Categories: Featured Articles » Practical Electronics
Number of views: 45187
Comments on the article: 0
What is the difference between the power supply for LED lamps and the electronic transformer for halogen lamps
When replacing halogen lamps with 12V in LED spotlights, the question often arises: "Do I need to change the power source?". For halogens, electronic transformers with an output voltage of 12 volts were used, and for led bulbs special power supplies (PSUs) with an output voltage of 12 volts are also sold. What is their difference and are they interchangeable? Let's figure it out!

What is an electronic transformer?
An electronic transformer is called a switching power supply circuit based on a transformer and a high-frequency generator based on semiconductor switches. They are powered by AC 220V, and at their output an alternating voltage with an effective value of about 12V.
The block diagram of the device is shown in the figure below.
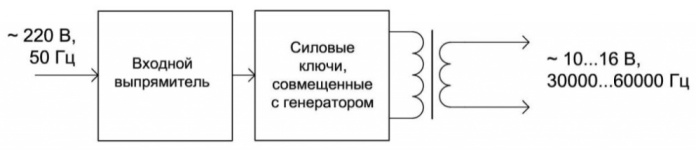
Here we see that the 220V power is first supplied to the rectifier, after which the rectified pulsating voltage with a frequency of 100 Hz is supplied to the power switch and generator assembly, consider an example of a typical circuit diagram of an electronic transformer.
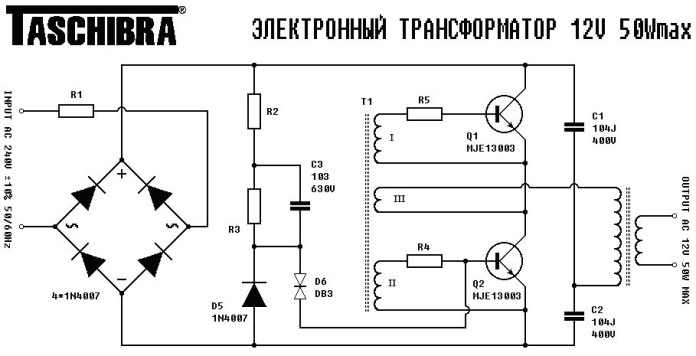
A typical push-pull circuit is shown here. Its feature is that for the keys to work in switching mode (switching) at a high frequency, they do not need PWM controllers or other specialized PM. In simple words, the operation of the oscillator is to switch the transistor as a result of the voltages induced on the windings of the pulse transformer and positive feedback.
What do we see in the diagram? The first thing that catches your eye is the lack of a diode bridge at the output, which means that the output voltage is variable, as well as the absence of circuits designed to stabilize the output voltage. You can learn more about the principle of their work by watching the video:
A similar scheme is at the heart of most chargers for mobile phones, Electronic ballasts for powering fluorescent lamps, including in energy-saving or compact fluorescent lamps in some variations and some modifications.
Consider the output waveforms.
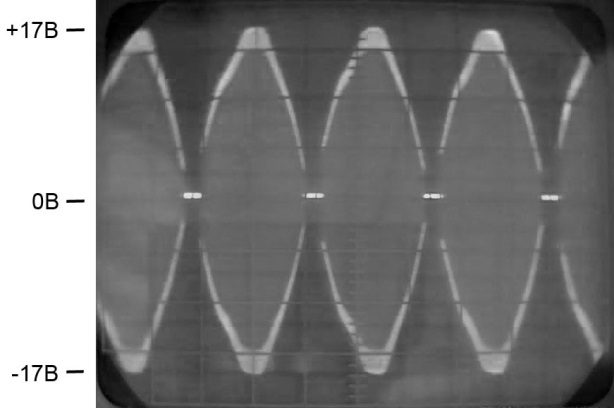
It can be seen that the alternating voltage whose amplitude fluctuates from zero to + and - 17V. Such changes in amplitude over time - repeat the ripple of the rectified network (100Hz). It turns out an interesting situation - there is a high-frequency output voltage that varies with a frequency of tens of thousands of hertz, while its amplitude varies from 0 to 17 volts with a frequency of 100 Hz or rectified 50 Hz. If you stretch the time axis and consider the form at the level of periods, then the picture will take the following form.
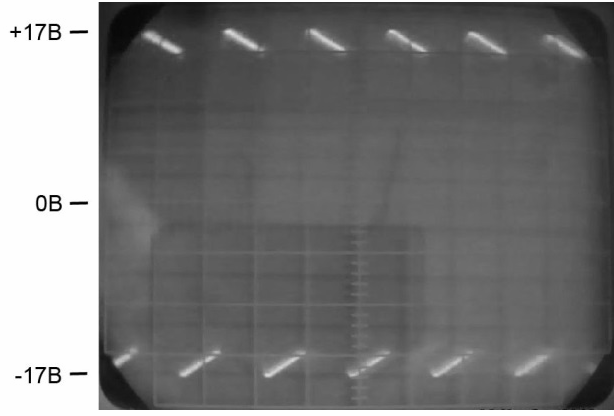
Here you can see that the signal in shape is far from the sine wave, but rather a rectangle with a slight slope towards the trailing edge.
Power Supplies for 12V LED Lamps
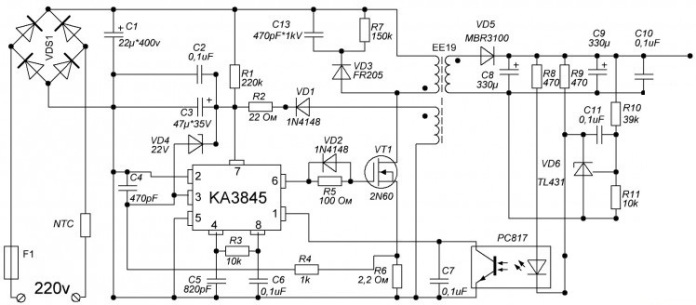
They are often called power supplies for LED strips, in fact, to connect both strips and lamps you need any source of constant stabilized voltage of 12V with minimal ripple. In practice, in the modern world switching power supplies, consider a typical scheme.
Or another option:
What do these two seemingly different schemes have in common? They are built on an integrated PWM controller that controls power switches - transistors, they can be both field and bipolar. In addition, in the output stage of the circuit you see a rectifier and capacitors for smoothing ripples (filter). All this means that at the output we get stabilized DC power supply. The magnitude of its ripple will depend on the load and capacity of the filtering capacitors.
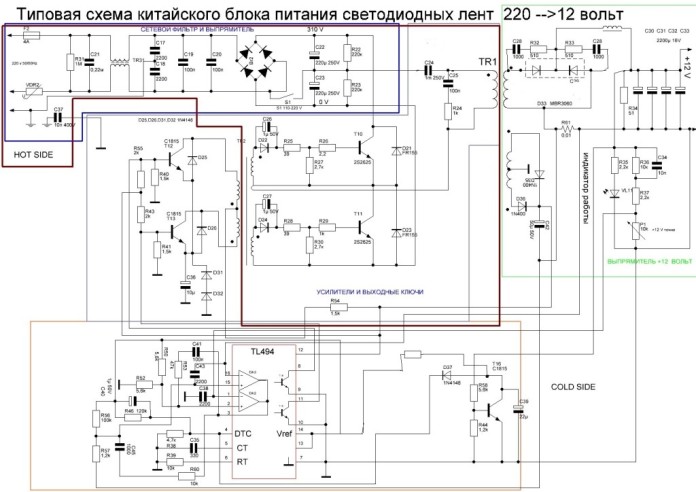
It can also be implemented on a self-generated circuit, similar to an electronic transformer, by adding feedback circuits to stabilize the output voltage. The result is a circuit like this.
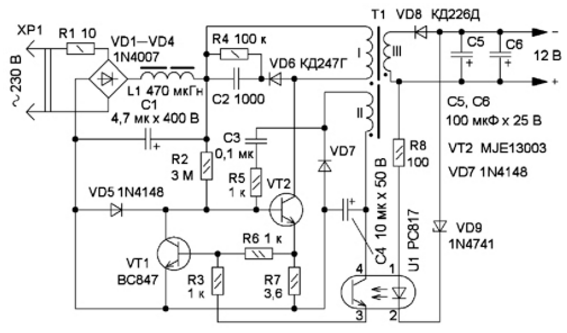
A similar design is used in the above-mentioned chargers for mobile phones; here, the feedback chain on the 11-volt Zener diode VD9 and the transistor optocoupler U1 is responsible for stabilization.
The principle of operation of such IIPs we considered in the article earlier - Circuit Design of LED Strip Power Supplies.
5 features and differences of PSU for LED strips and lamps from electronic transformers for halogen lamps
So, to summarize and answer the question: “why can’t you power LED lamps from an electronic transformer?”. To do this, we list the main features of these power supplies and the requirements for the operation of LED products.
1. To turn on LED strips and 12V lamps, you need constant voltage. Since the LEDs have a non-linear current-voltage characteristic - they are very sensitive to deviations of the supply voltage from the nominal, and if it is exceeded, they will quickly fail.
2. Electronic transformers give out a pulsating alternating high-frequency voltage. The magnitude of surges and peaks can reach 40 volts in some cases. This can lead to failure of the LEDs or drivers built into the LED lamp, as well as to their unstable operation.
3. Electronic transformers have such a characteristic as minimum load (see figure below). This means that if you connect a load less than that indicated on the power supply, it may either not start, or give large ripples, as well as disconnect or otherwise deviate from normal operation. This is critical, since halogen lamps consume much more power than LED lamps, so an electronic transformer can manifest itself in a similar way.
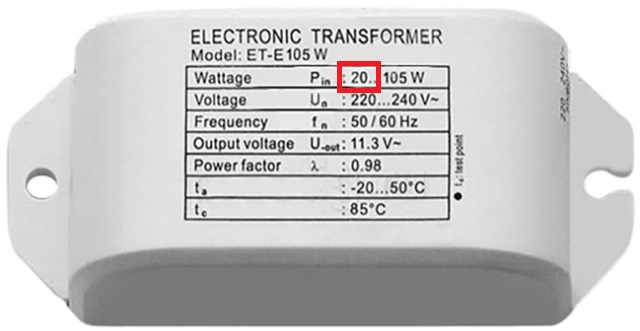
Power is indicated from 20 to 105 W, which indicates a limitation on the minimum connected power.
4. For power supplies for 12V lamps, the output voltage is both constant and stabilized.
5. For the supply of halogen lamps, there is no difference in the type of current (constant or alternating) with which it will be fed. The effective value of the voltage on it is important. Therefore, they are suitable for both options for power sources.
Conclusion
Do not use an electronic transformer to power LED products. Choose a power supply with a constant stabilized output voltage. Otherwise, your fixtures and lamps may fail. Also, be careful - luminaires designed to power a constant current source - a driver are now popular, this is a separate type of device! Read about it here -What is the difference between the power supply and the driver for LEDs
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
: