Categories: Featured Articles » Practical Electronics
Number of views: 9235
Comments on the article: 0
How to check triac
A triac is a type of thyristor. He, like the Trinistor, has three conclusions, but the triac pn junctions are not three, but five. Two stable states, “open” and “closed,” are also characteristic of a triac: moreover, the conductivity of the triac can be controlled in two directions, despite the fact that it has only one control electrode.
Due to its versatility, triac most often plays the role of a key in AC circuits for controlling various kinds of devices (for example, the engine of a grinder or a washing machine).
Take a look at the drawing. There are five transitions, which in their location are similar to two on-parallel connected trinistors. If you add plus to the electrode MT2, and minus to MT1, then the bottom-up sequence of n-p-n-p transitions is activated (ready for operation), and when the polarity changes, the sequence of top-down transitions n-p-n-p comes to our disposal. And still only one control electrode is enough.
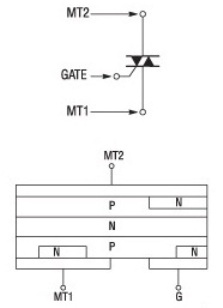
So, to control the conductivity state of the triac installed in some device, a control pulse is supplied to the control electrode G of the triac, the polarity of which is indicated relative to the MT1 output, and it depends on the current polarity of the switched voltage acting in the circuit, i.e., on the voltage applied to the conclusions of MT1 and MT2 of this triac.
If the terminal MT2 is under positive voltage relative to the terminal MT1, then the triac transition to the conducting state is possible with any polarity of the control voltage pulse applied to terminal G relative to the terminal MT1. If there is a minus on the MT2 terminal, and a plus on the MT1 terminal, then the negative polarity of the voltage applied to the G terminal will lead to the opening of the triac.
In order to “close” a triac, which is in a conducting state, it is necessary to de-energize the circuit switched by the triac (make its current lower than the holding current characteristic of this triac).
From what has been said above, it obviously follows that for testing a triac you can use a simple universal circuit designed for testing, which contains two decoupled power sources (for example, two transformer windings with rectifiers and filter capacitors).
Everyone can assemble such a scheme for himself. Two switches (SA1 and SA2) serve to change the polarity in the switched circuit and in the power supply circuit of the control electrode. The switches (buttons without locking) SB1 and SB2 are designed to open and to turn off the triac, respectively. The light bulb here serves as an indicator of the operability of the triac, since it is installed in a circuit switched by the triac.
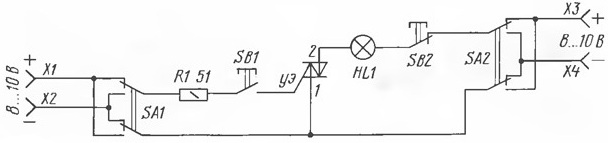
The circuit works like this. When the switches SA1 and SA2 are in the position shown in the figure, it is enough to press the SB1 button so that the functioning triac opens and the lamp immediately lights up. Then press SB2 - the lamp goes out, as the triac is locked. After that, the polarity of the control pulse is changed by the switch SA1.
Pressing SB1 will light up the lamp. The next step is to change the polarity in the switched circuit, for which click on SA2. Now the lamp should flash only when a negative voltage is applied to the control electrode, relative to the negative electrode of the triac.
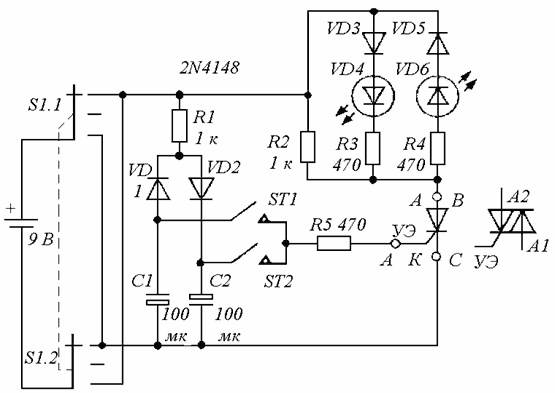
There is a simpler circuit with a “crown” battery and with LEDs. This scheme allows you to check not only triacs, but also trinistors. Switch S1 allows you to change the polarity of the power, and the buttons ST1 and ST2 give the user pulses of different polarity.
A working trinistor will conduct in only one direction, so only the VD4 LED will be an indicator.But the triac can open in the direction in which the power polarity is applied, and depending on pressing the ST1 or ST2 button. Pressing ST2 should not lead to the opening of the triac, if there is a plus on its lower output.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
