Categories: Featured Articles » Electrician at home
Number of views: 63261
Comments on the article: 5
Surge arresters in home wiring - types and wiring diagrams
 Any electrical equipment is created to work with a certain electrical energy, depending on the current and voltage in the network. When their value becomes larger than the designed norm, an emergency mode occurs.
Any electrical equipment is created to work with a certain electrical energy, depending on the current and voltage in the network. When their value becomes larger than the designed norm, an emergency mode occurs.
To prevent the possibility of its formation or to eliminate the destruction of electrical equipment, protection is called upon. They are created under the specific conditions of an accident.
Features of protection of home wiring from high voltage
The insulation of the household electrical network is calculated on the limit value of the voltage slightly above one and a half kilovolts. If it grows more, then a spark discharge begins to penetrate through the dielectric layer, which can develop into an arc that forms a fire.
To prevent its development, they create protections that work according to one of two principles:
1. disconnecting the electrical circuit of a house or apartment from high voltage;
2. The removal of the dangerous potential of overvoltage from the protected area due to its rapid redirection to the ground contour.
With a slight increase in voltage in the network, they are also called upon to correct the situation. stabilizers of various designs. But, for the most part, they are created to maintain the operating parameters of power supply in a limited range of its regulation at the input, and not as a protective device. Their technical capabilities are limited.
In home wiring, the voltage may increase:
1. for a relatively long period, when zero burning occurs in a three-phase circuit and the neutral potential shifts depending on the resistance of randomly connected consumers;
2. short-term impulse.
The first type of malfunction is successfully handled by the voltage monitoring relay. It constantly monitors the input parameters of the network and when they reach the upper set point, it disconnects the circuit from the power supply until the accident is eliminated.
The reasons for the appearance of short-term overvoltage pulses can be two situations:
1. simultaneous shutdown of several powerful consumers on the supply line when the transformer substation does not have time to instantly stabilize the system;
2. lightning strike to electrical equipment of power transmission lines, substations or houses.
The second option for the development of an accident is the greatest danger than in all previous cases. The strength of the lightning current reaches enormous quantities. In averaged calculations, it is taken at 200 kA.
It, when struck in the air terminal and during normal operation of the building's lightning protection, flows through the lightning rod to ground loop. At this moment, in all adjacent conductors, by the law of induction, an EMF is induced, the value of which is measured in kilovolts.
It can appear even in wiring disconnected from the network and burn its equipment, including expensive TVs, refrigerators, computers.
Lightning can strike an overhead power line in the building that feeds it. In this situation, line arresters normally work, damping its energy on the earth’s potential. But they are not able to completely eliminate it.
Part of the high-voltage pulse along the wires of the connected circuit will spread in all possible directions and will come to the input of the apartment building, and from it - to all connected devices to burn their weakest places: electric motors and electronic components.
As a result, we got two options for damage to expensive household electrical equipment in a residential building with the normal elimination of the consequences of a lightning strike in the lightning rod of our own building or power line with standard protection.The conclusion suggests itself: it is necessary to establish for them automatic protection against pulse discharges.
Types of surge suppressors for home wiring
An assortment of such protections is created for work in different conditions; it differs in design, materials used, and work technology.
The principles of the formation of the element base of the arrester
When creating surge protection, the technical capabilities of various design solutions are taken into account. For gas-filled arresters, it is characteristic that, after the passage of the discharge pulse, they support the flow of an additional current close in magnitude to the short circuit load. It is called an accompanying current.
Surge arresters, providing a tracking current of the order of 100 ÷ 400 amperes, themselves can become a source of fire and do not provide protection. They can not be installed to protect the insulation from breakdown between any phase, working and protective zero. Models of other types of arresters work quite reliably within the 0.4 kV network.
In home wiring, overvoltage protection takes precedence varistor devices. Under normal operating conditions of the electrical installation, they create very small leakage currents of up to several milliamps, and during the passage of the high-voltage pulse, the voltages are transferred to the tunnel mode as quickly as possible when they are capable of passing up to thousands of amperes.
Surge insulation classes of home electrical wiring for surge voltage
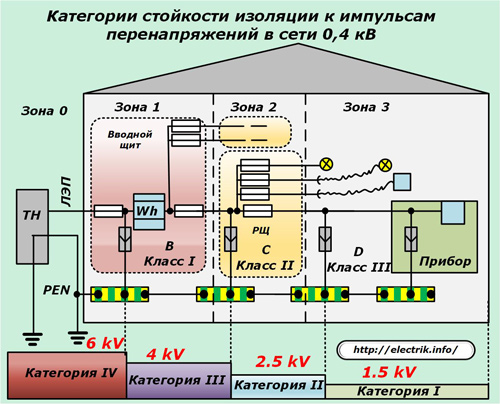
The electrical equipment of residential buildings is created in four categories, which are indicated by Roman numerals IV ÷ I and are characterized by the maximum permissible overvoltage of 6, 4, 2.5 and 1.5 kilovolts. Under these zones, surge protection is designed.
In the technical literature they are called "SPD"that stands for surge protection device. Manufacturers of electrical equipment for marketing purposes have introduced a more understandable definition for ordinary people - limiters. Other names can be found on the Internet.
Therefore, in order not to get confused in the terminology used, it is recommended to refer to the technical characteristics of the devices, and not just their name.
The main parameters of the relationship between the insulation resistance categories and the building danger zones and the application of the three classes of SPD for them will help to understand the figure below.
He demonstrates that an impulse of 6 kilovolts can come from the transformer substation along the power line to the input shield. Its value should reduce the class I surge suppressor in zone 1 to four kV.
In the distribution panel of zone 2, a class II limiter operates, reducing the voltage to 2.5 kV. Inside a living room with zone 3, an SPD of class III provides a final pulse reduction of up to 1.5 kilovolts.
As you can see, all three classes of limiters work comprehensively, sequentially and alternately reduce the overvoltage pulse to a value that is acceptable for insulation of the wiring.
If at least one of the constituent elements of this protection chain turns out to be faulty, the entire system will fail and an insulation breakdown will occur on the final device. It is necessary to use them comprehensively, and during operation it is required to check the technical condition of the technical condition at least by an external inspection.
Selection of varistors for different classes of surge suppressors
The equipment manufacturers of the SPD device supply varistor models selected according to the current-voltage characteristics. Their appearance and operating limits are shown on the corresponding chart.
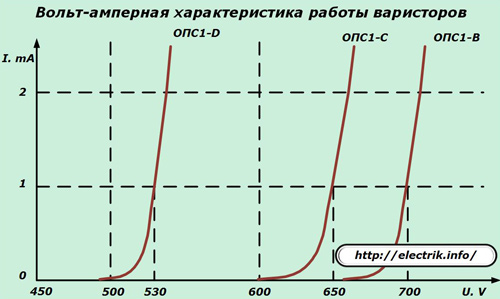
Each protection class has its own voltage and opening current. You can only install them in your place.
Principles for the formation of surge arresters
To protect the apartment’s power supply line, various principles for connecting an SPD can be used:
1. in phase;
2. out of phase;
3. combined.

In the first case, the longitudinal principle of protecting each wire against overvoltages relative to the ground loop is fulfilled, and in the second, the transverse between each pair of wires. Based on the collection of statistical data on the processing of faults and their analysis, it has been revealed that the arising antiphase surge surges create more damage and are therefore considered the most dangerous.
The combined method allows you to combine both of the previous methods.
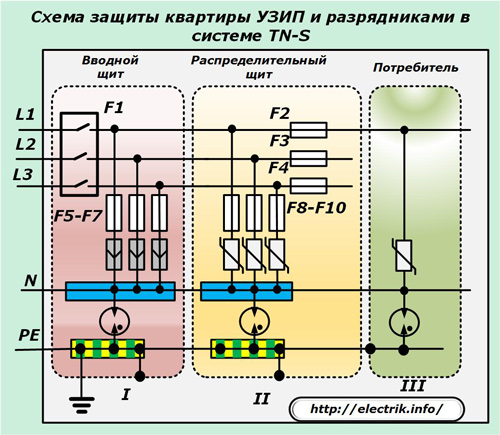
Connection options for surge suppressors for the TN-S grounding system
Circuit with electronic SPD and arresters
In this scheme, the surge arresters of all three classes eliminate the overvoltage pulses between the phases of the line and the working zero N along the wire-to-wire chains. The function of reducing common-mode overvoltages is assigned to arresters of a certain class due to their connection between the working and protective zero.
This method allows galvanically disconnecting PE and N between themselves. The neutral position of the three-phase network depends on the symmetry of the applied phase loads. It always has some kind of potential, which can be from fractions to several tens of volts.
If power supply systems with a pulsed load operate in the system, then high-frequency interference from them can be transmitted through the potential equalization and grounding circuits through the PE conductor to sensitive electronic devices, interfering with their work.
The inclusion of arrester in this case reduces the impact of these factors due to better galvanic isolation than electronic limiters on varistors.
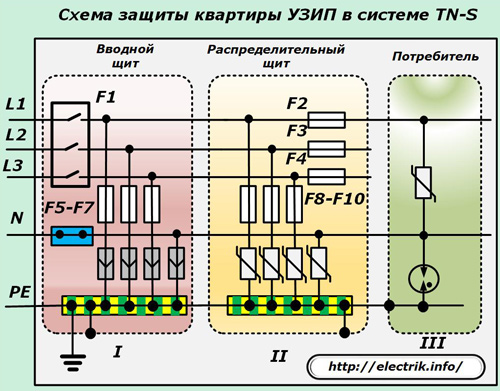
Circuits with electronic SPD in protection classes I and II
In this scheme, the protection against impulse voltages in the input and distribution boards is performed only by electronic arrester.
They eliminate all common-mode overvoltages (any wires relative to the ground loop).
In class III, the previous circuit works with an electronic arrester and a spark gap, providing protection (wire-to-wire) for the end user.
Features of the use of various models of arrester taking into account the sequence of cascades
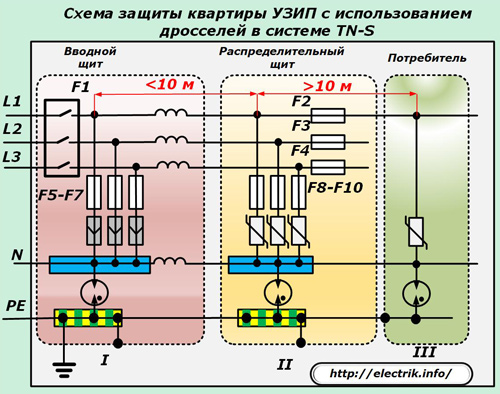
During the operation of surge protection stages, their coordination and coordination are required. It is carried out by removing the steps over a cable to a distance of more than 10 meters.
This requirement is explained by the fact that when a high-voltage pulse with a steep waveform enters the circuit due to the inductive resistance of the conductors, a voltage drop occurs on them. It is immediately applied to the first cascade, causing it to fire. If this requirement is not met, then the steps are bypassed when the protection does not work correctly.
Subsequent cascades of protection are connected by the same principle.
When it is located close to the design features of the equipment, additional pulse-type isolation chokes are artificially included in the circuit, creating a delay chain. Their inductance is tuned within 6-15 microgenry depending on the type of power input used in the building.
A variant of such a connection with a close arrangement of the input and distribution panels and the remote installation of end consumers is shown in the diagram.
When mounting a throttle in such a system, it is necessary to take into account their ability to reliably operate under the created loads and withstand their limit values.
For the convenience of servicing, surge protection together with throttle devices can be placed in a separate protective shield that sequentially connects the input device to the main switchboard of the house.
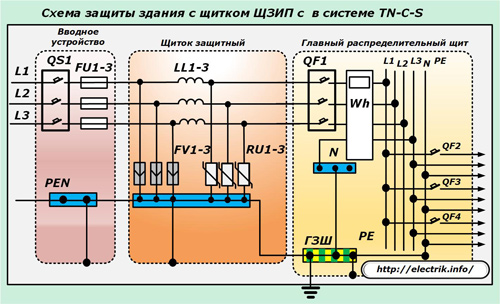
One of the options for a similar execution for a building made according to the TN-C-S grounding system is shown in the diagram below.
With this installation, all three classes of limiters can be placed in one place, which is convenient for maintenance. To do this, it is necessary to mount dividing chokes in series between the protection stages.
Structurally, the input device, main switchboard and protective shield with this method of mounting the circuit should be located as close as possible.
The combined arrangement of SPDs and reactors in one place - a protective shield allows you to exclude the ingress of overvoltage pulses already on the main switchgear equipment, in which the PEN conductor is separated.
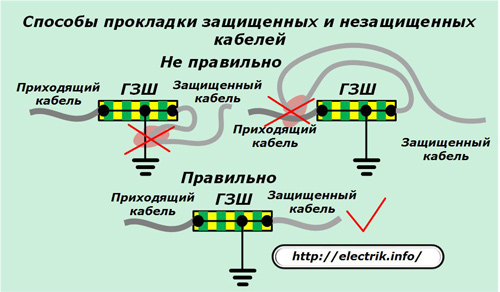
The connection of power cables to the MES has features: they must be laid along the shortest paths, avoiding joint contact for sections of the protected circuit and without protections.
Modern manufacturers are constantly updating their SPD designs using built-in pulsed isolation chokes. They made it possible not only to position the protection steps at close range over the cable, but also to combine them in a separate unit.
Now on the market, taking into account the implementation of this method, there are designs of SPDs of combined classes I + II + III or I + II. A different assortment of models of such arresters is produced by the Russian Hakel company.
They are created for different building earthing systems, work without installing additional protection levels, but require the fulfillment of certain installation specifications along the length of the connected cable. In most cases, it should be less than 5 meters.
For the normal operation of electronic equipment and to protect it from high-frequency interference, various filters are produced, which include an SPD of class III. They need to be connected to the ground loop through a PE conductor.
Features of the protection of complex household appliances from surge pulses
The life of a modern person dictates the need to use various electronic devices that process and transmit information. They are quite sensitive to high-frequency interference and pulses, do not work well or generally fail when they appear. To eliminate such malfunctions, an individual grounding of the device case, called functional, is used.
It is electrically separated from the protective PE conductor. However, when lightning strikes lightning protection between the grounding of a building or line and a functional electronic device, a discharge current will flow along the earth circuit, caused by an applied high-voltage overvoltage pulse.
It can be eliminated by equalizing the potentials of these circuits by installing a special arrester between them, which will equalize the potentials of the circuits in case of accidents and provide galvanic isolation in everyday operating conditions.
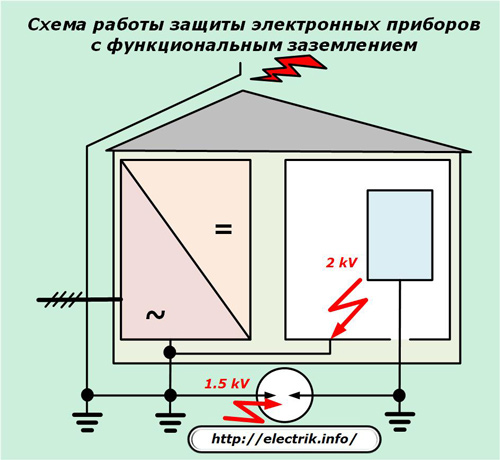
Hakel Digging also specializes in the production of such arresters.
Additional short circuit protection requirement
All SPDs are included in the circuit for equalizing potentials between its various parts in critical situations. It should be borne in mind that they themselves, despite the presence of built-in thermal protection for varistors, can be damaged and become a source of short circuit, which develops into a fire.
The protection on varistors may fail if the rated voltage is exceeded for a long time, due, for example, to zero burning in a three-phase supply network. Dischargers, unlike electronics, are not equipped with thermal protection at all.
For these reasons, all SPD designs are additionally protected by fuses operating during overloads and short circuits. They have a special complex design and are very different from models with a simple fusible insert.
The use of circuit breakers for such situations is not always justified: they are damaged by lightning impulses when the welding of power contacts occurs.
Using the protection circuit of an SPD with fuses, it is necessary to observe the principle of creating its hierarchy using selectivity methods.
As we see, in order to ensure reliable protection of home electrical wiring from surge surges, it is necessary to carefully approach this issue, analyze the probability of accidents in the design scheme taking into account the working grounding system, and select the most suitable arrester arresters for it.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
: