Categories: Featured Articles » Interesting Facts
Number of views: 62878
Comments on the article: 0
What is a Faraday cage?
Back in 1836, the English physicist and inventor Michael Faraday created a special device for shielding equipment from electromagnetic radiation. This device is relevant to this day, and, as before, bears the name of a scientist. It's about the Faraday cage.
This device is a protective cage made of highly conductive metal, and, as a rule, grounded. The principle of operation of this simple device is also quite simple:
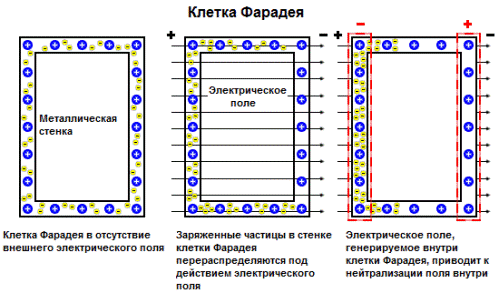
When an external electric field acts on the cell, the free electrons of the metal of the cell come into motion, and the opposite sides of the structure are charged so that their field compensates for the external electric field.
This can be checked in a simple experiment with two electroscopes and a Faraday cage charged from a high-voltage source: an electroscope attached to the inner surface of a Faraday brass cage and placed inside it will not show the presence of an electric charge, and an electroscope connected externally will show.
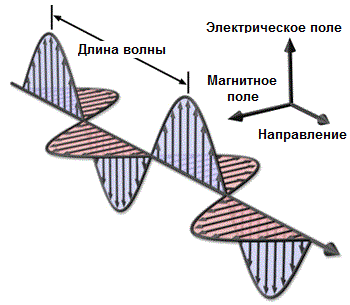
A constant magnetic field, unlike an electric field, will penetrate into the cell without hindrance. However, since the alternating electric field generating the alternating magnetic field is shielded by the cell, the alternating magnetic field does not penetrate into the cell, as it simply does not have time to arise. For this reason, the Faraday cage protects its internal space, and the objects in it, not only from the electric field, but also from the action of external electromagnetic waves.

If we pay attention to high frequencies, then electromagnetic waves of high frequency (compared with the size of the cell of the cell grid) will partially reflect from the cell, and will simply simply die out in the thickness of the metal, inducing eddy currents in it, and ultimately dissipate into the form of heat.
Nevertheless, the efficiency of the screening function of a Faraday cage is associated with the following parameters: with the depth of the surface layer (skin layer), with the thickness of the metal of the cell, and with the size of the opening with respect to the wavelength of the external radiation, from which shielding is required. So, for shielding cables, Faraday cages with conductors of a structure of well-conducting materials are used. The cell size, for the effective operation of the Faraday cage, must necessarily be much less than the wavelength of the screened radiation.

A type of Faraday cage everyone can meet in microwave. On the microwave door there is a metal grid, the cells of which are quite small in comparison with the wavelength created by the magnetron. The microwave operates at a frequency of 2450 MHz, and the wavelength here is slightly more than 12 cm, obviously, the grid on the microwave door easily shields this radiation, preventing it from going outside.
The role of the rest of the cell in the microwave is played by the metal chamber in which the heated food is located. By the way, if you put a cell phone in the microwave oven (off!), It will be out of the network coverage area, since the GSM standard cellular waves are even longer than the waves generated by the microwave magnetron.

There are metal suits that work on the principle of an individual Faraday cage, made of stainless steel and copper fibers. Such costumes are used by installers of high-voltage power lines, because even a disconnected line, many kilometers long, accumulates a dangerous amount of static charge on itself. A suit protects a person from electric shock.
Such protective sets based on silver cloth protect electricians from the harmful effects of the electromagnetic field of high-voltage installations, where the electrical component is very high. Such kits, according to their manufacturers, are designed to protect:
-
from exposure to an electric field of industrial frequency;
-
from the effects of bias current caused by an alternating electromagnetic field;
-
from exposure to intense electromagnetic radiation arising from a discharge between the contacts of the disconnectors;
-
from discharges of electric current when touching grounded or insulated objects, parts of equipment, as well as grass and small bushes;
-
from electrical injuries when exposed to induced or step voltage.
The kits create a closed shielded space around the body of a person dressed in a suit, excluding any penetration of the electric field inside. All elements of the kits are made of electrically conductive materials and are interconnected by channels of increased conductivity and electrically conductive contact leads. Thanks to such suits, the human body is shunted, and safe drainage of currents of electrostatic or capacitive nature is ensured.

Lovers Tesla coils also use costumes resembling individual Faraday cages. The current simply flows down the surface of the suit into conductive parts with less resistance, without causing damage to the person participating in the show.

As you can see, the Faraday cage is used today where a lot. High voltage electrical installations are enclosed in Faraday cages, Faraday cages are used in the show, finally, any production associated with dangerous microwave and other electromagnetic radiation is not complete without whole workshops and rooms enclosed in Faraday cages.

We hope that this article was useful to you, and now you understand how important a simple-looking device that resembles a regular box of mesh can be. After all, the Faraday Cage in various applications not only shields a variety of equipment sensitive to electric fields and radiation, but also protects people's health by preventing cancer, and many other diseases that can be caused by excessive exposure to electromagnetic radiation on a living organism.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
