Categories: How does it work
Number of views: 2634
Comments on the article: 0
Method of electromagnetic induction in wireless energy transfer
A method of transmitting electrical energy to a distance without using a conductive medium is called wireless transmission of electricity. By 2011, several successful experiments were carried out in the microwave range with capacities of several tens of kilowatts, while the efficiency was about 40%.
This happened first in 1975 in California and the second time in 1997 on Reunion Island. The longest distance was about one kilometer, an experiment was conducted to study the energy saving possibilities of one village without using a traditional cable.
Technologically, the principles of electric power transmission over a distance include, depending on the transmission distance, the following. At short distances at low powers - induction and resonance methods, such as in RFID tags and smart cards. At large distances and at high powers - the method of directional electromagnetic radiation in the range from UV to microwave.
Let's take a closer look at the induction method. Wireless transmission of energy through electromagnetic induction implies the use of the near electromagnetic field at distances commensurate with 17% of the wavelength. The bottom line is that the energy of the near field is not radiating in itself, there are only small radiation and resistive losses.

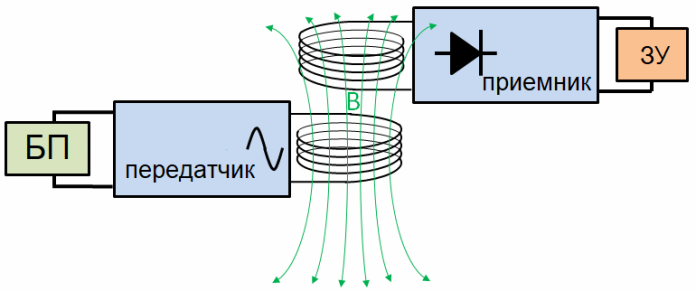
Electrodynamic induction works like this. When an alternating electric current passes through the primary winding, there is an alternating magnetic field around it, which simultaneously acts on the secondary winding, inducing a variable EMF and, accordingly, alternating current.
To obtain higher efficiency, the relative position of the primary and secondary windings should be close enough. If, under experimental conditions, the secondary winding begins to move away from the primary, then the part of the magnetic field reaching the secondary winding and crossing its turns will become smaller.
As the secondary winding is removed, even at a small distance, the induction coupling between the windings will eventually become so small that most of the energy transmitted by the magnetic field will be consumed extremely inefficiently and generally in vain.
A similar system is presented in its simplest form. in a classic electric transformer. After all, a transformer is the simplest device for wireless power transmission, since its primary and secondary windings are not galvanically connected to each other. The transfer of energy from the primary to the secondary is implemented in it through a process called mutual induction. The main function of the transformer is to increase or decrease the voltage supplied to the primary winding.
In contactless chargers for mobile equipment, for electric toothbrushes and in induction hobs, just methods of electrodynamic induction are implemented. The disadvantage in transferring energy in this way is that the effective action is very small. To achieve proper efficiency, the transmitter and receiver must be placed very, very close to each other, almost close to the principle that they can effectively interact with each other.
To increase the efficiency of the induction method, it is useful to introduce the phenomenon of electric resonance into such a system, which will increase the effective transmission distance. With the addition of an oscillatory circuit to the resonant circuit, it by its action to some extent increases the effective transmission distance. For resonance to occur, the transmitter and receiver loops must be tuned to the same common frequency.
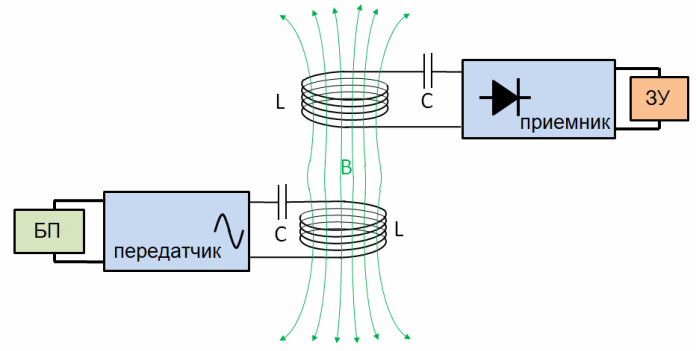
The performance of such a system can be further improved by correcting the waveform of the control current, deviating it from a sinusoidal to a transitional non-sinusoidal, pulse.
The pulsed energy transfer is then carried out in several cycles, and significant power can be transferred under such conditions from one LC circuit to another, and with a lower coupling coefficient than without using resonant circuits. The shapes of the coils do not change, and in any case they are flat spirals or single-layer solenoids with capacitors connected to them, necessary to tune the receiving element to the resonant frequency of the transmitter.
Traditionally, resonant electrodynamic induction is used in wireless battery chargers of mobile devices, like cell phones and medical implants, as well as in electric vehicles. Localized charging devices use the selection of a specific transmitter coil from a set of multilayer windings.
In this case, the resonance phenomenon works both in the circuit of the transmitting panel of the charger and in the receiving circuit of the charging module mounted on the charging device so that the efficiency of transmission and reception of energy is maximized. The technology of this configuration is universal, and can be used to wirelessly charge various gadgets equipped with appropriate resonant receivers.

The technique of this plan is adopted as part of the Qi wireless charging standard. This standard provides two options for energy transfer: low power - from 0 to 5 watts and medium power - up to 10 watts. The standard was developed after 2008 by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) for the induction transfer of energy up to 4 cm.
Equipment with Qi support includes a transmitter with a flat coil (it is located behind the plate), connected to a stationary power source, and a compatible receiver that is installed inside the charging device (also in the form of a flat coil). PWhen using the charger, the connected device is placed on the transmitter plate. In this case, the principle of electromagnetic induction between these two flat coils, as in a transformer, applies.

Qi is used today in some devices: Apple, Asus, HTC, Huawei, LG Electronics, Motorola Mobility, Nokia, Samsung, Xiaomi, Sony, Yota Devices. The goal of the consortium is to create a single standard for induction charging technology to make wireless chargers a familiar attribute of public places, such as cafes, airports, sports arenas, etc.
Resonance electrodynamic induction is also used to directly wirelessly power devices that do not have batteries inside. These include RFID tags and contactless smart cards. A similar principle for the transfer of electrical energy applies. in Tesla transformer - from the primary circuit - the inductor - to the resonator located inside it. The Tesla transformer itself, in turn, also serves as a wireless energy transmitter, only more electrostatic than electromagnetic.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
