Categories: Featured Articles » Interesting electrical news
Number of views: 15067
Comments on the article: 1
Lithium ion batteries
 The principle of operation of any electric battery is the accumulation of electrical energy during a chemical reaction that occurs when a charging electric current flows through a battery, and the generation of electric energy when a discharge current flows during a reverse chemical reaction.
The principle of operation of any electric battery is the accumulation of electrical energy during a chemical reaction that occurs when a charging electric current flows through a battery, and the generation of electric energy when a discharge current flows during a reverse chemical reaction.
The reversibility of the chemical reaction in the battery allows you to repeatedly discharge and charge the battery. This is the advantage of batteries over disposable current sources, ordinary batteries, in which only discharge current is possible.
As the medium for charge transfer from one battery electrode to another, an electrolyte is used - a special solution, due to the chemical reaction of which with the material on the electrodes, both direct and reverse chemical reactions in the battery are possible, which makes it possible to charge the battery and his rank.
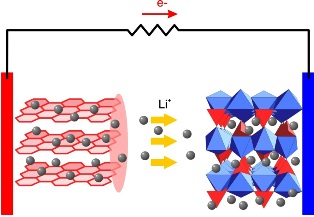
Today, one of the most promising types of batteries is lithium ion battery. In these batteries, aluminum acts as the negative electrode (cathode), and copper as the positive electrode (anode). The electrodes can have a different shape, as a rule, it is a foil in the form of a cylinder or an oblong package.
Apply on aluminum foil cathode material, which most often can be one of three: lithium cobaltate LiCoO2, lithium ferrophosphate LiFePO4, or lithium manganese spinel LiMn2O4, and graphite is applied to a copper foil. Lithium ferrophosphate LiFePO4 is the only, currently safe cathode material in terms of explosion hazard and environmental friendliness in general.

Polymer electrolytes that can incorporate lithium salts into their composition, due to their plasticity, make it possible to produce lithium-ion batteries with a large internal surface and almost any shape, and this significantly increases both the manufacturability of the production and the overall dimensions.
In the process of charging such a battery, lithium ions move through the electrolyte, and are embedded in the crystal lattice of graphite on the anode, forming lithium graphite compound LiC6. During the discharge, the reverse process occurs - lithium ions move to the cathode (oxidizer) from the anode, and electrons move to the cathode in the external circuit, as a result, the process acquires electrical neutrality.
The nominal voltage of a lithium-ion battery is 3.6 volts, however, the potential difference during charging can reach 4.23 volts. In connection with this fact, the charge is produced at the maximum allowable voltage of not more than 4.2 volts.
Some lithium compounds can easily ignite if the voltage is exceeded, therefore, traditionally, they are built into lithium-ion batteries charge level controllersthat do not allow exceeding the critical voltage. Another safety feature is the integrated valve to relieve excess pressure inside the bag.
Lithium-ion batteries have already taken their rightful place in the market of portable household appliances. These are batteries for cell phones, cameras, camcorders, tablets, players, etc.

Lithium Ferrophosphate LiFePO4 It is considered the most promising cathode material due to its environmental friendliness. Lithium cobaltate LiCoO2, in turn, is toxic and environmentally harmful, and for batteries based on it, only 50% of the ions can be extracted from the structure of the compound, because if you completely remove lithium from it, the structure will become unstable, cobalt will go into oxidation state + 4 and will be able to oxidize oxygen, and the released atomic oxygen will oxidize the electrolyte, and an explosion will occur.Batteries with increased capacity (based on LiCoO2) are extremely explosive.
Lithium ferrophosphate LiFePO4 was proposed as the cathode material of batteries for more powerful devices in 1997 by John Goodenough.
Lithium ferrophosphate is present in the earth's crust, and will not create any environmental problems in the future. Oxygen cannot be released from it, since it is all very strongly bound by phosphorus with the formation of a stable phosphate ion. However, for the possibility of using this material, it had to be fragmented into small particles, otherwise it would remain an insulator due to its very low conductivity. The particles were made lamellar with small sizes along the direction of motion of lithium ions, then they were coated with a nanometer layer of carbon.
Such LiFePO4 nanoparticles are able to charge in 10 minutes, and if the coating is still modified, the charge time will be reduced to 1-3 minutes. In the future, it is this material that will be able to provide power to electric vehicles for 10 years. Already technologically possible charge-discharge cycle in 5-10 minutes with complete safety.
From the point of view of modern science, the development and release of even portable nanoaccumulator It will not take long to wait, and the word is only for the wide technological implementation of developments. As for the prospects of electric vehicles, now we can already assume that they will become the main mode of transport in the cities of the near future.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:

