching power supply circuit based on a transformer and a high-frequency generator based on semiconductor switches. They are powered by AC 220V, and at their output an alternating voltage with an effective value of about 12V. The 220V power is first supplied to the rectifier, after which the rectified pulsating voltage with a frequency of 100 Hz is supplied to the power switch and generator assembly, consider an example of a typical circuit diagram of an electronic transformer ...
Resistor power: designation on the diagram, how to increase what to do if there is no suitable
 In circuits of electronic equipment, one of the most common elements is a resistor, its other name is resistance. It has a number of characteristics, among which there is power. In this article we will talk about resistors, what to do if you do not have an element that is suitable for power, and why they burn out.
In circuits of electronic equipment, one of the most common elements is a resistor, its other name is resistance. It has a number of characteristics, among which there is power. In this article we will talk about resistors, what to do if you do not have an element that is suitable for power, and why they burn out.
The main parameter of the resistor is the nominal resistance. The second parameter by which it is selected is the maximum (or maximum) power dissipation. Temperature coefficient of resistance - describes how much resistance changes when its temperature changes by 1 degree Celsius. Permissible deviation from the face value. Typically, the scatter of resistor parameters from one declared in the range of 5-10%, it depends on GOST or the technical specifications for which it is produced, there are exact resistors with a deviation of up to 1%, usually cost more ...
How to check a field effect transistor
 To check the health of the field-effect transistor, you can use any digital multimeter with the diode “ringing” function. This function works in such a way that allows you to measure the direct voltage drop at the p-n junction, which will be displayed on the display of the multimeter during testing.
To check the health of the field-effect transistor, you can use any digital multimeter with the diode “ringing” function. This function works in such a way that allows you to measure the direct voltage drop at the p-n junction, which will be displayed on the display of the multimeter during testing.
In the process of this test, the multimeter is able to pass current through the circuit under test within a few milliamps, and if the voltage drop turns out to be too small, then if the device has a sound alert function, it will clear. And since p-n junctions are present in any field-effect transistor, we can expect a completely adequate result. Before checking the field effect transistor for continuity, short-circuit with a foil all its terminals for a second to remove static charge, to discharge all its transient capacitances ...
Electronic Circuit Troubleshooting Methods
 Most often, people are interested in electronics in order to be able to repair a device. Only a small part of lovers are engaged in self-development. Although theoretical knowledge provides a general understanding of how the components work, it’s much more important to know how to test them for repairs. We will tell you how to find a malfunction in an electronic circuit with your own hands, eyes and a simple tool.
Most often, people are interested in electronics in order to be able to repair a device. Only a small part of lovers are engaged in self-development. Although theoretical knowledge provides a general understanding of how the components work, it’s much more important to know how to test them for repairs. We will tell you how to find a malfunction in an electronic circuit with your own hands, eyes and a simple tool.
Before carrying out repairs it is important to determine what the problem is - this process is called diagnostics. So, we can distinguish two stages of testing electronic devices. It does not always happen that the device is completely “dead”, you need to check if the device does not turn on at all, or turns on and off immediately, or some specific buttons or functions do not work.For example, when repairing LCD monitors, there is such a problem as a backlight failure. At the same time, the monitor may or may not turn on completely then its indicator blinks ...
Inductor to protect against common mode noise generated by a switching power supply
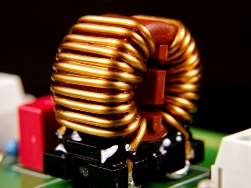 Common-mode choke is the most important component of the input filter of any switching power supply. The fact is that during the operation of a pulse converter of any topology, when switching field-effect transistors, common-mode interference occurs, which propagate in the conductors and along the tracks of the printed circuit boards.
Common-mode choke is the most important component of the input filter of any switching power supply. The fact is that during the operation of a pulse converter of any topology, when switching field-effect transistors, common-mode interference occurs, which propagate in the conductors and along the tracks of the printed circuit boards.
These interferences are harmful high-frequency impulse currents that flow simultaneously along the plus and minus wires, and in the same direction. If these interference eventually gets into the AC power network, then they can not only lower the quality of functioning of the devices connected to the network in the neighborhood, but even disable them, especially the signal circuits of digital units. For this reason, today all household appliances, which in principle can become sources of common-mode interference, are equipped with common-mode chokes ...
Chip 4046 (K564GG1) for devices with resonance retention - the principle of operation
 When creating a power electronic device with resonance retention in the LC circuit, a resonant controller circuit is designed to synchronize the received oscillations with control pulses coming from the driver. The task of this controller is to keep resonant oscillations in the LC circuit by exciting it in time with its own oscillations.
When creating a power electronic device with resonance retention in the LC circuit, a resonant controller circuit is designed to synchronize the received oscillations with control pulses coming from the driver. The task of this controller is to keep resonant oscillations in the LC circuit by exciting it in time with its own oscillations.
The controller needs to receive a signal from the loop from the loop containing data on the current frequency and phase of free oscillations in it, after which, relying on these data, support the driver stage in synchronization with these frequencies and phases, then the resonance in the loop will automatically save. To build such a controller, the CD4046 chip or its domestic counterpart K564GG1 is suitable. Let's look at the device of this microcircuit, the purpose of its conclusions and the connection diagram of the mounted componentsto understand what you are dealing with if necessary ...
Simple RC circuit for rectangular pulse delay
 During the development of a pulse converter controller, for example, to construct a circuit with resonance retention, it may be necessary to delay the edges of the pulses and the decay of the pulse sequence when a rectangular signal is applied from one block of the circuit to another.
During the development of a pulse converter controller, for example, to construct a circuit with resonance retention, it may be necessary to delay the edges of the pulses and the decay of the pulse sequence when a rectangular signal is applied from one block of the circuit to another.
Sometimes a simple circuit consisting of two logical inverters and an RC circuit is suitable for solving this problem. For this purpose, it is convenient to use a microcircuit, which is a set of inverters with sufficiently defined thresholds. An example of such a microcircuit is 74N0404, there are 6 “NOT” logic elements in it, and it turns out that on one such microcircuit it is theoretically possible to construct 3 delay circuits according to the scheme below. In practice, when the decay of the square-wave pulse arrives at the input of the first inverter, the leading edge arrives at the RC circuit from its output, and charging of the capacitor begins ...
Bootstrap capacitor in a half-bridge control circuit
 Integrated circuits - half-bridge drivers, such as, for example, IR2153 or IR2110, involve the inclusion in the general circuit of a so-called bootstrap (detached) capacitor for independent power supply to the upper key control circuit. While the bottom key is open and conducting current, the bootstrap capacitor is connected through this open bottom key to the negative power bus, and at this time it can receive charge through the bootstrap diode directly from the driver's power source.
Integrated circuits - half-bridge drivers, such as, for example, IR2153 or IR2110, involve the inclusion in the general circuit of a so-called bootstrap (detached) capacitor for independent power supply to the upper key control circuit. While the bottom key is open and conducting current, the bootstrap capacitor is connected through this open bottom key to the negative power bus, and at this time it can receive charge through the bootstrap diode directly from the driver's power source.
When the lower key is closed, the bootstrap diode stops supplying charge to the bootstrap capacitor, because the capacitor is disconnected from the negative bus at the same moment, and now can function as a floating power source for the gate control circuit of the upper half-bridge key. Such a solution is quite justified, because the power often required for key management is relatively small, and the energy spent can simply be periodically replenished ...
