Categories: Featured Articles » Practical Electronics
Number of views: 4341
Comments on the article: 0
Types of modern integrated circuits - types of logic, cases
All modern microcircuits are divided into three types: digital, analog and analog-digital, depending on what type of signals they work with. Today we’ll talk about digital microcircuits, since most microcircuits in electronics are digital, they work with digital signals.
A digital signal has two stable levels - a logical zero and a logical unit. For microcircuits made according to different technologies, the levels of logical zero and unity differ.
Inside the digital microcircuit, there can be various elements whose names are known to any electronic engineer: RAM, ROM, comparator, adder, multiplexer, decoder, encoder, counter, trigger, various logic elements, etc.
To date, digital circuits of TTL (transistor-transistor logic) and CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) technologies are most common.
In TTL technology chips, the zero level is 0.4V, and the unit level is 2.4V. For CMOS technology chips, the zero level is almost zero, and the unit level is almost equal to the supply voltage of the chip. The zero voltage of the CMOS chip is obtained by connecting the corresponding output to the common wire, and the high level voltage is connected to the power bus.
The name of the microcircuit indicates its series, which reflects the type of technology by which this microcircuit is made. Different microcircuits have different speeds, varying in the limiting frequency, in the permissible output current, power consumption, etc. The table below shows some types of microcircuits and their characteristics.
Characteristics of popular chip types
When designing a circuit of an electronic device, they try to use primarily chips of the same type of logic in order to avoid inconsistencies in the levels of digital signals (upper and lower levels).
The choice of specific chip logic is based on the required operating frequency, power consumption and other characteristics of the chip, as well as its cost. However, sometimes it is not possible to get by with one type of microcircuit, because one part of the designed circuit may require, for example, a higher speed, characteristic of ESL technology microcircuits, and the other, low power consumption, typical of CMOS chips.
In such cases, developers sometimes have to resort to using additional level converters, although it is often possible to do without them: the output signal from the CMOS chip can be fed to the TTL input, but it is not recommended to supply the signal from the TTL chip to the CMOS chip. Next, let's look at the most popular cases of modern microcircuits.
Dip
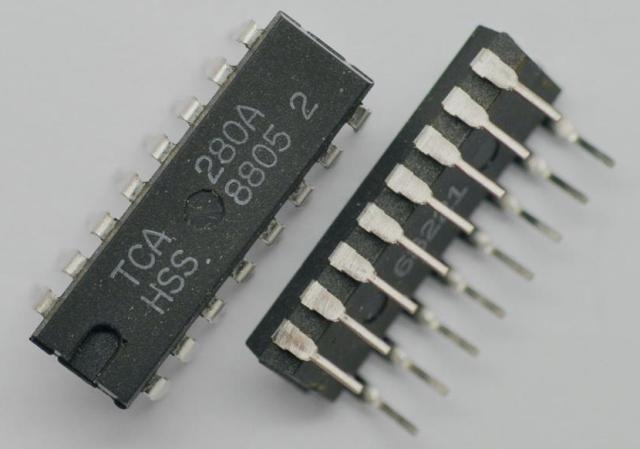
A classic rectangular case with two rows of leads often found on old boards. PDIP - plastic case, CDIP - ceramic case. Ceramics has a coefficient of thermal expansion close to a semiconductor crystal, therefore the CDIP - case is more reliable and durable, especially if the microcircuit is used in severe climatic conditions.
The number of outputs is indicated in the chip designation: DIP8, DIP14, DIP16, etc. The TTL-logic 7400 series chips have a traditional DIP14 package. This case is well suited for both automated and manual assembly during output installation (into holes on the board).
Components in DIP packages are usually available with a number of pins from 8 to 64. The pitch between the pins is 2.54 mm, and the row spacing is 7.62, 10.16, 15.24 or 22.86 mm.
The pin numbering starts from the top left and goes counterclockwise. The first conclusion is located near the key - a special recess or a circular recess on one of the edges of the microcircuit housing.If you look at the marking from above, with the housing of the microcircuit facing down, the first output will always be from the top left, then the count goes on the left side down, then on the right side from the bottom up.
SOIC

Rectangular housing of microcircuits for surface (planar) mounting. Two rows of pins are located on both sides of the chip. Almost SOIC cases occupy almost a third, and sometimes half as much space as DIP cases on boards, and the SOIC case is three times thinner than DIPs.
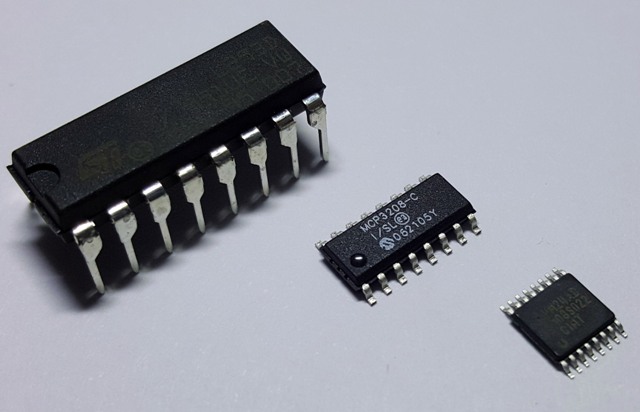
The numbering of conclusions, if you look at the chip from above, begins to the top left of the key in the form of a round recess, then goes counterclockwise. The cases are designated SO8, SO14, etc., in accordance with the number of pins: 8, 14, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, and 54. The distance between the pins is 1.27 mm. Almost all modern DIP microcircuits today have analogues for planar mounting in SOIC packages.
PLCC (CLCC)

PLCC - plastic and СLCC - ceramic planar cases of square shape with contacts along the edges on four sides. This case is designed for soldering by surface (planar) mounting on a board or for installation in a special panel (often called a "crib").
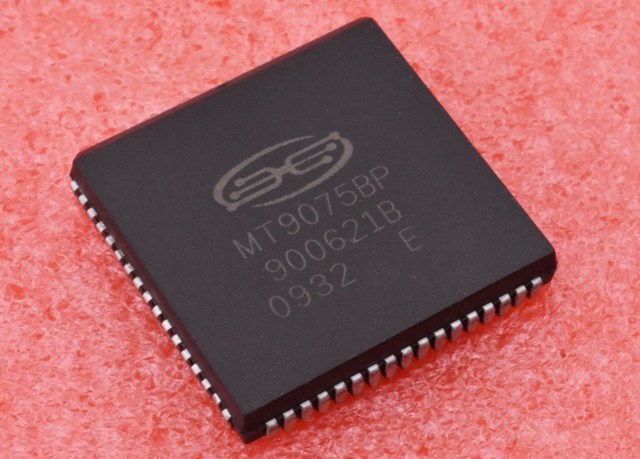

Currently, flash memory chips in the PLCC package, which are used as BIOS chips on motherboards, are widely used. If necessary, a radiator can easily be installed on a microcircuit, just like on a SOIC. The pitch between the legs is 1.27 mm. The number of conclusions from 20 to 84.
TQFP
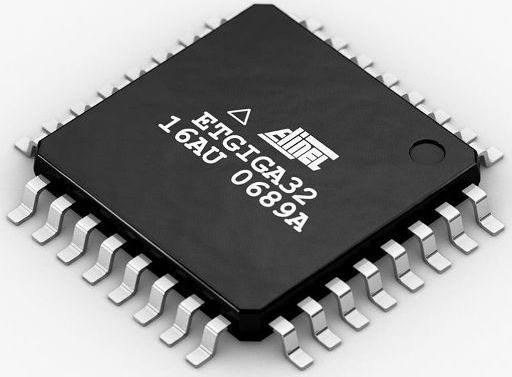
TQFP is a thin square surface-mount microcircuit case similar to PLCC. It has a smaller thickness (only 1 mm) and has a standard pin size (2 mm).
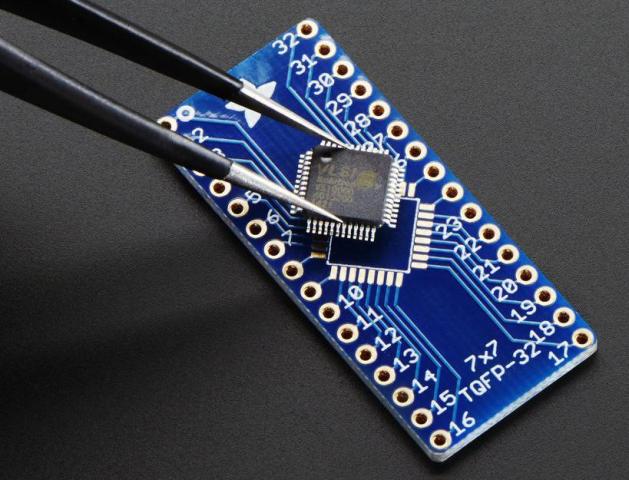
The possible number of conclusions is from 32 to 176 with a size of one side of the case from 5 to 20 millimeters. Copper leads are used in increments of 0.4, 0.5, 0.65, 0.8 and 1 millimeter. TQFP allows you to solve problems such as increasing the density of components on printed circuit boards, reducing the size of the substrate, reducing the thickness of the enclosures of devices.
See also: How do integrated circuits
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
