Categories: Featured Articles » Electrician at home
Number of views: 9347
Comments on the article: 2
How to protect the apartment from overvoltage
Light bulbs burn out from power surges, household appliances fail, and even an emergency situation in apartment wiring can occur. Increased voltage is observed during phase imbalance and other problems on the line. Let's figure out how you can protect the electrical equipment of an apartment from overvoltage.

Causes
So, for what reasons is the excess voltage in the network?
1. Phase imbalance.
2. Surge surges or the so-called power surges.
3. Fluctuations caused by the difference in load at different times of the day or season.
It is worth noting that GOST 29322-2014 says: “the supply voltage should not differ from the rated voltage of the system by more than ± 10%”, which for 220V lies in the range 198-242V.
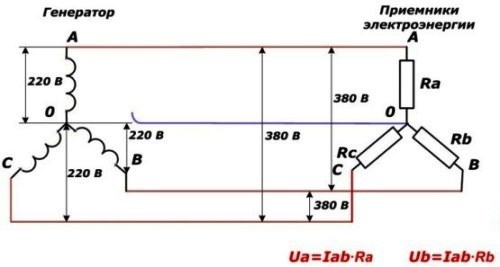
Phase imbalance
It occurs as a result of the complete burning off of the zero conductor at the entrance to the house, apartment or from the TP, or a strong deterioration of its contact. Moreover, all single-phase consumers, which in most cases are apartments, turn out to be connected in series to Ulinear.
Then the voltage between them is distributed according to Ohm's law, where the resistance R is the reduced resistance of the load connected in the apartments. In simple terms, where little devices are connected and they have low power, the voltage will be high, and where powerful heaters are connected - low.
By the way, when burning zero at the input, a phenomenon such as “two phases in sockets” is characteristic.
Surge Surge
Often arise as a result of turning off the power of electrical appliances or their group. Welding works also belong to the same reason, most often this happens in the private sector, when some homemaker once again decides to “weld” a gate or a fence.

Also, surges in the power supply network can occur due to poor contact on the overhead power line (VLEP),
Due to weather conditions, such as wind, blizzard, rain, thunderstorm, voltage can also “jump”. This is due to their effect on VLEP.
Seasonal or daily fluctuations
At different times of the day, voltage fluctuations occur due to the load changing, for example, in the evening, when people come home from work they turn on electric stoves, heaters and other electrical appliances, the current increases and voltage drops as a result, and at night when everyone is sleeping and the load decreases - the voltage can, on the contrary, be increased.
In summer, voltage can also increase, because electric boilers and other equipment are turned off. Although in summer cities there are voltage drops due to the fact that air conditioners are starting to work everywhere.

In simple terms, voltage fluctuations are due to the fact that the substation has the ability to adjust the voltage either by switching wires to the taps of the windings, or using special systems. So in order to provide some average voltage level under a certain load, a certain value is set. As a result, when the load is large - it can sag, and when the load is small - on the contrary, increase.

Effects
As a result of prolonged high voltages, high power is released on the heating devices, which reduces the service life. With significant excesses, semiconductor and other electronic components of household appliances — diodes, transistors, and input filter capacitors — can fail.

The consequences of surge surges are essentially the same, but the amplitude of the pulses in this case can reach several kilovolts.
Different developments are likely:
-
Blown fuses of electrical appliances;
-
Failure of circuit components;
-
Tripping of circuit breakers;
-
In the most negative cases, fires are possible.
Protection methods
To protect the apartment from overvoltage, either stabilizers are used that normalize the voltage to a normal level, or turn off the power at critical network parameters.
In this regard, two types of devices can be distinguished:
-
Regulatory (stabilizers or manual LATRs);
-
Switching (ILV, LV, USM, etc.).
Let's consider their features separately.
Voltage relay
Under the name "voltage relay" on the modern market there are many devices, ranging from the "nameless" of China, ending with the popular and recognized models, so we can distinguish the following:
Operating principle:
-
There is a built-in relay to disconnect the circuit;
-
Monitors the voltage in the network;
-
You can set the upper and lower limit of permissible supply voltages;
-
When the voltage in the mains becomes more or less than the set limits, the relay will turn off and the protected circuit will be de-energized. It can be either a separate electrical appliance or the entire apartment;
-
Does not save against surge voltages;
-
Protects only from over or under voltage.
Depending on the model, the device can operate as a relay:
-
Maximum;
-
Minimum;
-
The maximum and minimum voltage.
This functionality allows you to provide protection only from high or low voltage, which will reduce the number of failures or shutdowns of the electrical installation. In some cases, lower values of the supply network are acceptable for operation, and in some cases, vice versa (for example, the electric motor does not "like" low voltage - the torque decreases significantly and the current rises).
By execution there are:
-
For installation on a DIN rail in an electrical panel;
-
To connect to a power outlet (outlet relays).
By the number of phases - single-phase and three-phase. When assembling a three-phase switchboard, you can also use three single-phase voltage relays.
Both versions are equally good - you can secure a separate device with a socket relay, for example, by installing a device to protect the refrigerator, or a group of devices, for example, a computer connected via an extension cord.
Consider some popular models for mounting on a DIN rail:
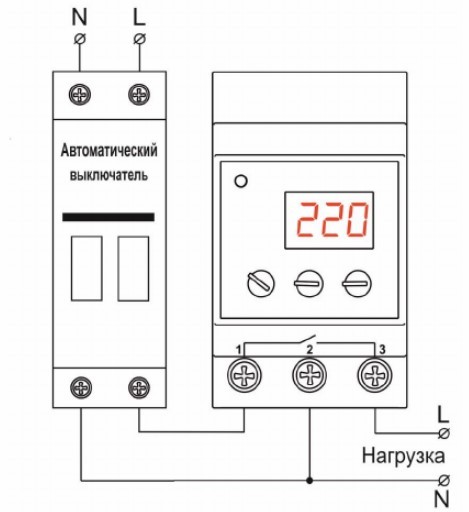
RN-106 or RN-104 - models differ only in rated current - 63 and 40 A, respectively. The response control range for Umin (minimum voltage) is from 160 to 210 V, and for Umax is from 230 to 280V. You can also set the time after which automatic restart will occur (also called automatic reclosure or turn-on delay) - from 5 to 900 s. The device has convenient and intuitive adjustment controls.
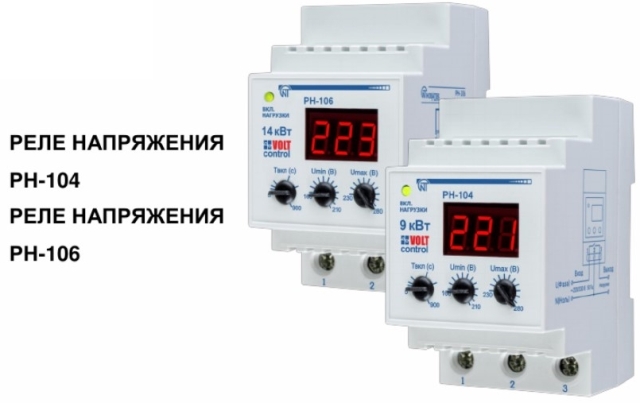

The wiring diagram is pretty standard for similar devices.
RN-111M and RN-113M - This is a voltage relay from the same manufacturer, but more allows you to use it in a wider range of tasks, to limit only the maximum or minimum voltage, or both thresholds. The main thing of the 111th and 113th models is the rated current of 16 and 32A, respectively, as well as the RN-113M takes 1 model in the shield more than 111M. The remaining characteristics of him, like other devices of this type are similar.
Please note that the device has a power supply circuit separated from the executive circuit, and a relay with a normally-closed contact is installed at the output, which also allows for the implementation of a larger number of protective automation circuits.

Using the RN-113M as an example, the connection diagram can be performed in two versions, depending on the function performed (limiting the upper, lower, or both voltage levels). For RN-111M - the same.
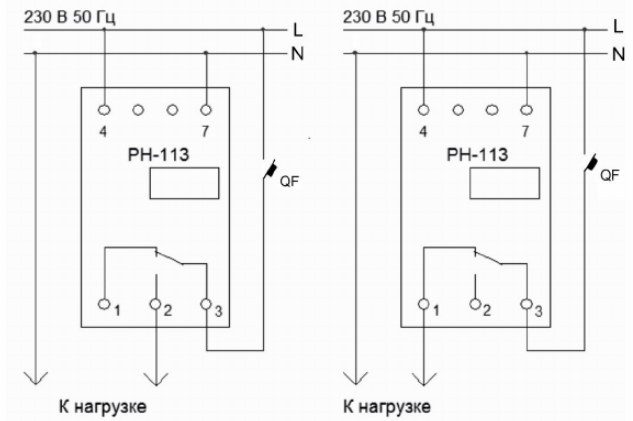
Note that the voltage relay must be installed in the circuit protected by a circuit breaker (on the QF circuit), since the overwhelming majority of models do not have an overload protection function.
To increase the power that the relay commutes, use a contact starter, connecting its coil instead of the load, and the load itself to the power contacts of the KM.
See also: Connection diagrams of voltage relays in single-phase and three-phase networks
SPD and SPE
Surge Protection Device (SPD) It is used to protect not from high voltage, but from high-voltage surges (impulses). They are devices that, when a surge voltage of several kilovolts occurs, discharge the pulse energy to the ground.
An example of such a device is the SPE - surge suppressor. Inside of which a varistor is installed.

As already mentioned, the device is connected between the phase and protective conductor. In case of use TN-C systems (without grounding) - installation between phase and zero after the machine is allowed.
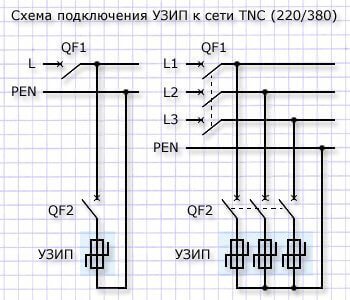
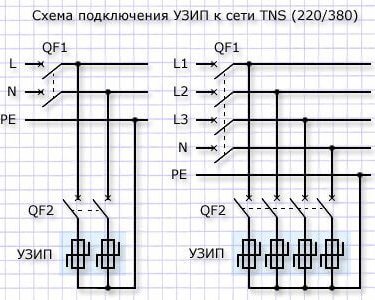
The main disadvantage of these devices is that they are conditionally disposable. If the energy of the high-voltage pulse was greater than that which the varistor in the SPE can dissipate, then it will fail.
But note that the installation of devices such as SPD should be carried out only after consultation with an experienced electrician. Since the device itself can be dangerous if installed, for example, up to a circuit breaker, then the short-circuit current will be very high in case of a breakdown of the SPD, and only the nearest circuit breaker can disconnect the circuit, and it will be very bad if the latter is already in the KTP . Also, one must not forget that the SPD can also work due to natural aging.
Ultrasound
I want to say a separate word about such devices as UZM-50Ts and its counterparts manufactured by the MEANDR ECM, this is a combined device, it provides the functions of a voltage relay, and protection against high-voltage pulses, and a volt-ampere meter. At the same time, the manufacturer recommends using it in conjunction with a full-fledged SPD. This is due to the low power of the varistor. Specifications are listed below:
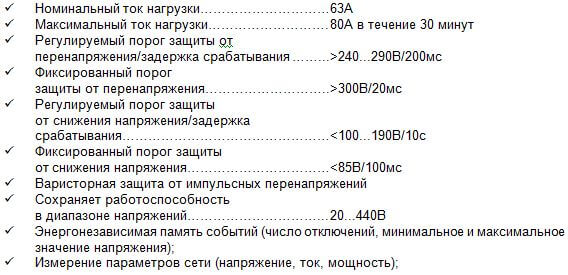
In addition to the controls (two buttons), on the device’s body there is a three-digit indicator, which displays the settings during adjustment, status and current voltage, current or power consumption.

The connection diagram is quite simple, it is given below.
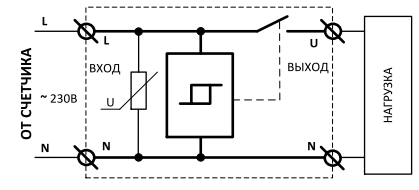
Stabilizer
And finally, to ensure stable voltage in the household network, as well as protection against power surges, Surge Protectors. They are:
-
relay;
-
electronic;
-
electromechanical;
-
ferroresonance;
-
inverter.
The cheapest option is relay, and the most expensive is inverter. It is worth noting that ferroresonance devices are currently rarely used. They were used in Soviet times to power televisions. One of the popular manufacturers is the domestic RESANTA, an example of the products of which you see below.

Relay, electronic and electromechanical stabilizers are built on the basis of an autotransformer, only the way of switching the taps from its windings differs. Switching can be done using:
-
relay;
-
servo drive and movable brush (electromechanical);
-
triacs (electronic)
In more detail, we examined their working principle and types in the article - Network voltage stabilizers 220V
In short, the mains voltage stabilizer is a device that maintains the same value of the output voltage when the input voltage changes, within the limits established by the design. Adjustment takes place smoothly (servo-driven devices) and with a given step (relay or electronic).
By power, these devices are both low-power - at 500 watts, for powering individual devices, and capable of protecting the entire apartment - with a capacity of more than 10 kW. By the number of phases - single-phase and three-phase. In the photo below you can observe the three-phase model "RESANTA ASN-15000/3-EM", with a power of 15 kW.
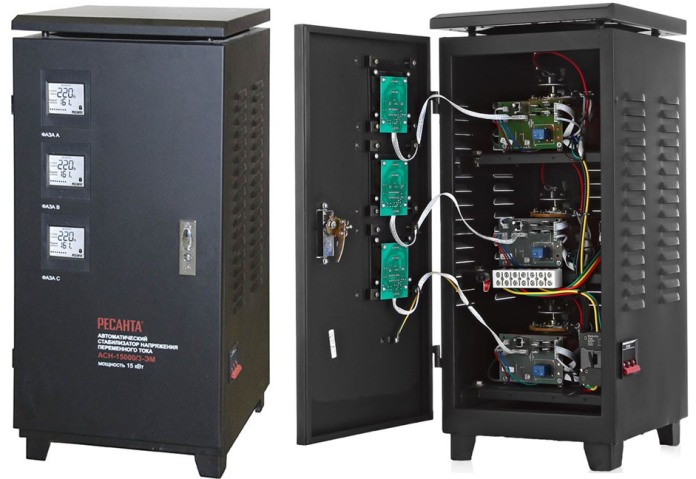

Conclusion
Visitors often ask "what is the best stabilizer or voltage relay?". This question cannot be answered unambiguously, since these are different devices. But if you install a voltage relay in front of the stabilizer, then protect not only the power network of your home, but also the expensive stabilizer itself. While for the protection of individual electrical appliances, it is possible to use both stabilizers and socket voltage relays, and these devices are paired.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
