Categories: Electric installation work
Number of views: 18898
Comments on the article: 0
Why do you need a heat shrink tube: types, specifications, how to use it
A heat shrink tube is a material for insulating electrical connections. It is used instead of electrical tape, but paired with it provides reliable and durable insulation. The principle of operation of the heat shrink tube is to change its size when heated. It is also called shrink or shrink cambric.
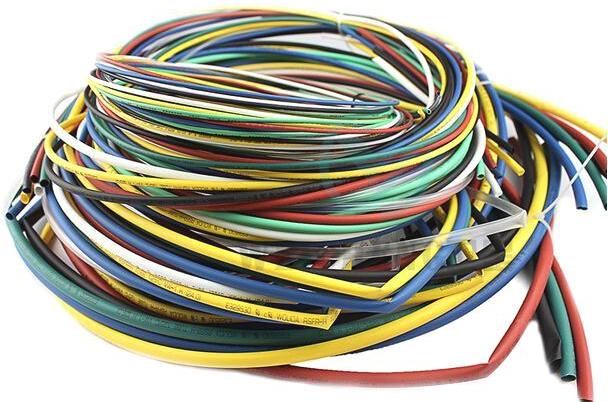

Shrinkage replaced the classic cambric. Previously, pvc cambric was used for marking and insulation of wires. For marking purposes, it was actively used in automotive wiring and relay circuits, in switchboards.
On it inscriptions well kept marker or felt-tip pen. When installing household wiring in junction boxes, they were also used. In this case, cambric was put on a twist, its end was heated and squeezed with pliers, after which it was glued, and the part that was on the side of the wires was wrapped with electrical tape.
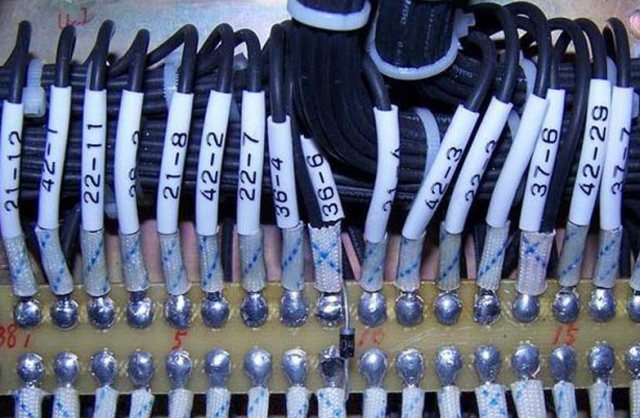

Shrink Types
Shrink can be of different colors, among which you can highlight the option with colors ground bus (yellow green) and transparent. Other options most often go monochrome. You can also find heat-shrink tubing with printed markings, similar to the one shown in the figure above.
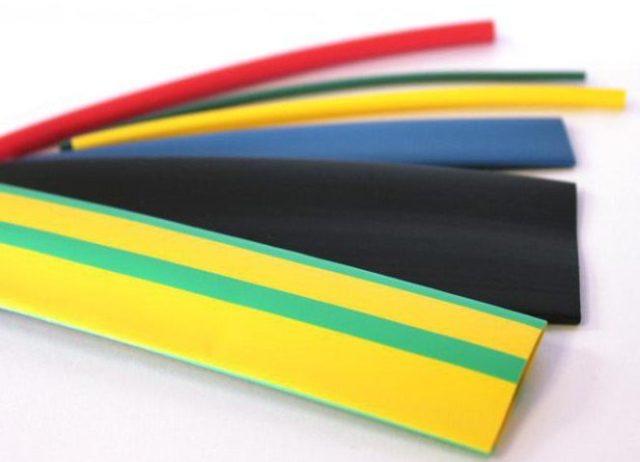
Also distinguish it by material:
-
Polyolefin. Based on polyethylene with plasticizers, dyes and additives that suppress combustion. They can be used in the temperature range from -50 ° C to 125 ° C. With prolonged contact with fuels and lubricants, integrity is violated.
-
Elastomers based on synthetic rubber. Resistant to temperatures up to 175 ° C and the effects of fuels and lubricants. They are expensive.
-
PVC tube. They poorly tolerate temperature effects, are used at temperatures from -20 ° C to 80 ° C, and toxic substances are released when ignited.
-
Polyester (PET). Resistant to chemical influences, durable.
-
Fluoropolymer tubes.
-
Transparent PTFE Shrink Tubing
-
Silicone Flexible, non-toxic. Despite the good electrical insulating properties, it does not tolerate contact with fuels and lubricants.
The wall thickness is divided into:
-
Thin;
-
Medium
-
Thick ones.
It is easy to guess that the insulating properties and strength depend on the thickness of the walls. Some materials do not tolerate ultraviolet radiation. The tube can be corrugated or fluorescent, these are additional properties.
According to the coefficient of shrinkage, the tubes are "reduced" in diameter from 2 to 6 times. Most often on sale there are those that are reduced by 2 times (at least in my city). The packaging usually indicates the diameter before shrinkage, and the minimum diameter after shrinkage, respectively, you can isolate the cables in this range in this way. Sometimes indicated in the form of a fraction: B / A, where B is the diameter BEFORE the shrinkage, and A is the diameter after shrinkage.
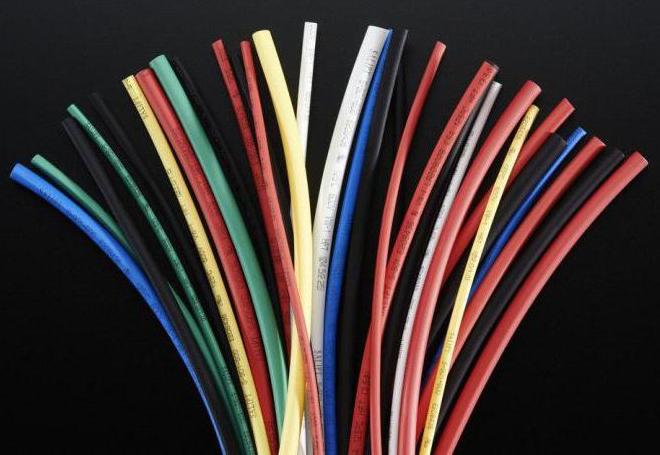

Using heat shrink for insulation and labeling
The classic use of shrink tubing is the electrical insulation of contacts. You can seat any joints cable lugs and terminalsleaving bare the detachable part. Shrinkable terminals of the type "MAMA", typical for automotive wiring. Their design allows this to be done while maintaining the functionality of the plug connection.

In order to seat the tube, you need to bring a heat source to it, it can be a lighter, hair dryer or soldering iron. If you do not have experience with it, it is best and better to do this with a building hair dryer or a hair dryer from a soldering station. A hair dryer will not work, its temperature is often less than necessary.

To do this, blow the tube from different sides, while avoiding local overheating, otherwise it begins to melt or swell.
If you have overheated the heat shrink, it is better to cut it off and use a new one, or on top of the damaged one, wrap the blue tape insulated with time.
The next option is to use a fire source: matches, lighters, burners. It requires speed and accuracy of work. So it is very easy to overheat, so you need to perform quick movements along and across the tube. The flame usually envelops the shrink and evenly seats it, but it is still better to walk from all sides.
If you are not sure what you can sit down with fire, try to do it at a distance from the connection, the hot air from the flame is quite suitable for this work.
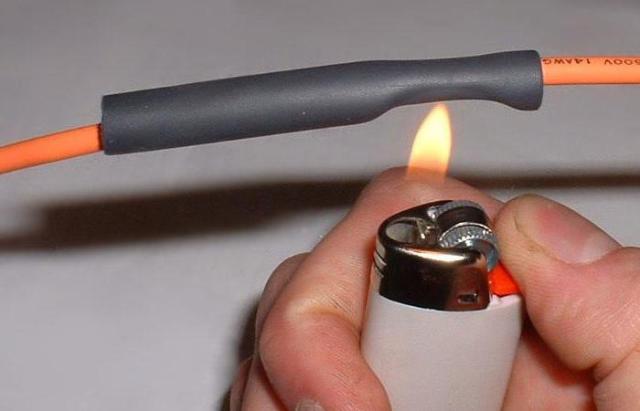

The third option is a soldering iron tip, it’s better not to do it with the tip of the tip, but closer to its base, so you won’t ruin the tinned part and put the pipe down. The technique is the same. Personally, I had the best fit EPSN type soldering iron, in it the sting is fixed with a bolt in the casing. Here in the place where the bolt is twisted into the casing, there is a right angle, with its help the tape immediately seated in two planes.
Heat shrinkage provides good insulation, it can be used as in low-voltage circuits (for example, 12V when connecting LED strips or repairing automotive wiring).
Tip:
In order to get a good joint seal, there are two options. The first is to wrap the edges of the tube with several layers of electrical tape. So the tube will not slip over time from the junction of the wires, and moisture will not enter. The second option is to cut off the tube with a margin and pour a little hot glue from the gun between it and the wire. After which to seat, so you get a kind of cork from hot melt glue.
It may seem to you that shrinkage is a thin material and will be poorly insulated. Do not worry about this, first try to break it. It is quite dense. In addition, after sitting, the tube becomes thicker, its mechanical and electrical insulating properties are improved.
Nuance: longitudinal shrinkage of the tube
Sometimes there is the problem of incomplete isolation of terminals, sleeves and twists. This is due to the fact that in addition to shrinkage in diameter, the tube is shortened in length. In quality products, no more than 2%, but sometimes fakes or cheap Chinese come across when you seem to cut off with a margin, but in the end up to 20% of the length disappears somewhere.
Quote: “Train better on cats.”
Therefore, it is better to pre-train on a piece of wire and notice how much length is lost during the compression process.
Where can not be used?
You can not use heat shrink in places with high temperature, for example, when repairing teapots, irons and other heaters, also applies to many types of electrical insulation. For such purposes, there are special heat-resistant fiberglass cambric.

They are designed for these purposes and perfectly tolerate heat.
Do not hope that heat shrink will save the wire if it rubs against something, here you need either many layers of electrical tape in the place of contact with a foreign body, or a gasket made of rubber, or corrugation plastic or metal.
Where else is used? Examples of unusual use of heat shrink
It is often used to form an insulating layer. for lithium batteries, for example size 18650, which are actively used in electronic cigarettes. On the market there is a wide range of patterns and colors of such tubes. It is needed to prevent accidental shorting of the battery poles, because lithium banks without protection can easily fail, with a large heat generation and fireworks.
Another use case is suitable for electricians. If you do not have a screwdriver with an insulated sting, and a layer of electrical tape thickens it too much, then heat shrink is perfect for this.You will get an insulating uniform and thin layer that will save you from accidental electric shock or short circuits when working with electrical equipment. This is useful for both household electricians (220V) and automotive (12-24V).
And of course, such material has found application and not for electrical purposes. I propose to consider a small selection of non-traditional use of heat shrink.
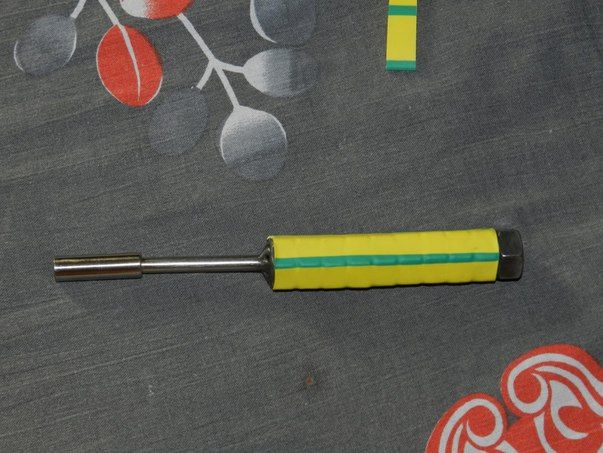
For example, you can tighten the sliding handle of a screwdriver.

Or make a fishing tackle “fly” from a double hook.

And if you put a key on the handle, they will not ring in your pocket.

To protect against fracture and restore the headphone cords and USB cables of smartphones, you need to put the heat shrink in the place where the cable is usually damaged.
You can come up with a number of applications, for example, to prevent slipping something or to prevent falling out of tubular elements or rods from grooves (as an option on sun shields on Lada and other cars) and much more.
conclusions
The heat shrink tube is a versatile material that provides good electrical and good mechanical protection. It can be used in a number of tasks, both electrical and household.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
