Categories: Auto electrician
Number of views: 2656
Comments on the article: 0
Vehicle electrical system
The development of electronics and semiconductor technology in the early 21st century has led to the fact that no modern car can do without an extensive power supply network, called the car's on-board network.
The vehicle’s on-board network is a direct current power system, and includes both sources and consumers of electric energy. While the thermal energy of the burned fuel is directly suitable only for providing mechanical movement, electric energy is universal, and is able to power a variety of devices, ranging from lamps in headlights to a spark ignition system.
So, there are only two sources of energy in a car: a battery (usually lead acid) and generatorreceiving mechanical rotation directly from an internal combustion engine. And since the battery is also a consumer during recharging, the main source of energy in a modern car is ultimately the burned fuel.
His energy rotates the engine, and he, in turn, is the generator rotor, which produces electricity for the on-board network, charging the battery, and then the battery feeds the starter and on-board network of the car.
If you try to list all the consumers powered by the vehicle’s on-board network, it’s unlikely that you can name all the possible ones, because in principle you can connect anything.
However, the main elements are almost the same everywhere: a battery, a starter, an excitation winding of the generator, a spark ignition system, headlights and side lights, an alarm, a ventilation system, heated windows and seats, an acoustic system and everything related to car audio, a cigarette lighter and all that It can be powered by a GPS navigator, a DVR, a charger for a mobile phone, laptop, etc. A separate system is the on-board electronics responsible for starting the engine and so on.

Of course, the vehicle’s on-board network includes, in addition to sources and consumers, distribution and protective devices, such as fuse boxes, various switches, buttons, switches, switches, relays, power units, etc.
All this is connected by electrical wiring, which is made of stranded copper wires of various sections in a special gas-oil-resistant insulation. Wires are not scattered all over the body, they are collected in neat harnesses and laid along the body, to which are attached using clamps and clips.
Wiring harnesses are often assembled with PVC tape, and not laid bare, but inside molded plastic or corrugated tubes. Sometimes you can find wiring elements enclosed in a Bowden shell (like a wire laid inside a dense spring with a small pitch) or even in a metal pipe.

The wires of the vehicle’s on-board network, depending on their purpose, are distinguished by the color of insulation so that nothing is confused during installation and dismantling: depending on whether they belong to a particular unit or system circuit, each wire has its own color - marking.
In the documentation for a particular car, the manufacturer always provides the wiring diagram with the color marking of all the wires, which is especially useful and often necessary during maintenance and during troubleshooting, during diagnostics, etc.
In all modern cars, blocks, devices and harnesses are interconnected via multi-pin connectors of various types, as well as bolted connections and terminals.This, firstly, simplifies installation and dismantling during repair and preventive (diagnostic) work, and secondly, makes the joints detachable and, at the same time, durable, resistant to wear and tear with multiple disconnect connections.
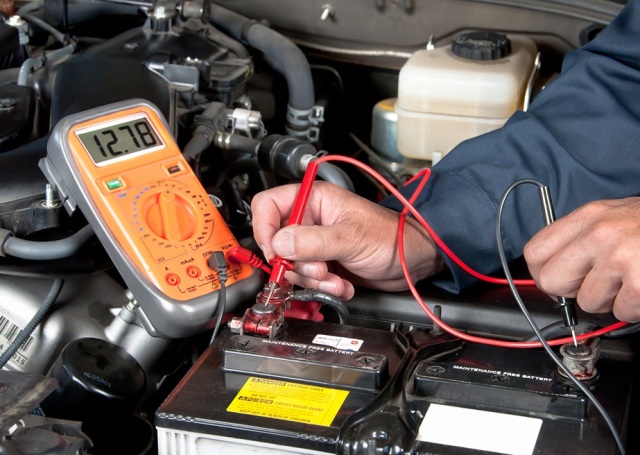

Today, almost everywhere in cars, the on-board network has a constant supply voltage of 12 volts. In the last century, it was still possible to meet cars with an on-board voltage of 6 volts. Today, only occasionally does this occur, and then only on motorcycles.
All cars of modern production use a voltage of 12 volts. On heavy trucks, an increased voltage of 24 volts is used. For tractors, the starter operates from 24 volts, and the rest of the on-board network - from 12 volts.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
