Categories: Electrical connection of equipment
Number of views: 23020
Comments on the article: 2
How to connect an electric heating boiler: differences between different schemes
For heating an individual residential building, systems that use the transfer of liquid coolant through pipelines to heating batteries, in which heat is transferred to the surrounding air and return of the cooled liquid back for subsequent heating, are becoming increasingly used.
In this case, a boiler is usually understood as a sealed metal vessel in which the heat carrier is heated, and the term “electric” defines the type of energy used.
According to the principle of the use of electricity, boilers are:
1. indirect heating;
2. direct action;
3. induction type.
They have a completely different design, differ in degrees of safety, require a different attitude when connected to the wiring.
Indirect electric boiler
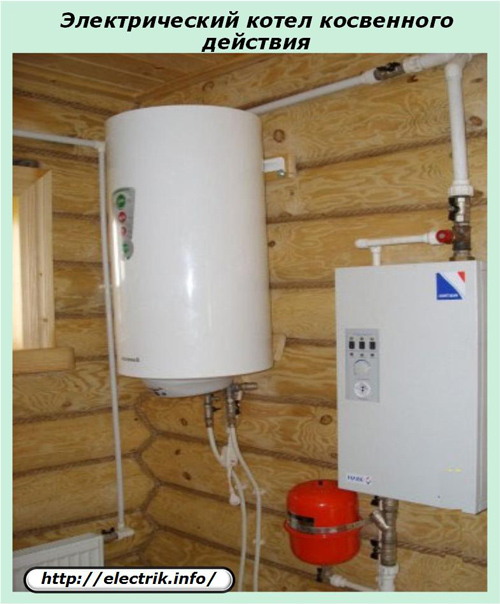

The term "indirect action" refers to indirect heating carried out by an electric current passing through a heating element with a purely resistive resistance. As a result of this phenomenon, according to the Joule – Lenz law, the temperature of a conductor specially placed in a liquid rises.
The heat released on the resistance is removed by the heat carrier. Thermal heating elements, or as they are abbreviated as TENY, are available in different capacities for operation in AC or DC circuits with different voltages.
Design Features
Inside the metal casing of the boiler, electric heating elements are mounted, washed by the coolant.
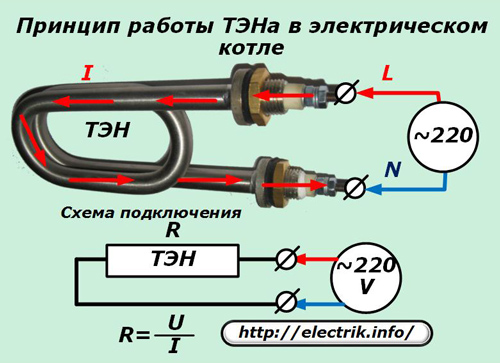
They consist of a sealed metal tubular body with a nichrome alloy thread mounted inside, having a certain electrical resistance and capable of withstanding the rated heating power.
This thread, with both ends, is mounted inside a metal tube and connected to output connectors made by screw thread for connecting electrical wires.
The cavity between the tube body and the nichrome thread is separated by a layer of heat-conducting material with high dielectric properties - a special kind of sand. The ends of the element are sealed and equipped with tips for mounting on the boiler lid.
A functioning heater, therefore, has a certain electrical resistance, which can be measured with an ordinary ohmmeter or tester, or calculated from the power value given on the case.
For example, a voltage converter of 1 kW consumes a current of I = 1000/220 = 4.54 amperes when operating at a voltage of 220 volts and has an electrical resistance of R = 220 / 4.54 = 48.5 Ohm.
The second health parameter of the heater is the quality of the insulation resistance between the conductive nichrome thread and the housing. To measure it, you must use a special device - megaohmmeter.
For domestic heating, 220 volt models with a load power of the order of one kilowatt are usually used. When a larger amount of heat is required, then the heating elements are collected in parallel chains in a single-phase network or connected in identical groups in a three-phase network.
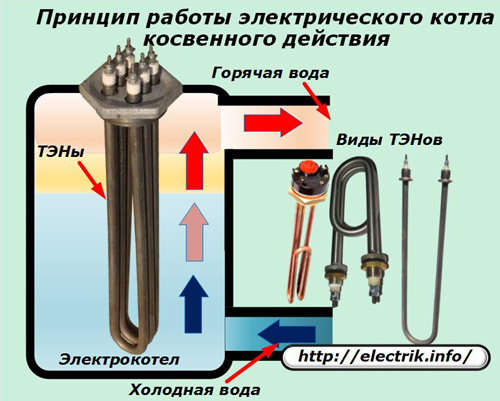
Two flanges are made in the boiler for communication with coolant lines:
1. at the lower inlet, a stream of cold water is pumped;
2. the heated liquid leaves the upper outlet.
When the current passes through the resistance of the heating element, heat is released, which is transmitted through the insulation layer to the metal casing and is removed from the heating element by the coolant flow. Due to this, when working, a balance is created between the heat released by electric energy and the removed liquid pumped through the boiler.
Each heating element with its working part must be completely immersed in the liquid in order for the heat removal to pass efficiently and evenly. If this is violated, for example, due to the formation of an air congestion or leakage of liquid, which led to a decrease in its level in the boiler, it is possible that the thread, insulation or housing of the heating element will burn out and be destroyed.
A simple home-made electric boiler on the video:
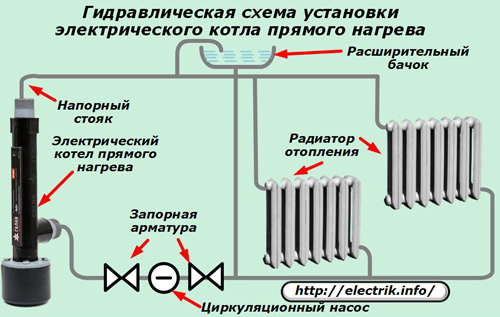
Hydraulic connection diagram
The indirect indirect electric boiler is manufactured at the factory in a beautiful modern building, which can:
-
install on the floor of the room;
-
hang on the wall.
After it is tightly fixed to the building construction, the hydraulic circuit of the heating system of the home is assembled.
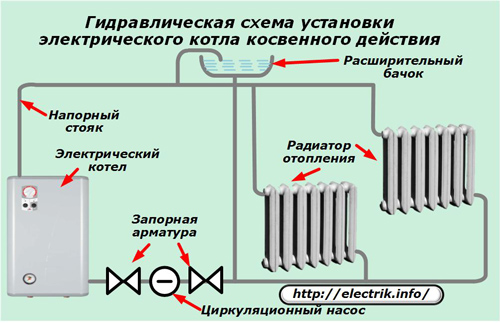
For her use:
-
heating radiators connected by parallel chains between the pressure and drain (return) lines of the coolant transportation;
-
expansion tank, designed to drain air bubbles from the pumped liquid;
-
shut-off valves, allowing you to switch the hydraulic circuit in various operating modes;
-
closed-circuit circulation pump;
-
valve: back pressure, safety, bypass;
-
sensors of the control system of the main technological processes;
-
automation equipment, control logic and protections.
If the circulation pump is excluded from operation, the circuit can function due to natural circulation, when the cold heat carrier goes down and the heated one goes up. However, this will require complex hydraulic and thermal calculation, which, in addition, will require additional equipment setup.
The pump always provides quick pumping of the coolant along the mains and increases the heating efficiency.
Direct-acting electric boiler

The term "direct action" means that to ensure heating, a path is created for the electric current to pass directly through the liquid coolant bypassing any intermediate elements.
For this, the electrodes for supplying the phase and working zero are mounted directly in the line of water pumped through the boiler body. Since its specific resistance strongly depends on the concentration of dissolved salts, the degree of purity of the coolant affects the magnitude of the passing electric current and the degree of heating.
Design Features
Direct-acting devices in their shape and dimensions differ significantly from the classic definition of the word "boiler". Their body is made in the form of a segment of an ordinary pipe, equipped with:
1. nozzles for connection with pressure and return lines;
2. phase and working zero connectors for connecting to the electrodes of the electrical circuit.
Due to this, the dimensions of the device are quite small in size and weight, which significantly saves space in the boiler room in comparison with analogues of indirect action.
The electric current passed through the coolant through the electrodes is limited only by the resistance of the brine, which depends on a number of operational characteristics, and may at some point exceed the nominal value.
Since the heat generated by electricity is directly generated in the coolant without loss of transmission through other additional media, the power reduction in the circuit under consideration is less than in the previous one, and the efficiency is higher.
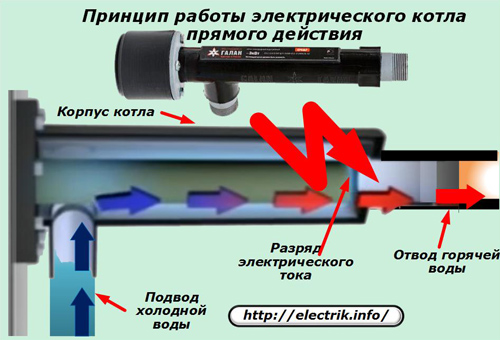
Due to the simplicity of mechanical structures, such devices are quite cheap, which is their advantage. In this case, one of the electrodes must be placed directly on the pipeline body, and the second should be built into the coolant flow.
The electrode method of heating the liquid requires the creation of a special medium for the passage of electric current - brine. When used in household devices, the following disadvantages appear:
-
the coolant in the form of liquid solutions enters into electrochemical processes with all metallic materials. When using aluminum, the radiator body corrodes in a few years, and the cast-iron structures last a little longer, but they also clog constantly and require cleaning;
-
circulation pumps for heating systems are designed to work in an environment of clean water or antifreeze with various anti-corrosion additives. Tests of their designs for long-term operation in brine were not carried out.
Wiring diagram
Fundamentally, the hydraulic heating system of a direct-acting boiler is no different from an indirect heating circuit. As before, a cold water line is mounted on the inlet pipe, and a hot pressure line is installed on the outgoing pipe.
The remaining elements of the circuit, depending on local heating tasks, can completely copy the previous design.
Both pictures show the simplest, most typical arrangement of hydraulic circuit elements. A real design created for specific conditions of heating the premises will always have some deviations and additions.
Quite often, not a single-circuit reduced circuit is used, but a minimum consisting of two groups with independent executive and governing bodies. A simple example is an additional circuit that produces hot water for domestic purposes, for example, in the bathroom and kitchen.
Induction type electric boiler

To heat the coolant, this design uses Foucault eddy currents induced in a special heating element - an inductor.
Design Features
The supply voltage is supplied to the coil of a coil made of an insulated electrical wire. Due to the phenomenon of induction, induction currents passing through a closed circuit are induced in the core magnetic core. In this case, the inductor metal is heated.
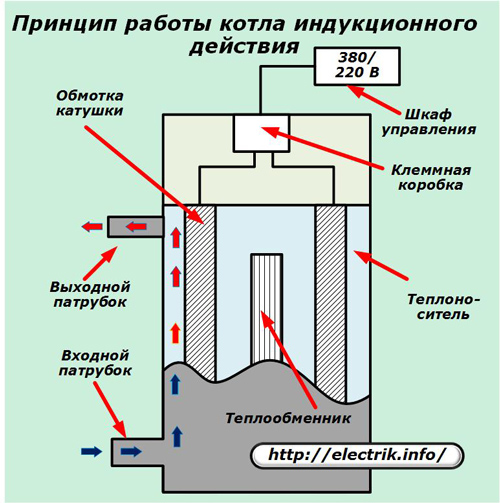
Liquid coolant is constantly pumped through this space and removes heat to the hydraulic system.
During operation of the induction boiler, small vibrations of the inductor occur, which protect the walls from scale formation.
When using currents of industrial frequency, constructions of impressive dimensions are obtained. In order to reduce the dimensions and weight of the boiler, high-frequency voltage conversion up to 1 ÷ 20 kHz is used, which forms the corresponding magnetic field.
The induction boiler can be placed in a protective casing with good insulation.
Ensuring safe operation conditions for direct and indirect boilers
When comparing the principle of operation of a heating element with an electric discharge of current in a coolant, various conditions for their application are created when, for all types of boilers, the casing is made of metal and filled with a conductive liquid.
When using a heating element, current flows through a nichrome filament, is isolated from the casing by a dielectric layer, which does not allow the phase potential to pass to the casing.
In a direct heating boiler, current is generated in the coolant in contact with the surface of the boiler body. As a result, there is a phase potential on it, which violates certain safety rules, creates the prerequisite for a person to receive electrical injury.
The design issues of high-speed electrical protections for such structures have not yet been resolved. The use of conventional RCD designs or diflavtomats that control the appearance of leakage currents in the circuit does not make sense, because they will constantly operate, blocking the supply of the phase potential to the housing.
In the designs of indirect boilers, the use of RCDs is quite reasonable and appropriate. It will not allow a person to fall under the action of the phase potential. This can be understood with the help of explanatory pictures.
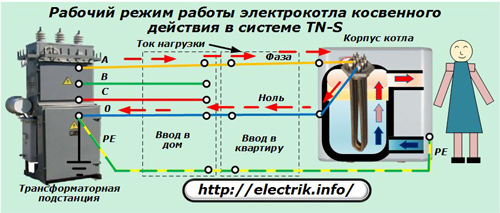
Under normal operating conditions, current flows exclusively along the internal circuit isolated from the housing.
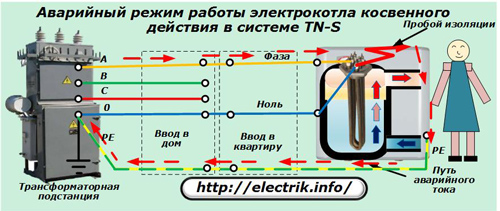
When the insulation of an electric boiler with indirect heating is broken, the leakage current through the housing will penetrate the PE conductor and through it to the ground loop. The RCD setpoint is set so that the residual current device trips and with its power contacts removes the supply voltage from the circuit, which eliminates human injury.
Thus, under the conditions of safe use, direct heating boilers lose significantly. If they are mechanically damaged for any reason, an open circuit is created for the current to flow, which will leave a dangerous phase potential on the housing. And then the case decides everything ...
Scheme of connection to the electrical system
We will consider the entire heating circuit of the boiler as the actuator for heating:
-
direct action - between the electrodes integrated in the housing;
-
indirect heating - connected in parallel to the heating elements;
-
induction - terminal box with windings.
Then the rest of the circuit can be represented by a simplified view with elements of automation, control and current protection against overload and short circuit.
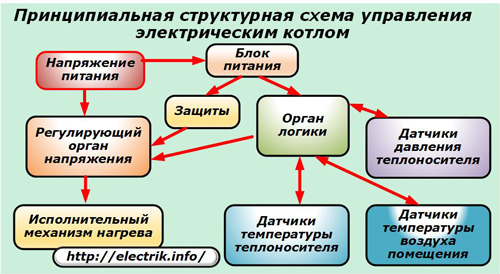
The supply voltage from the switchboard through the regulatory body is supplied to the heating actuator and power supply (protections and logic).
With their sensors, the protections scan the main technical parameters and, when they go beyond the limits of possible regulation, put the boiler out of operation.
Recently, the automation logic body has been increasingly performed on the basis of microprocessor technologies that provide advanced functionality. He receives information from sensors for the temperature of the coolant, indoor air, fluid pressure inside the system, processes it and maintains the temperature inside the boiler by adjusting the voltage on the actuator.
See also: How to choose a thermostat for an electric heating boiler
Conclusion: the article makes an attempt to generalize the connection diagrams of electric boilers of various designs without specifying the manufacturers, breaking them into main groups according to the principle of operation, to analyze their weak and positive sides. And how much this helped you - share your opinion in the comments.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
