Categories: Featured Articles » Sources of light
Number of views: 7412
Comments on the article: 0
Modern LED lamps: what to look for when choosing
LED lighting fixtures and lamps are no longer a novelty for a long time, but often an ordinary person does not understand what he is buying at the store and whether a simple light bulb can somehow affect his health. The fact is that the quality of a light source is not determined by its power and how much light it gives out. These are just quantitative indicators, an indicator of the quality of light is the ripple coefficient and color rendering index.

What determines the quality of the lamps
As already mentioned, the quality of the lamps determines not their brightness, but such indicators as the ripple coefficient and color rendering index. These two characteristics determine both the perception of light and your well-being. You may have noticed that when you spend a lot of time, for example, in a garage with old fluorescent lamps, your head sometimes starts to hurt and there is some feeling of unnatural surroundings, and if you go out into the sun everything seems much more saturated and more pleasant for the eye. And it's not about the lighting itself. The definitions of some basic terms will be discussed later.
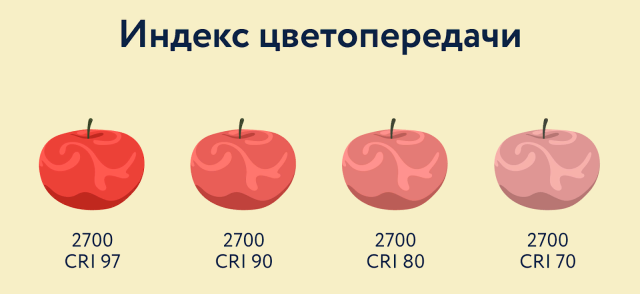
The speech in the example above was color rendering index. This parameter determines how the spectral composition of light provides the reality of the perception of objects.
You will not be able to measure it at home. This is done with the help of specialized expensive equipment, the cost of an average device lies in the region of $ 500-1000.
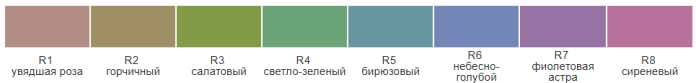
It is indicated in the characteristics of the source as CRI (color rendering index) or Ra. And it is determined by comparing the transmission of 8 test colors illuminated by a specific light source.
The ripple factor is no less important. Its values should be as close as possible to 0%, that is, the light should be as pulsating as possible. This parameter can be measured by almost every budget meter even. Or conduct an indirect check with a mobile phone camera, more on that later.
Interesting:
Regulatory documents establishing requirements for the quality of lighting:
-
SanPiN 2.2.1 / 2.1.1.1278–03 Hygienic requirements for natural, artificial and combined lighting of residential and public buildings
-
SP 52.1333.2011 Natural and artificial lighting. Updated edition of SNiP 23-05-95 * So, to summarize and consider all the characteristics separately.
-
The power of the lamp depends on the number of connected LEDs and the efficiency of the power source.
-
The luminous flux depends on the quality of the LEDs, the materials that were used in their production. There is information on the Internet about LEDs whose luminous flux reaches 140 lumens per 1 Watt of power, but in reality, modern lighting fixtures and lamps use LEDs that give 90-110 Lm / W. This is the figure from which it is worth starting from when calculating lighting.
-
The color rendering index depends especially on the phosphor - it determines the spectrum of the emitted light.
-
The ripple coefficient of the light flux depends only on the power source. We will consider their typical schemes later. In short, the statement that the simpler the circuit is, the more ripple is not entirely true. Even in the cheapest circuit built on a quenching capacitor, it is easy to achieve an acceptable level of ripple, using the normal selection of a smoothing capacitor. At the same time, as in power circuits with a current source (driver), with poor smoothing of the ripples at the input, ripples of the output parameters and the light flux are observed, respectively.
The device of LED lamps and lamps for 220V
LED luminaires and lamps can be divided into 5 components:
1. Power supply or driver. Its task is to convert the mains voltage into a stabilized voltage or current to ensure uninterrupted operation of the LEDs in nominal mode.
2. LEDs. They can be located on a printed circuit board or in separate mounting heat transfer substrates of the Star type. They are found both in discrete form and in the form of matrices or COB LEDs.
3. The radiator. Its purpose is to remove heat from the LEDs. In case of overheating, their service life is significantly reduced.
4. Case. Even a high-quality and properly selected radiator will not be able to remove heat from the LEDs if it is placed in an improperly designed small case without the possibility of heat removal. Sometimes the housing and the radiator are one structurally integrated part - this solution is used in most LED lamps. Although filament LEDs do not have a radiator and they radiate heat into the interior of the bulb like spirals of an incandescent lamp.
5. The basement. If we are talking not about a solid lamp, but about a lamp, then the base serves to connect it to the power. It happens threaded or pin type.
Source of power
If we consider the most popular budget price segment, then today in lamps with a base E27 (the usual and most common threaded base in our country), they use power circuits with a transformerless driver on integrated circuits. They can be recognized by the presence of an element on the board, either similar to a transistor in a three-body case with axial terminals of the TO92 type, or in an octopus case designed for surface mounting such as SOIP-8 (and the like) and a small inductor located nearby.
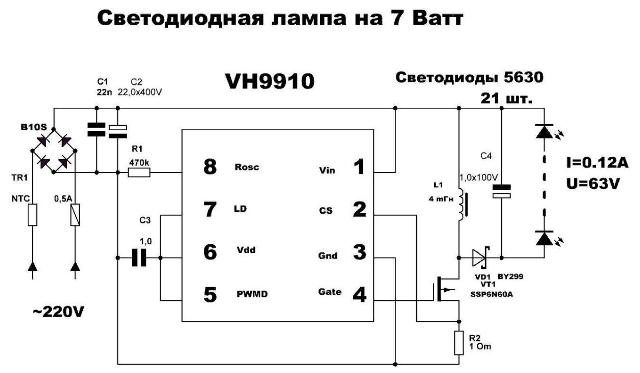
Typical Transformerless Pulse Driver Circuit
This is a good power option, the ripple coefficient of such lamps is quite acceptable and they shine for a long time, nevertheless, the LEDs and the power source itself are usually not protected from power surges.
Earlier in cheap Chinese bulbs used quenching capacitor power supply. Such a scheme was not distinguished by reliability, low ripple and high efficiency. The fact is that the lack of stabilization led to the fact that the LEDs were fed either a low or high current with deviations of the supply voltage from the nominal 220V. Accordingly, in houses where the voltage often exceeds the nominal, they quickly burned out. At the same time, in 90% of cases 1 or 2 LEDs burn out, and since all the LEDs on the board are connected in series, everything stopped burning.
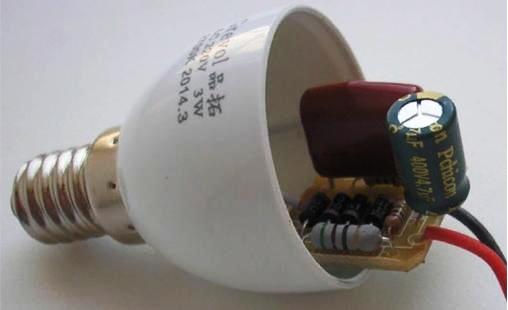
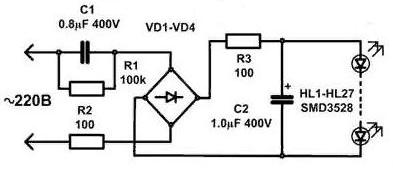
The appearance and power supply circuit with damping capacitors - the difference in the number of parts is evident, and with the capacitance C2 - the ripples are smoothed. The Chinese are saving on it.
Now such a scheme continues to be actively used in cheap LED lamps, despite the presence of a large amount of free space in the housing, as well as in tube lamps with G5 and G13 sockets, and lamps for spotlights such as G4, GU 5.3 and others. It is not always clear what this decision is connected with.
Although it is impossible to state unequivocally, it all depends on the lamp manufacturer, for example, the T5 and T8 lamps of the Svetorezerv plant have a pretty good concept as a whole.
Both the first and second decisions are inherent in the lower price segment, in particular for manufacturers such as:
-
ERA;
-
Navigator
-
LEEK;
-
IEC
-
ASD;
-
Online.
This does not mean that such lamps are bad, just their selection must be approached with caution.
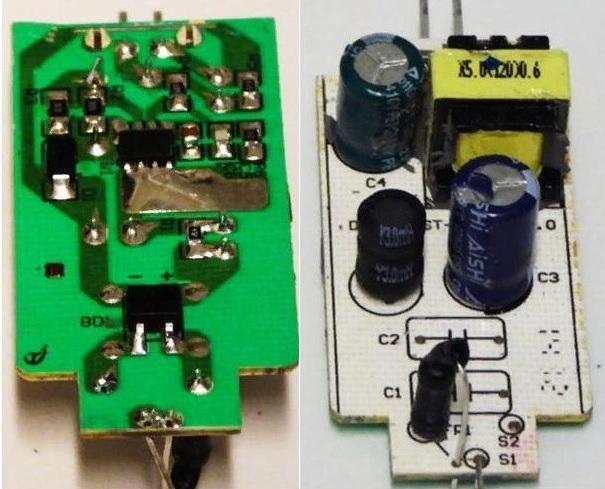
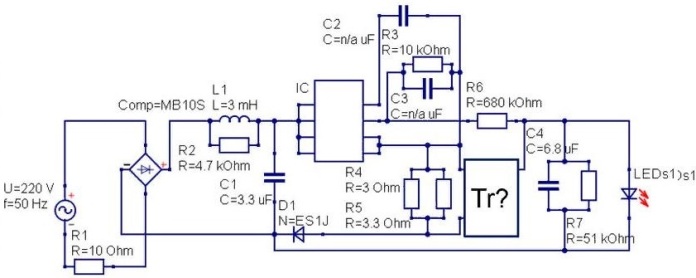
An example of a driver board and its circuit from a Gauss lamp
In expensive LED-light sources from manufacturers such as Gauss, Philips, Osram use more advanced power sources. Most often, these are full-fledged drivers (pulsed current sources) with a transformer and high efficiency. The presence of a transformer provides reliable galvanic isolation from the network, respectively, the risk of failure of the capacitors is reduced, and thanks to the current feedback, its good stabilization is ensured.
LEDs
In LED lamps and fixtures use SMD LEDs such sizes:
-
3528;
-
5050;
-
2835;
-
5630;
-
5730;
-
3014 (rare).

In spotlights and some high-power lamps and luminaires, they also use LED arrays or COB-LEDs, sometimes they are called CHIP-LEDs. In terms of its structure, this matrix of LEDs is coated with a single phosphor layer, it differs from a set of discrete LEDs in that all the crystals are already interconnected at the stage of production of this module.

All manufacturers of even the cheapest products have long abandoned the use of 5-mm LEDs, which are mounted through the holes in the board due to their low efficiency and high production costs.

But nothing other depends on the case in which the LED is made except the heat transfer parameters. The parameters affecting lighting depend on the light-emitting crystal itself, the properties of its PN transition. Therefore, buying cheap products with supposedly powerful 5730 LEDs (they are produced in versions of 0.5 and 1 W) often come across fakes that match the characteristics of already obsolete 3528.
The same applies to phosphors, because the color rendering index depends on it. In different sources, there is information that, by selecting certain proportions in the phosphor, it is possible to bypass the index check, having obtained a match in the standards only for control colors, despite the fact that color rendering problems are visible to the naked eye.

The photo shows an example of a lamp with a "good" declared index, but with a greenish tint
A relatively new type of LEDs are filament filaments, a large number of manufacturers make such lamps, and Tomich’s Lisma lamps can be distinguished from domestic ones.

Outwardly, they are very similar to classic incandescent lamps, LEDs are located inside the bulb, and the driver is in the base. The limited space of threaded sockets often does not allow to assemble a high-quality driver in them, nevertheless, such lamps are popular and they give good performance in all respects. It is worth noting that the power of one filament is about 1 Watt, this allows you to approximately evaluate the actual power of the lamp, not looking at the packaging, but counting the number of threads. The author of the following video clearly demonstrates what is inside the filament lamp.
Their advantage is the classic appearance and uniform direction of light in all directions. However, particularly picky critics complain that shadows from the filaments themselves are observed in the propagation of the light flux. This is more nitpicking than a remark.
The most high-quality LEDs from companies:
-
CREE (USA);
-
OSRAM Opto Semiconductors (Germany);
-
Nichia (Japan).
Low voltage lamps and fixtures
A separate word deserves lamps that are powered from a network with a reduced DC voltage of 12V and fixtures that turn on from a separate driver. Both of them for the most part came to replace halogen spotlights. For the latter, electronic transformers were previously used.
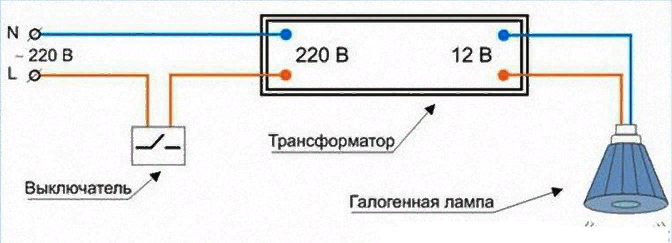
Now lamps powered by 12V are powered from power supplies either individual for each lamp or one per group of lamps, which is used more often similarly to the supply of halogen lamps.
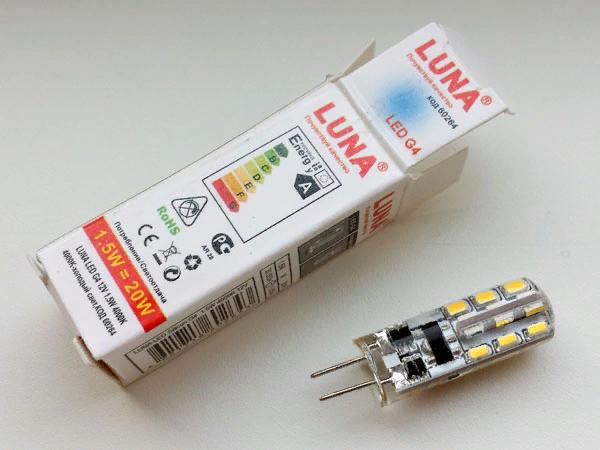

An example of an LED lamp with a G4 socket and a 12 V power supply
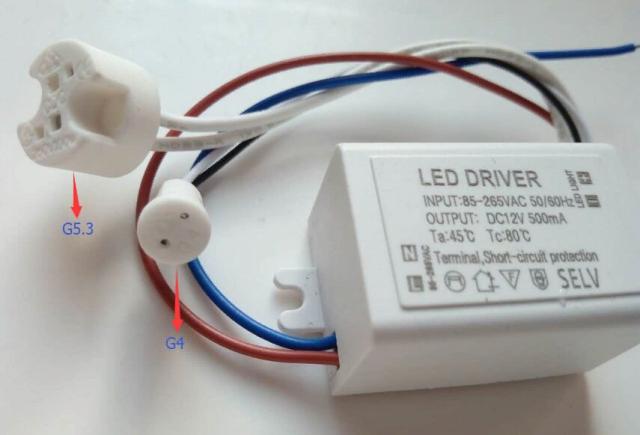

An example of another version of the power supply for such lamps, note that it says "Driver", although this is a voltage source, not a current
Frequently Asked Question:
How to dim a 12V lamp for spotlights? The brightness of such bulbs is regulated using a 12V dimmer for LED strip. Regulate them with a 220V dimmer will not work. The name of the power supply unit, dimmer, controller "for LED strip" is tied because the tape first entered the mass market of LED products.

Important:
Often users ask what to do if the drivers for the lights are on, is it possible to replace it with a power supply for all the lights at once. The answer is NO.The fact is that they are powered by current sources, on their case the connection diagram to the lamp is usually indicated and it does not imply the connection of several pieces in a group.
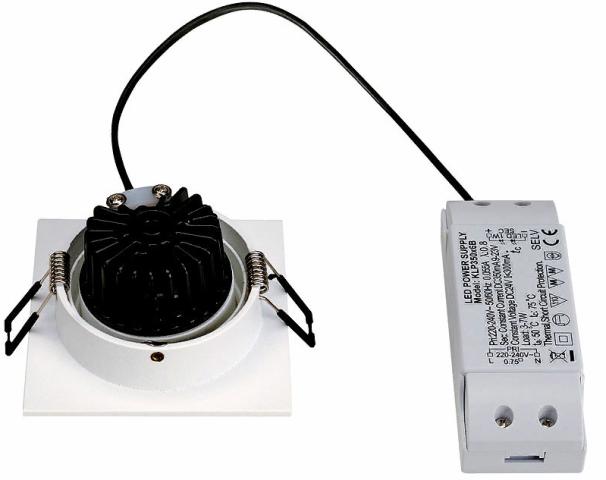

An example of a lamp with a driver

The appearance of such a driver
Pay attention to the characteristics, namely to the OUTPUT section - output voltages of 30-68V, which indicates stabilization of the current, not voltage, its circuit sets depending on the number of connected LEDs and their parameters.
How to choose a lamp?
If you do not want to buy expensive products from European manufacturers, then pay attention to a number of tips when purchasing, because you can not see in most cases LEDs (if they are covered with a diffusing cap, and it is glued), and the driver is completely hidden in the lamp housing. Anticipating ambiguous comments, I will say in advance that this is only my vision and personal opinion about buying cheap bulbs.
1. The power of the lamp is directly proportional to its size and weight. Although this sounds a little ridiculous, nevertheless, with two equally cheap lamps of the same power, I will give preference to the one that is heavier and more different in size. The fact is that the heavier the lamp, the more likely it is that the manufacturer put a normal radiator in it, placed the LEDs on a normal heat transfer substrate with a printed circuit board, and installed at least some kind of driver board. Unfortunately, the real choice has to be made blindly.
2. If it is possible to turn on the lamp for at least a couple of minutes - see how quickly it heats up, the lamp housing should be hot, but not hotter than the temperature that the hand still suffers. That is 50-60 degrees. The temperature of modern LED crystals should not exceed 100-150 degrees Celsius, and it will be really higher than the temperature of the heat dissipating case.
3. If you have a light meter, you can measure the pulsation coefficient of the lamp directly in the store, although not as accurately as you could in the laboratory. Well, if there is no light meter, then use the camera of your smartphone. When hovering over the lamp in the picture, no running stripes should be observed. Check out the video below.
Radex Lupin - measures ripple and light, at the time of writing, its price is about 5000 ($ 72.28)
Interesting:
GOST R 54945-2012 permits measuring pulsations with the following instruments:
-
Multichannel radiometer "Argus";
-
Pulse meter-luxmeter "Argus 07", "TKA-PKM" / 08;
-
Pulsemeter-luxmeter "TKA-PKM" / 08;
-
Light meter-bright meter-pulse meter "Ecolight-01", "Ecolight-02".
I no longer know the real ways to distinguish good LED-lamps from the bad ones from the range of cheap models. Therefore, you should be aware of what you are buying and for what purpose, for example, into the corridor or the bathroom, the quality of the light source does not really matter. But the lighting in the workshop or above the desk should be excellent and meet all sanitary standards.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
