Categories: Featured Articles » Practical Electronics
Number of views: 40679
Comments on the article: 1
Triac Control: Powerful AC Load Control
For the purpose of switching loads in AC circuits it is convenient to use triacs, which are a type of thyristor, but differing from the thyristor in the ability to open conduct current in both directions.

The first designs of triacs were already considered in 1963, then, for example, the Mordovian Research Electrotechnical Institute already filed a patent for a symmetric thyristor (Patent SU 349356 A, Dumanevich AN and Evseev Yu.A.), and General Electric was engaged in commercial implementation of the same product called "Triac" in the West.
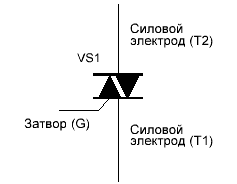
Then like a thyristor There are clearly defined cathodes, anodes, and a control electrode. At the triac, the cathode and anodes change places during its operation, depending on the current direction at the current moment.
Of course, the signal to the control electrode (gate) of the triac is always supplied relative to a specific conditional cathode, but the current through the open triac can flow in any direction, and in this sense the triac in the open state can be considered as two diodeincluded in counter-parallel.
The triac is distinguished by a five-layer semiconductor structure. Equivalently more accurately, it can be represented in the form of two triode thyristors connected in opposite parallel, and the control electrode, in contrast to the thyristor, is only one.
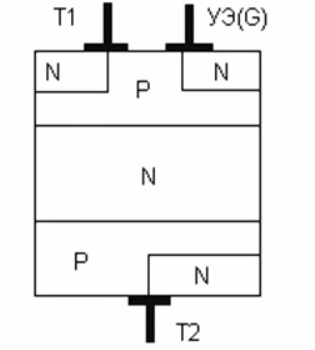
To control a powerful load, the triac, like a switch, is connected in series to the load circuit. And then: in the closed state, the triac will be closed, the load will be de-energized, and when a trigger voltage is applied to the triac's control electrode, conductivity will appear between the triac's main electrodes - current will flow through the load. Moreover, current can flow through an open triac in any direction, not like a thyristor.
To keep the triac open, there is no need to hold the control signal on the control electrode, just give a signal, after which the current will be established and will continue to flow - this is the difference between the triac and the transistor. When the current through the triac (through the load circuit) drops below the holding current (for alternating current - at the moment the current passes through zero), the triac closes, and to unlock it, it will be necessary to re-apply the unlocking signal to the control electrode.
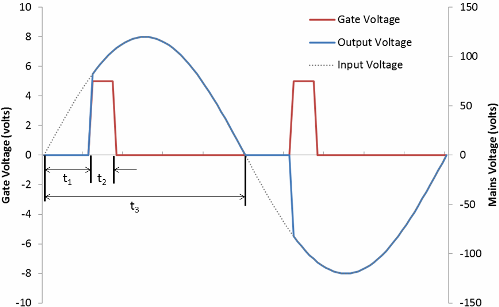
The polarity of the control voltage supplied to the control electrode of the triac can either be negative or coincide with the polarity of the voltage applied to the conditional anode. For this reason, such control is popular when the control signal is supplied directly from the conditional anode through the limiting circuit and the circuit breaker - just enough current is set to unlock the triac.
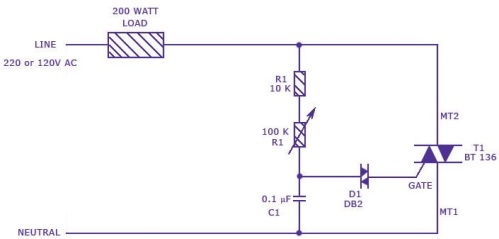
Due to the deep positive feedback, for example, with an inductive load, high rates of change in the voltage or current of the triac can lead to untimely unlocking of the triac, and to a large instantaneous power, which will be quickly dissipated on the crystal, and will be able to destroy it. To protect against harmful emissions, a varistor is installed in parallel with the triac in some circuits, and RC snubbers are used to protect against high dU / dt values.
Using a triac instead of a relay:
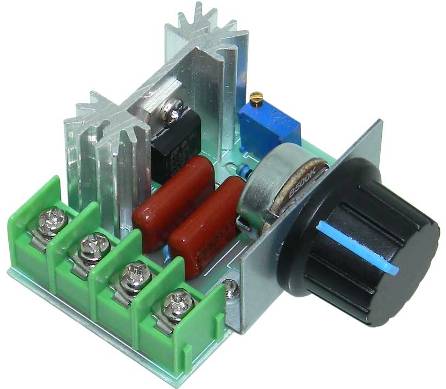
Triac power regulators for controlling various powerful loads in AC circuits are very popular today. These regulators for lamps are called dimmers, and regulators for different instruments, for collector motors - simply triac regulators. Their circuits are quite compact and simple, because it is enough to periodically apply 0.7 volts to the control electrode of the triac at a current of the order of 10 mA, which is easily implemented using an RC circuit, and in a more complex form - based on a PWM controller, on the same 555 timer.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
