Categories: Auto electrician
Number of views: 3345
Comments on the article: 0
What is battery self-discharge?
If the battery is not used for some time, keeping its external circuit open, then a few days later you can find that the voltage level at its terminals has become significantly lower than it was originally. This is due to the phenomenon of self-discharge - a normal phenomenon for any battery, but if the self-discharge is too intense, then the norm develops into a problem - the capacity noticeably decreases, it would seem, for no apparent reason.
Let's look at this topic, consider the essence and ways of preventing this kind of trouble. It would be advisable to consider the problem of self-discharge by the example of a lead-acid battery in a car, because whoever, and motorists know firsthand how sometimes it can be overwhelming if the battery itself discharges simply while in a muffled car in a parking lot or in a garage, and its circuit was accurately open.
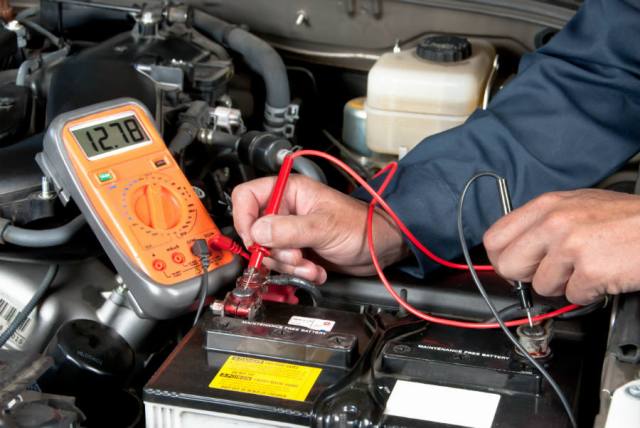

As known, battery - This is a chemical current source, and it works thanks to the chemical processes that occur at the electrodes and in the electrolyte. At a higher temperature of the electrolyte, the processes proceed more intensively, at a low temperature - less intensively. And this temperature factor is significant not only during operation, it is relevant when storing the battery, it must always be taken into account.
One way or another, self-discharge proceeds according to two mechanisms: they separate surface and internal self-discharge. Dirt, water and other liquids present on the battery case form a highly resistive, seemingly almost invisible, nonetheless conductive circuit, along which surface self-discharge is realized. Internal self-discharge is associated with reactions between electrodes and electrolyte.

A more intense reaction occurs at the anode, the negative electrode, where lead, interacting with sulfuric acid, forms a salt (lead sulfate), while hydrogen is released.
At the cathode, the positive electrode, lead oxide is less actively interacting with sulfuric acid, however, here too, a salt formation reaction occurs with the release of water and oxygen. Accordingly, the higher the density of the electrolyte (the more the battery is charged) and the higher the storage temperature of the battery, the faster self-discharge takes place. The presence of impurities in the electrolyte also promotes self-discharge, therefore, the cleaner the electrolyte, the more close to normal the self-discharge intensity will be.
To estimate the quantitative value of self-discharge, first measure the capacity of the battery C before storage, then wait for the storage time t, and then measure the capacity of the battery at the end of storage Ct. So they find the value of self-discharge in percent for a certain time, for example, for a month or for a quarter. For lead-acid starter car batteries, 7% is considered the norm in two weeks at an ambient temperature of 20 ° C.
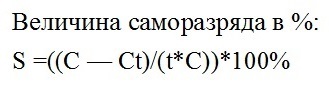
In an effort to reduce the self-discharge of their batteries, car battery manufacturers are trying to make their electrodes such as to avoid any significant chemical reactions to them during storage. For this purpose, a dopant, calcium, is added to the lead of the anode, and inhibitors are added to the electrolyte. They seek to avoid harmful impurities that contribute to self-discharge, and use only pure starting materials.
As for motorists who want to avoid strong self-discharge, it remains for them to keep their battery housings dry and clean, and for self-made electrolyte use only pure acid and distilled water.
See also at i.electricianexp.com
:
