Categories: Interesting Facts, Sources of light
Number of views: 25875
Comments on the article: 9
The effect of LED lamps on human health
 The whole civilized world is gradually, but with more and more decisive, switching to LED lighting, and this is not at all surprising, since LEDs open a new era in the technology of light production itself, so this highly effective technology claims to be the main one of its kind in 21 century. But how will the use of LEDs affect human health? We will try to figure it out now.
The whole civilized world is gradually, but with more and more decisive, switching to LED lighting, and this is not at all surprising, since LEDs open a new era in the technology of light production itself, so this highly effective technology claims to be the main one of its kind in 21 century. But how will the use of LEDs affect human health? We will try to figure it out now.
Let's start with the environmental aspect associated with the content or absence of heavy metals in LED lamps. Were very popular recently energy saving fluorescent lampscontaining mercury vapor in the flask, and this is a fact that causes unreasonable fears. In the event of a malfunction, the disposal of such lamps should be carried out in a special way, they cannot simply be taken and thrown into the bin, and, as a result, in many countries the distribution of these lamps is on the verge of being prohibited.

LED lamps, in turn, are devoid of this drawback. Moreover, in their design there is no more heavy metals than in electronic wrist watches or a cell phone. Therefore, LED lamps, unlike fluorescent lamps, are safe for both humans and the environment, they do not contain potentially hazardous substances.

Now about the light itself. LED lamps are characterized by the complete absence of ultraviolet radiation in their spectrum over the entire range of color temperatures used for lighting - from 3000K to 6500K.
This means that even when using powerful LED light sources, you can not be afraid of harmful ultraviolet exposure to the eyes or skin. It is worth remembering that not only the sun emits ultraviolet in its spectrum, but also incandescent lamps have it.
In addition, ordinary incandescent and fluorescent lamps flicker with a frequency of 100 Hz, which causes fatigue, harms vision, as well as the nervous system of a person as a whole.
High-quality LED flicker lamps do not have this, they have a built-in special electronic driver that makes the light of the LED lamp even and comfortable for both our eyes and the nervous system. However, you can’t look directly at the working powerful LED, you can damage the retina.
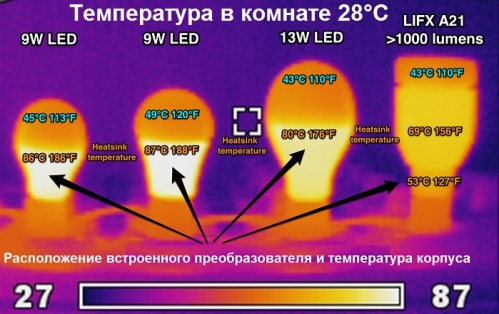
Recall about heating. When working with LED lamps, an important feature related to heat generation, which manufacturers always take into account, is noteworthy. Since several small LEDs are placed in the lamp housing over a small area, it is required to remove heat from their substrates with the help of an additional radiator, the role of which is sometimes played by the lamp housing itself.
Thus, it is not allowed to heat the product above, in the worst case, about 90 degrees Celsius, depending, of course, on the power of the LED lamp itself - for low-power lamps, the maximum body temperature is much lower. This is not near with incandescent lamps, which are capable of causing severe skin burns when accidentally touched, even a few minutes after turning off. High-quality LED lamps will not cause burns.

Finally, LED bulb bulbs are made from durable, shatterproof, materials such as plastic or polycarbonate. For this reason, there is no danger of getting a cut (even if you manage to break the diffuser), which can not be said about incandescent lamps, nor about fluorescent lamps, which, when broken, produce numerous sharp fragments that can cause cuts.
In conclusion, it will not be amiss to say that the latest studies of the effects of LED light on humans have shown that the soft light of LED lamps not only helps normalize the emotional state of people, but also helps maintain mental health, reducing stress in the work teams of office workers.
German scientists recently discovered the rejuvenating effect of LED light on skin cells, and medical research in recent years has generally shown that LED light accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues and even neurons, these studies are ongoing, and medicine will probably soon receive another effective healing tool in its arsenal.
As you can see, LED lamps are not only safe for human health, but even useful!
Read also on this topic: LED usage examples
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:

